-by 计算机视觉life 公众号旗下开源学习小组:SLAM研习社
附部分内容讲解视频:
ORBSLAM2源码讲解专题1:ORB特征点提取与均匀化策略
ORBSLAM2源码讲解专题2:Oriented Fast神奇高效的代码实现方式
ORB-SLAM源码讲解专题3:ORBSLAM2的单目初始化
ORBSLAM2原理代码详解19- 图像描述子转化为BowVector和FeatureVector
全网最详细的ORB-SLAM2精讲:原理推导+逐行代码分析,请:点击查看, 课程大纲如下:
第01讲-ORB-SLAM2优点、流程框架介绍、运行注意事项、可视化结果分析
第02讲-SLAM系统构造函数、特征点图像金字塔、构造灰度质心圆
第03讲-ORB特征提取构造函数/仿函数、图像帧构造函数、计算图像金字塔并进行扩充
第04讲-提取ORB特征点、四叉树实现均匀化分布
第05讲-利用灰度质心计算ORB特征点方向,实现旋转不变性
第06讲-ORB描述子steer brief计算原理及代码实现
第07讲-去畸变、计算图像边界、特征点网格划分
第08讲-两帧图像稀疏立体匹配
第09讲-单目初始化中的特征点搜索匹配、搜索候选匹配特征点
第10讲-单目初始化中特征匹配点对筛查、隐藏bug解析修正
第11讲-单目初始化中随机选择点集、归一化原理、直接线性变换求解单应矩阵
第12讲-单目初始化中基础矩阵推导计算、根据得分确定最佳单应矩阵和基础矩阵
第13讲-卡方检验原理及其在ORB-SLAM2中的用处
第14讲-单目初始化中从单应矩阵恢复位姿、根据三角化检验位姿
第15讲-单目初始化中从基础矩阵得到最佳位姿及三维点
第16讲-初始化中构建初始化地图、计算地图点具有代表性的描述子、计算平均观测方向
第17讲-初始化关键帧更新共视关系、尺度归一化
第18讲-视觉词袋BoW的应用背景及论文关键点解读
第19讲-离线字典生成原理、图像描述子用BoW转化为BowVector和FeatureVector
第20讲-参考关键帧跟踪当前普通帧、仅位姿优化
第21讲-恒速模型跟踪当前普通帧
第22讲-跟踪丢失后的重定位方法
第23讲-局部地图跟踪中创建局部关键帧和局部地图点
第24讲-局部地图跟踪中用局部地图点搜索匹配
第25讲-关键帧定义应用及选择方法、创建及插入关键帧
第26讲-三种不同跟踪方法的对比、梳理完整跟踪流程
第27讲-局部建图线程处理新关键帧、检查删除地图点
第28讲-局部建图线程关键帧之间生成新的地图点
第29讲-局部建图线程里两级局部关键帧地图点融合
第30讲-局部建图线程里localBA过程
第31讲-局部建图线程剔除关键帧及整个线程梳理
第32讲-闭环线程中寻找初始闭环候选关键帧
第33讲-闭环线程中根据闭环连续性进一步确定闭环候选关键帧
第34讲-为什么需要计算Sim3?开启Sim3代码流程
第35讲-闭环线程中通过估计的Sim3变换互相投影来获得更多的匹配对
第36讲-闭环线程中固定地图点用G2O进行Sim3优化
第37讲-闭环线程中闭环候选连接关键帧地图点投影匹配
第38讲-闭环线程中闭环矫正SIM3位姿传播
第39讲-闭环线程中闭环矫正SIM3位姿修正地图点
第40讲-闭环线程中闭环相连关键帧组投影匹配融合地图点
第41讲-ORB-SLAM2中的essential graph,spanning tree原理
第42讲-闭环线程中的essential graph优化代码实现
第43讲-闭环线程中的全局BA
第44讲-全网最详细的EPnP原理推导(上)
第45讲-全网最详细的EPnP原理推导(下)
第46讲-ORB-SLAM2中EPnP源码详解(上)
第47讲-ORB-SLAM2中EPnP源码详解(下)
第48讲-全网最详细的SIM3原理推导(上)
第49讲-全网最详细的SIM3原理推导(下)
第50讲-ORB-SLAM2中SIM3源码详解(上)
第51讲-ORB-SLAM2中SIM3源码详解(下)
第52讲-CMake简介、常用指令介绍
第53讲-CMake编程实战
第54讲-深入理解进程、线程、并发
第55讲-多线程编程实战-熟悉thread, join, detach
第56讲-多线程编程实战-数据共享问题
第57讲-多线程编程实战-多线程互斥锁的多种实现方法
第58讲-多线程编程实战-死锁问题及解决方法
第59讲-ORB-SLAM2中的多线程调度解析
第60讲-ORB-SLAM2工程实践问题及改进建议
关注公众号:计算机视觉life,第一时间获取SLAM、三维视觉干货
Authors: Raul Mur-Artal, Juan D. Tardos, J. M. M. Montiel and Dorian Galvez-Lopez (DBoW2)
13 Jan 2017: OpenCV 3 and Eigen 3.3 are now supported.
22 Dec 2016: Added AR demo (see section 7).
ORB-SLAM2 is a real-time SLAM library for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D cameras that computes the camera trajectory and a sparse 3D reconstruction (in the stereo and RGB-D case with true scale). It is able to detect loops and relocalize the camera in real time. We provide examples to run the SLAM system in the KITTI dataset as stereo or monocular, in the TUM dataset as RGB-D or monocular, and in the EuRoC dataset as stereo or monocular. We also provide a ROS node to process live monocular, stereo or RGB-D streams. The library can be compiled without ROS. ORB-SLAM2 provides a GUI to change between a SLAM Mode and Localization Mode, see section 9 of this document.
