RVT: Robotic View Transformer for 3D Object Manipulation
Ankit Goyal, Jie Xu, Yijie Guo, Valts Blukis, Yu-Wei Chao, Dieter Fox
CoRL 2023 (Oral)
If you find our work useful, please consider citing:
@article{,
title={RVT: Robotic View Transformer for 3D Object Manipulation},
author={Goyal, Ankit and Xu, Jie and Guo, Yijie and Blukis, Valts and Chao, Yu-Wei and Fox, Dieter},
journal={CoRL},
year={2023}
}
-
Tested (Recommended) Versions: Python 3.8. We used CUDA 11.1.
-
Step 1 (Optional): We recommend using conda and creating a virtual environment.
conda create --name rvt python=3.8
conda activate rvt
- Step 2: Install PyTorch. Make sure the PyTorch version is compatible with the CUDA version. One recommended version compatible with CUDA 11.1 and PyTorch3D can be installed with the following command. More instructions to install PyTorch can be found here.
conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
- Step 3: Install PyTorch3D. One recommended version that is compatible with the rest of the library can be installed as follows. Note that this might take some time. For more instructions visit here.
curl -LO https://github.com/NVIDIA/cub/archive/1.10.0.tar.gz
tar xzf 1.10.0.tar.gz
export CUB_HOME=$(pwd)/cub-1.10.0
pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d.git@stable'
--- skip if already done while installing Colosseum ---
- Step 4: Install CoppeliaSim. PyRep requires version 4.1 of CoppeliaSim. Download and unzip CoppeliaSim:
- Ubuntu 16.04
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Ubuntu 20.04
Once you have downloaded CoppeliaSim, add the following to your ~/.bashrc file. (NOTE: the 'EDIT ME' in the first line)
export COPPELIASIM_ROOT=<EDIT ME>/PATH/TO/COPPELIASIM/INSTALL/DIR
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$COPPELIASIM_ROOT
export QT_QPA_PLATFORM_PLUGIN_PATH=$COPPELIASIM_ROOT
export DISLAY=:1.0
Remember to source your .bashrc (source ~/.bashrc) or .zshrc (source ~/.zshrc) after this.
--- skip if already done while installing Colosseum ---
- Step 5: Clone the repository with the submodules using the following command.
git clone --recurse-submodules [email protected]:robot-colosseum/rvt_colosseum.git && cd rvt_colosseum && git submodule update --init
Now, locally install RVT and other libraries using the following command. Make sure you are in folder RVT.
pip install -e .
pip install -e rvt/libs/PyRep
pip install -e rvt/libs/RLBench
pip install -e rvt/libs/YARR
pip install -e rvt/libs/peract_colab
You can download a pre-trained RVT agent trained on the 20 RLBench tasks from Colosseum without any perturbations
cd rvt
bash run_train.sh
min_var_num=0
max_var_num=500
total_processes=50
processes_per_gpu=3
bash run_eval_variations.sh $min_var_num $max_var_num $total_processes $processes_per_gpu
This file launches parallel evaluation processes. Adjust the number of processes to run in parallel based on GPU number and size availability. The task_list can be edited inside run_eval_variations.sh to run specific task or variation number.
To train RVT on all RLBench tasks, use the following command (from folder RVT/rvt):
python train.py --exp_cfg_path configs/all.yaml --device 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
We use 8 V100 GPUs. Change the device flag depending on available compute.
- default parameters for an
experimentare defined here. - default parameters for
rvtare defined here. - the parameters in for
experimentandrvtcan be overwritten by two ways:- specifying the path of a yaml file
- manually overwriting using a
optsstring of format<param1> <val1> <param2> <val2> ..
- Manual overwriting has higher precedence over the yaml file.
python train.py --exp_cfg_opts <> --mvt_cfg_opts <> --exp_cfg_path <> --mvt_cfg_path <>
The following command overwrites the parameters for the experiment with the configs/all.yaml file. It also overwrites the bs parameters through the command line.
python train.py --exp_cfg_opts "bs 4" --exp_cfg_path configs/all.yaml --device 0
Download the pretrained RVT model. Place the model (model_14.pth trained for 15 epochs or 100K steps) and the config files under the folder runs/rvt/. Run evaluation using (from folder RVT/rvt):
python eval.py --model-folder runs/rvt --eval-datafolder ./data/test --tasks all --eval-episodes 25 --log-name test/1 --device 0 --headless --model-name model_14.pth
Download the officially released PerAct model.
