A unified modular hypervisor based on ArceOS.
English | 中文
AxVisor is a hypervisor implemented based on the ArceOS unikernel framework. Its goal is to leverage the foundational operating system features provided by ArceOS to implement a unified modular hypervisor.
"Unified" refers to using the same codebase to support x86_64, Arm (aarch64), and RISC-V architectures simultaneously, in order to maximize the reuse of architecture-independent code and simplify development and maintenance costs.
"Modular" means that the functionality of the hypervisor is decomposed into multiple modules, each implementing a specific function. The modules communicate with each other through standard interfaces to achieve decoupling and reuse of functionality.
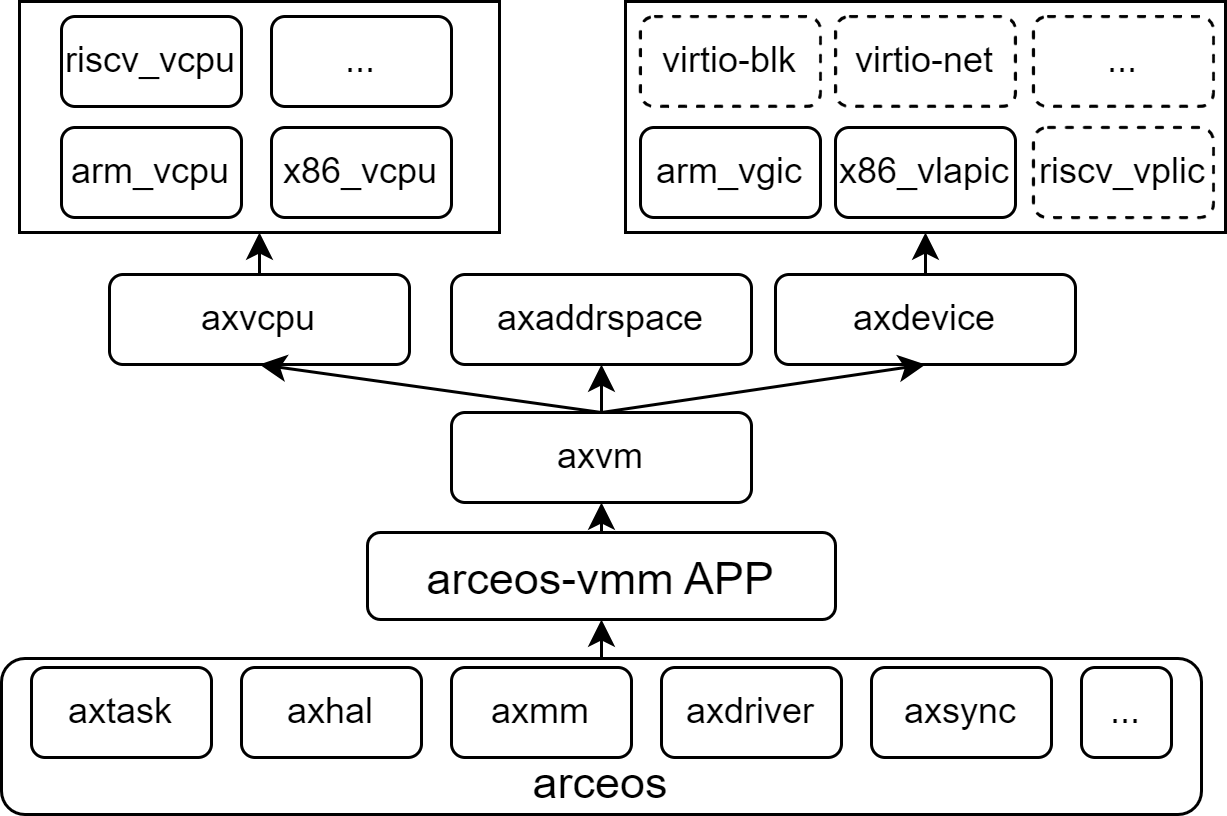
The software architecture of AxVisor is divided into five layers as shown in the diagram below. Each box represents an independent module, and the modules communicate with each other through standard interfaces.
The complete architecture description can be found in the documentation.
Currently, AxVisor has been verified on the following platforms:
- QEMU ARM64 virt (qemu-max)
- Rockchip RK3568 / RK3588
- 黑芝麻华山 A1000
Currently, AxVisor has been verified in scenarios with the following systems as guests:
- ArceOS
- Starry-OS
- NimbOS
- Linux
- currently only Linux with passthrough device on aarch64 is tested.
- single core: config.toml | dts
- smp: config.toml | dts
After AxVisor starts, it loads and starts the guest based on the information in the guest configuration file. Currently, AxVisor supports loading guest images from a FAT32 file system and also supports binding guest images to the hypervisor image through static compilation (using include_bytes).