[Monocular] Raúl Mur-Artal, J. M. M. Montiel and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 1147-1163, 2015. (2015 IEEE Transactions on Robotics Best Paper Award). PDF.
[Stereo and RGB-D] Raúl Mur-Artal and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 1255-1262, 2017. PDF.
[DBoW2 Place Recognizer] Dorian Gálvez-López and Juan D. Tardós. Bags of Binary Words for Fast Place Recognition in Image Sequences. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 1188-1197, 2012. PDF
ORB-SLAM2 is released under a GPLv3 license. For a list of all code/library dependencies (and associated licenses), please see Dependencies.md.
For a closed-source version of ORB-SLAM2 for commercial purposes, please contact the authors: orbslam (at) unizar (dot) es.
If you use ORB-SLAM2 (Monocular) in an academic work, please cite:
@article{murTRO2015,
title={{ORB-SLAM}: a Versatile and Accurate Monocular {SLAM} System},
author={Mur-Artal, Ra\'ul, Montiel, J. M. M. and Tard\'os, Juan D.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Robotics},
volume={31},
number={5},
pages={1147--1163},
doi = {10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671},
year={2015}
}
if you use ORB-SLAM2 (Stereo or RGB-D) in an academic work, please cite:
@article{murORB2,
title={{ORB-SLAM2}: an Open-Source {SLAM} System for Monocular, Stereo and {RGB-D} Cameras},
author={Mur-Artal, Ra\'ul and Tard\'os, Juan D.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Robotics},
volume={33},
number={5},
pages={1255--1262},
doi = {10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103},
year={2017}
}
We have tested the library in Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04 and 16.04, but it should be easy to compile in other platforms. A powerful computer (e.g. i7) will ensure real-time performance and provide more stable and accurate results.
We use the new thread and chrono functionalities of C++11.
We use Pangolin for visualization and user interface. Dowload and install instructions can be found at: https://github.com/stevenlovegrove/Pangolin.
We use OpenCV to manipulate images and features. Dowload and install instructions can be found at: http://opencv.org. Required at leat 2.4.3. Tested with OpenCV 2.4.11 and OpenCV 3.2.
Required by g2o (see below). Download and install instructions can be found at: http://eigen.tuxfamily.org. Required at least 3.1.0.
We use modified versions of the DBoW2 library to perform place recognition and g2o library to perform non-linear optimizations. Both modified libraries (which are BSD) are included in the Thirdparty folder.
We provide some examples to process the live input of a monocular, stereo or RGB-D camera using ROS. Building these examples is optional. In case you want to use ROS, a version Hydro or newer is needed.
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/raulmur/ORB_SLAM2.git ORB_SLAM2
We provide a script build.sh to build the Thirdparty libraries and ORB-SLAM2. Please make sure you have installed all required dependencies (see section 2). Execute:
cd ORB_SLAM2
chmod +x build.sh
./build.sh
This will create libORB_SLAM2.so at lib folder and the executables mono_tum, mono_kitti, rgbd_tum, stereo_kitti, mono_euroc and stereo_euroc in Examples folder.
-
Download a sequence from http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download and uncompress it.
-
Execute the following command. Change
TUMX.yamlto TUM1.yaml,TUM2.yaml or TUM3.yaml for freiburg1, freiburg2 and freiburg3 sequences respectively. ChangePATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDERto the uncompressed sequence folder.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/TUMX.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER
-
Download the dataset (grayscale images) from http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
-
Execute the following command. Change
KITTIX.yamlby KITTI00-02.yaml, KITTI03.yaml or KITTI04-12.yaml for sequence 0 to 2, 3, and 4 to 12 respectively. ChangePATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDERto the uncompressed dataset folder. ChangeSEQUENCE_NUMBERto 00, 01, 02,.., 11.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_kitti Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/KITTIX.yaml PATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDER/dataset/sequences/SEQUENCE_NUMBER
-
Download a sequence (ASL format) from http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
-
Execute the following first command for V1 and V2 sequences, or the second command for MH sequences. Change PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER and SEQUENCE according to the sequence you want to run.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER/mav0/cam0/data Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam0/data Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
-
Download the dataset (grayscale images) from http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
-
Execute the following command. Change
KITTIX.yamlto KITTI00-02.yaml, KITTI03.yaml or KITTI04-12.yaml for sequence 0 to 2, 3, and 4 to 12 respectively. ChangePATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDERto the uncompressed dataset folder. ChangeSEQUENCE_NUMBERto 00, 01, 02,.., 11.