Put the downloaded policy under the runs folder with the recommended folder layout: runs/peract_official/seed0.
Run the evaluation using:
python eval.py --eval-episodes 25 --peract_official --peract_model_dir runs/peract_official/seed0/weights/600000 --model-name QAttentionAgent_layer0.pt --headless --task all --eval-datafolder ./data/test --device 0
- If you get qt plugin error like
qt.qpa.plugin: Could not load the Qt platform plugin "xcb", try uninstalling opencv-python and installing opencv-python-headless
pip uninstall opencv-python
pip install opencv-python-headless
- If you have CUDA 11.7, an alternate installation strategy could be to use the following command for Step 2 and Step 3. Note that this is not heavily tested.
# Step 2:
pip install pytorch torchvision torchaudio
# Step 3:
pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d.git@stable'
-
If you are having issues running evaluation on a headless server, please refer to NVlabs/RVT#2 (comment).
-
If you want to generate visualization videos, please refer to NVlabs/RVT#5.
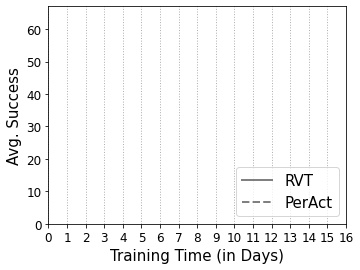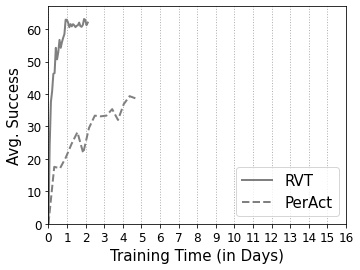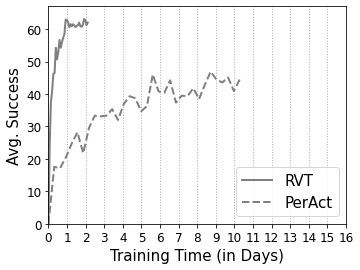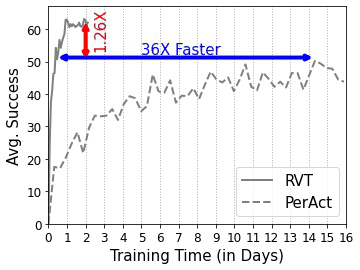
RVT is both faster to train and performs better than PerAct.
For training on 18 RLBench tasks, with 100 demos per task, we use 8 V100 GPUs (16 GB memory each). The model trains in ~1 day.
Note that for fair comparison with PerAct, we used the same dataset, which means duplicate keyframes are loaded into the replay buffer. For other datasets, one could consider not doing so, which might further speed up training.
Q. Why do you use pe_fix=True in the rvt config?
For fair comparison with offical PerAct model, we use this setting. More detials about this can be found in PerAct code. For future, we recommend using pe_fix=False for language input.
In the PerAct paper, for each task, the best checkpoint is chosen based on the validation set performance. Hence, the model weights can be different for different tasks. We evaluate PerAct and RVT only on the final checkpoint, so that all tasks are strictly evaluated on the same model weights. Note that only the final model for PerAct has been released officially.
We hypothesize that it is because of the sampling based planner used in RLBench, which could be the source of the randomization. Hence, we evaluate each checkpoint 5 times and report mean and variance.
Q. Why did you use a cosine decay learning rate scheduler instead of a fixed learning rate schedule as done in PerAct?
We found the cosine learning rate scheduler led to faster convergence for RVT. Training PerAct with our training hyper-parameters (cosine learning rate scheduler and same number of iterations) led to worse performance (in ~4 days of training time). Hence for Fig. 1, we used the official hyper-parameters for PerAct.
Q. For my use case, I want to render images at real camera locations (input camera poses) with PyTorch3D. Is it possible to do so and how can I do that?
Yes, it is possible to do so. A self-sufficient example is present here. Depending on your use case, the code may need be modified. Also note that 3D augmentation cannot be used while rendering images at real camera locations as it would change the pose of the camera with respect to the point cloud.
For questions and comments, please contact Ankit Goyal.
We sincerely thank the authors of the following repositories for sharing their code.
License Copyright © 2023, NVIDIA Corporation & affiliates. All rights reserved.
This work is made available under the Nvidia Source Code License. The pretrained RVT model is released under the CC-BY-NC-SA-4.0 license.