AxVisor is written in the Rust programming language, so you need to install the Rust development environment following the instructions on the official Rust website. Additionally, you need to install cargo-binutils to use tools like rust-objcopy and rust-objdump.
$ cargo install cargo-binutilsIf necessary, you may also need to install musl-gcc to build guest applications.
Since configuring the guest is a complex process, AxVisor chooses to use TOML files to manage the guest configurations. These configurations include the virtual machine ID, virtual machine name, virtual machine type, number of CPU cores, memory size, virtual devices, passthrough devices, and more. In the source code, the ./config/vms directory contains some example templates for guest configurations.
In addition, you can use the axvmconfig tool to generate a custom configuration file. For detailed information, refer to the axvmconfig documentation.
-
Build a client image file suitable for your own architecture. Taking the ArceOS mainline code as an example, run
make PLATFORM=aarch64-qemu-virt SMP=1 A=examples/helloworldto generatehelloworld_aarch64-qemu-virt.bin. -
Create a disk image file and place the guest machine image into the file system.
-
Use the
make disk_imgcommand to generate an empty FAT32 disk image file nameddisk.img. -
Manually mount
disk.img, and then place your guest machine image into the file system.$ mkdir -p tmp $ sudo mount disk.img tmp $ sudo cp /PATH/TO/YOUR/GUEST/VM/IMAGE tmp/ $ sudo umount tmp
-
-
Modify the configuration items in the corresponding
./configs/vms/<ARCH_CONFIG>.tomlimage_location="fs"indicates loading from the file system.kernel_pathspecifies the path to the kernel image in the file system.entry_pointspecifies the entry address of the kernel image.kernel_load_addrspecifies the loading address of the kernel image.- others
-
Execute
make ACCEL=n ARCH=aarch64 LOG=info VM_CONFIGS=configs/vms/arceos-aarch64.toml APP_FEATURES=fs runto build AxVisor and start it in QEMU.
-
Build a client image file suitable for your own architecture. Taking the ArceOS mainline code as an example, run
make PLATFORM=aarch64-qemu-virt SMP=1 A=examples/helloworldto generatehelloworld_aarch64-qemu-virt.bin. -
Modify the configuration items in the corresponding
./configs/vms/<ARCH_CONFIG>.tomlimage_location="memory"indicates loading from the memory.kernel_pathkernel_path specifies the relative/absolute path of the kernel image in the workspace.entry_pointspecifies the entry address of the kernel image.kernel_load_addrspecifies the loading address of the kernel image.- others
-
Execute
make ACCEL=n ARCH=aarch64 LOG=info VM_CONFIGS=configs/vms/arceos-aarch64.toml runto build AxVisor and start it in QEMU.
d8888 .d88888b. .d8888b.
d88888 d88P" "Y88b d88P Y88b
d88P888 888 888 Y88b.
d88P 888 888d888 .d8888b .d88b. 888 888 "Y888b.
d88P 888 888P" d88P" d8P Y8b 888 888 "Y88b.
d88P 888 888 888 88888888 888 888 "888
d8888888888 888 Y88b. Y8b. Y88b. .d88P Y88b d88P
d88P 888 888 "Y8888P "Y8888 "Y88888P" "Y8888P"
arch = aarch64
platform = aarch64-qemu-virt-hv
target = aarch64-unknown-none-softfloat
build_mode = release
log_level = info
smp = 1
[ 0.020822 0 axruntime:130] Logging is enabled.
[ 0.026419 0 axruntime:131] Primary CPU 0 started, dtb = 0x44000000.
[ 0.028520 0 axruntime:133] Found physcial memory regions:
[ 0.030673 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x40080000, PA:0x400d6000) .text (READ | EXECUTE | RESERVED)
[ 0.033564 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x400d6000, PA:0x400ef000) .rodata (READ | RESERVED)
[ 0.035313 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x400ef000, PA:0x400f5000) .data .tdata .tbss .percpu (READ | WRITE | RESERVED)
[ 0.037083 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x400f5000, PA:0x40135000) boot stack (READ | WRITE | RESERVED)
[ 0.038622 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x40135000, PA:0x4013b000) .bss (READ | WRITE | RESERVED)
[ 0.040643 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x4013b000, PA:0x48000000) free memory (READ | WRITE | FREE)
[ 0.042907 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x9000000, PA:0x9001000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.045011 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x9040000, PA:0x9041000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.047070 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x9100000, PA:0x9101000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.049093 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x8000000, PA:0x8020000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.051081 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0xa000000, PA:0xa004000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.053120 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x10000000, PA:0x3eff0000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.055229 0 axruntime:135] [PA:0x4010000000, PA:0x4020000000) mmio (READ | WRITE | DEVICE | RESERVED)
[ 0.057642 0 axruntime:208] Initialize global memory allocator...
