-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 960
detections
This project utilizes a custom multi-layer detection model - The more detections you have for a specific target, the better detection rate and results
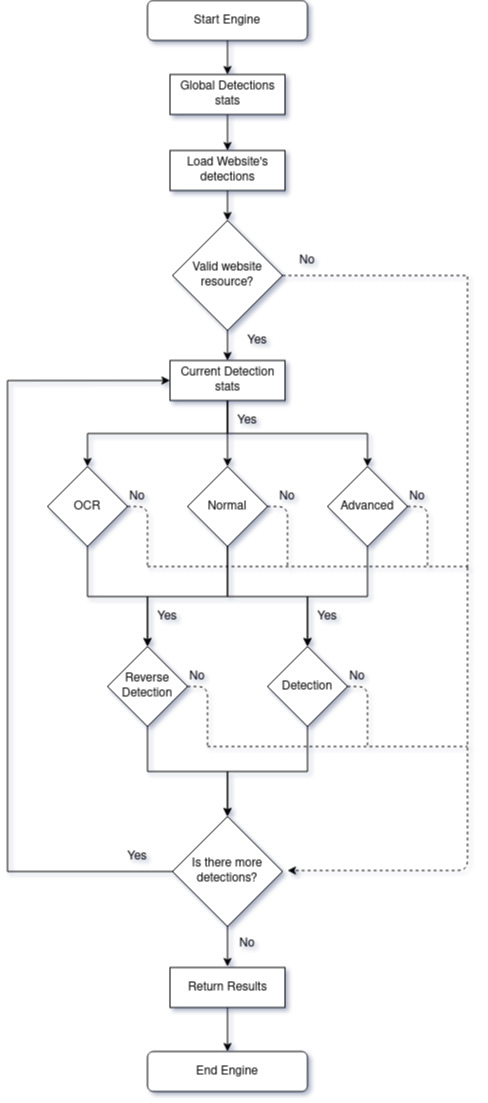
social-analyzer/sites.json file has a list of items called website entries
[
{
"url": "This is the target website with {username}",
"detections": [
{
"return": "What does the evaluation from finding some string return? (false or true)",
"string": "A string to detect on",
"type": "There 3 type of detections: ocr, normal or advanced"
}
],
"selected": "Auto select this item on loading the project? (false or true)",
"timeout": "Add Time out (in seconds), if 0 then it will use 5 seconds",
"implicit": "Add Implicit Time out (in seconds), if 0 then it will use 5 seconds",
"type": "What is the website category? (One-word E.g. Fun)"
}
]The detections key is a list of items, each item is a detection that returns true or false when the logic is evaluated and matched the return value
"detections": [
{
"return": "false",
"string": "page not found",
"type": ""
}
]A detection is term for any detection that returns true and counted as a hit. It's usually used in combination with other detections that return true. The easiest way of understanding this detection is to think of something that you do not want to detect on
- Example: A website returns
Hello {username} - Detection: Check if
resource is unavailableis not in the source code or not
{
"return": "true",
"string": "resource is available",
"type": "normal"
}Reverse Detection is a term I use for any detection that returns false and counted as a hit. It's usually used in a combination with other detections that return true. The easiest way of understanding this type is to think of something that you do not want to detect on
- Example: A website returns
resource is unavailableif an error has occurred - Detection: Check if
resource is unavailableis not in the source code or not
{
"return": "false",
"string": "resource is unavailable",
"type": "normal"
}An Optical Character Recognition (OCR) checks if a website screenshot contains the detection string or not
- Example: A website returns an image that contains
404 page not found! - Detection: Check if
page not foundin the output from OCR or not
{
"return": "false",
"string": "page not found",
"type": "ocr"
}A normal detection checks if a website source code contains the detection string or not (It's similar to going to a website and clicking view page source)
You can also detect on some source code like tags etc..
- Example: A website returns
username is: johndoe - Detection: Check if
username isin the source code or not
{
"return": "true",
"string": "username is",
"type": "normal"
}An advanced detection checks if the website contains the detection string or not (It's similar to going to a website and right-clicking on an item then choosing to inspect feature - This option is very helpful if the target website manipulates DOM)
You cannot detect source code like tags, I will add this feature later on
- Example: A website returns `username is: johndoe
- Detection: Check if
username isin the inspected website or not
{
"return": "true",
"string": "username is",
"type": "advanced"
}This project is universal and allows the detecting of non-English words. You only need to have that non-English sentence or word in the string filed.
Example: The target South Korean website https://example.ccc has a publicly available profile for johndoe that can be accessed at https://example.ccc/p/johndoe. The result is johndoe profile that does not include 오류 and has 프로필
[
{
"url": "https://example.ccc/p/{username}",
"detections": [
{
"return": "false",
"string": "오류",
"type": "normal"
},
{
"return": "true",
"string": "프로필",
"type": "normal"
}
],
"selected": "false",
"timeout": 0,
"implicit": 0,
"type": "other"
}
]Example: If a website does not have page not found then add 1 to the counter. If the website has your name is: then add 1 to the counter. This means that we have 2 out 2 detections that are valid in the logic
"detections": [
{
"return": "false",
"string": "page not found",
"type": "normal"
},
{
"return": "true",
"string": "your name is:",
"type": "normal"
}
]Example: The target website https://example.ccc has a publicly available profile for johndoe that can be accessed at https://example.ccc/p/johndoe. The result is johndoe profile that does not include page not found and has your name is: johndoe
[
{
"url": "https://example.ccc/p/{username}",
"detections": [
{
"return": "false",
"string": "page not found",
"type": "normal"
},
{
"return": "true",
"string": "your name is:",
"type": "normal"
}
],
"selected": "false",
"timeout": 0,
"implicit": 0,
"type": "other"
}
]You can add {username} to the second detection item for more accuracy as the following
[
{
"url": "https://example.ccc/p/{username}",
"detections": [
{
"return": "false",
"string": "page not found",
"type": "normal"
},
{
"return": "true",
"string": "your name is: {username}",
"type": "normal"
}
],
"selected": "false",
"timeout": 0,
"implicit": 0,
"type": "other"
}
]Detection are tested with my Dedicated Testing System called Macaw before and after pushing them to this GitHub (Some tests are Site Status, Name Checking, Similarity Checking & Alexa Metrics)
- Make sure that you have a legit website and has a higher Alexa ranking otherwise Macaw will flag it
- Focus on adding more detections to a website (Do not focus on adding more websites with lower detection quality)