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_kitti Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/KITTIX.yaml PATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDER/dataset/sequences/SEQUENCE_NUMBER
-
Download a sequence (ASL format) from http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
-
Execute the following first command for V1 and V2 sequences, or the second command for MH sequences. Change PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER and SEQUENCE according to the sequence you want to run.
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/mav0/cam0/data PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/mav0/cam1/data Examples/Stereo/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam0/data PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam1/data Examples/Stereo/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
-
Download a sequence from http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download and uncompress it.
-
Associate RGB images and depth images using the python script associate.py. We already provide associations for some of the sequences in Examples/RGB-D/associations/. You can generate your own associations file executing:
python associate.py PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/rgb.txt PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/depth.txt > associations.txt
- Execute the following command. Change
TUMX.yamlto TUM1.yaml,TUM2.yaml or TUM3.yaml for freiburg1, freiburg2 and freiburg3 sequences respectively. ChangePATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDERto the uncompressed sequence folder. ChangeASSOCIATIONS_FILEto the path to the corresponding associations file.
./Examples/RGB-D/rgbd_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/RGB-D/TUMX.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER ASSOCIATIONS_FILE
- Add the path including Examples/ROS/ORB_SLAM2 to the ROS_PACKAGE_PATH environment variable. Open .bashrc file and add at the end the following line. Replace PATH by the folder where you cloned ORB_SLAM2:
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=${ROS_PACKAGE_PATH}:PATH/ORB_SLAM2/Examples/ROS
- Execute
build_ros.shscript:
chmod +x build_ros.sh
./build_ros.sh
For a monocular input from topic /camera/image_raw run node ORB_SLAM2/Mono. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. See the monocular examples above.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Mono PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
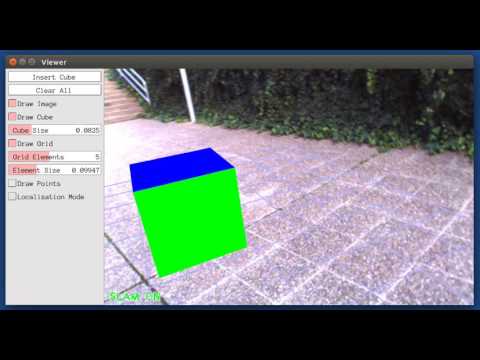
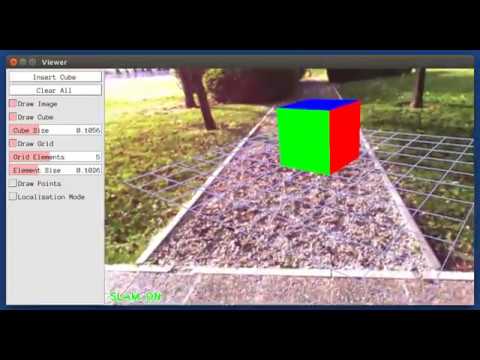
This is a demo of augmented reality where you can use an interface to insert virtual cubes in planar regions of the scene.
The node reads images from topic /camera/image_raw.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 MonoAR PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
For a stereo input from topic /camera/left/image_raw and /camera/right/image_raw run node ORB_SLAM2/Stereo. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. If you provide rectification matrices (see Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml example), the node will recitify the images online, otherwise images must be pre-rectified.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Stereo PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE ONLINE_RECTIFICATION
Example: Download a rosbag (e.g. V1_01_easy.bag) from the EuRoC dataset (http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets). Open 3 tabs on the terminal and run the following command at each tab:
roscore
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Stereo Vocabulary/ORBvoc.txt Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml true
rosbag play --pause V1_01_easy.bag /cam0/image_raw:=/camera/left/image_raw /cam1/image_raw:=/camera/right/image_raw
Once ORB-SLAM2 has loaded the vocabulary, press space in the rosbag tab. Enjoy!. Note: a powerful computer is required to run the most exigent sequences of this dataset.
For an RGB-D input from topics /camera/rgb/image_raw and /camera/depth_registered/image_raw, run node ORB_SLAM2/RGBD. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. See the RGB-D example above.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 RGBD PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
You will need to create a settings file with the calibration of your camera. See the settings file provided for the TUM and KITTI datasets for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras. We use the calibration model of OpenCV. See the examples to learn how to create a program that makes use of the ORB-SLAM2 library and how to pass images to the SLAM system. Stereo input must be synchronized and rectified. RGB-D input must be synchronized and depth registered.
You can change between the SLAM and Localization mode using the GUI of the map viewer.
This is the default mode. The system runs in parallal three threads: Tracking, Local Mapping and Loop Closing. The system localizes the camera, builds new map and tries to close loops.
This mode can be used when you have a good map of your working area. In this mode the Local Mapping and Loop Closing are deactivated. The system localizes the camera in the map (which is no longer updated), using relocalization if needed.