[ 0.059377 0 axruntime:209] use TLSF allocator.
[ 0.072071 0 axmm:60] Initialize virtual memory management...
[ 0.136312 0 axruntime:150] Initialize platform devices...
[ 0.137733 0 axhal::platform::aarch64_common::gic:67] Initialize GICv2...
[ 0.143653 0 axtask::api:73] Initialize scheduling...
[ 0.151435 0 axtask::api:79] use FIFO scheduler.
[ 0.152744 0 axruntime:176] Initialize interrupt handlers...
[ 0.157472 0 axruntime:186] Primary CPU 0 init OK.
[ 0.159027 0:2 axvisor:17] Starting virtualization...
[ 0.160968 0:2 axvisor:19] Hardware support: true
[ 0.168619 0:4 axvisor::vmm::timer:103] Initing HV Timer...
[ 0.170399 0:4 axvisor::hal:117] Hardware virtualization support enabled on core 0
[ 0.295531 0:2 axvisor::vmm::config:33] Creating VM [1] "arceos"
[ 0.301423 0:2 axvm::vm:113] Setting up memory region: [0x40000000~0x41000000] READ | WRITE | EXECUTE
[ 0.334424 0:2 axvm::vm:156] Setting up passthrough device memory region: [0x8000000~0x8050000] -> [0x8000000~0x8050000]
[ 0.339431 0:2 axvm::vm:156] Setting up passthrough device memory region: [0x9000000~0x9001000] -> [0x9000000~0x9001000]
[ 0.341925 0:2 axvm::vm:156] Setting up passthrough device memory region: [0x9010000~0x9011000] -> [0x9010000~0x9011000]
[ 0.343758 0:2 axvm::vm:156] Setting up passthrough device memory region: [0x9030000~0x9031000] -> [0x9030000~0x9031000]
[ 0.345559 0:2 axvm::vm:156] Setting up passthrough device memory region: [0xa000000~0xa004000] -> [0xa000000~0xa004000]
[ 0.348819 0:2 axvm::vm:191] VM created: id=1
[ 0.350749 0:2 axvm::vm:206] VM setup: id=1
[ 0.352526 0:2 axvisor::vmm::config:40] VM[1] created success, loading images...
[ 0.355270 0:2 axvisor::vmm::images:24] Loading VM[1] images from memory
[ 0.363583 0:2 axvisor::vmm:29] Setting up vcpus...
[ 0.368014 0:2 axvisor::vmm::vcpus:176] Initializing VM[1]'s 1 vcpus
[ 0.370802 0:2 axvisor::vmm::vcpus:207] Spawning task for VM[1] Vcpu[0]
[ 0.374805 0:2 axvisor::vmm::vcpus:219] Vcpu task Task(5, "VM[1]-VCpu[0]") created cpumask: [0, ]
[ 0.378878 0:2 axvisor::vmm:36] VMM starting, booting VMs...
[ 0.380775 0:2 axvm::vm:273] Booting VM[1]
[ 0.382631 0:2 axvisor::vmm:42] VM[1] boot success
[ 0.387436 0:5 axvisor::vmm::vcpus:240] VM[1] Vcpu[0] waiting for running
[ 0.390048 0:5 axvisor::vmm::vcpus:243] VM[1] Vcpu[0] running...
d8888 .d88888b. .d8888b.
d88888 d88P" "Y88b d88P Y88b
d88P888 888 888 Y88b.
d88P 888 888d888 .d8888b .d88b. 888 888 "Y888b.
d88P 888 888P" d88P" d8P Y8b 888 888 "Y88b.
d88P 888 888 888 88888888 888 888 "888
d8888888888 888 Y88b. Y8b. Y88b. .d88P Y88b d88P
d88P 888 888 "Y8888P "Y8888 "Y88888P" "Y8888P"
arch = aarch64
platform = aarch64-qemu-virt
target = aarch64-unknown-none-softfloat
build_mode = release
log_level = warn
smp = 1
Hello, world!
[ 0.416823 0:5 axvisor::vmm::vcpus:288] VM[1] run VCpu[0] SystemDown
[ 0.419035 0:5 axhal::platform::aarch64_common::psci:98] Shutting down...Feel free to fork this repository and submit a pull request.
You can refer to these discussions to gain deeper insights into the project's ideas and future development direction.
AxVisor, as a modular hypervisor, has many components used as Crates. You can use the tool/dev_env.py command to localize the relevant Crates, making it easier for development and debugging.
This project exists thanks to all the people who contribute.
AxVisor uses the following open-source license:
- Apache-2.0
- MulanPubL-2.0
- MulanPSL2
- GPL-3.0-or-later