-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 29
Hatohol server technical information
Kazuhiro Yamato edited this page Jul 10, 2014
·
18 revisions
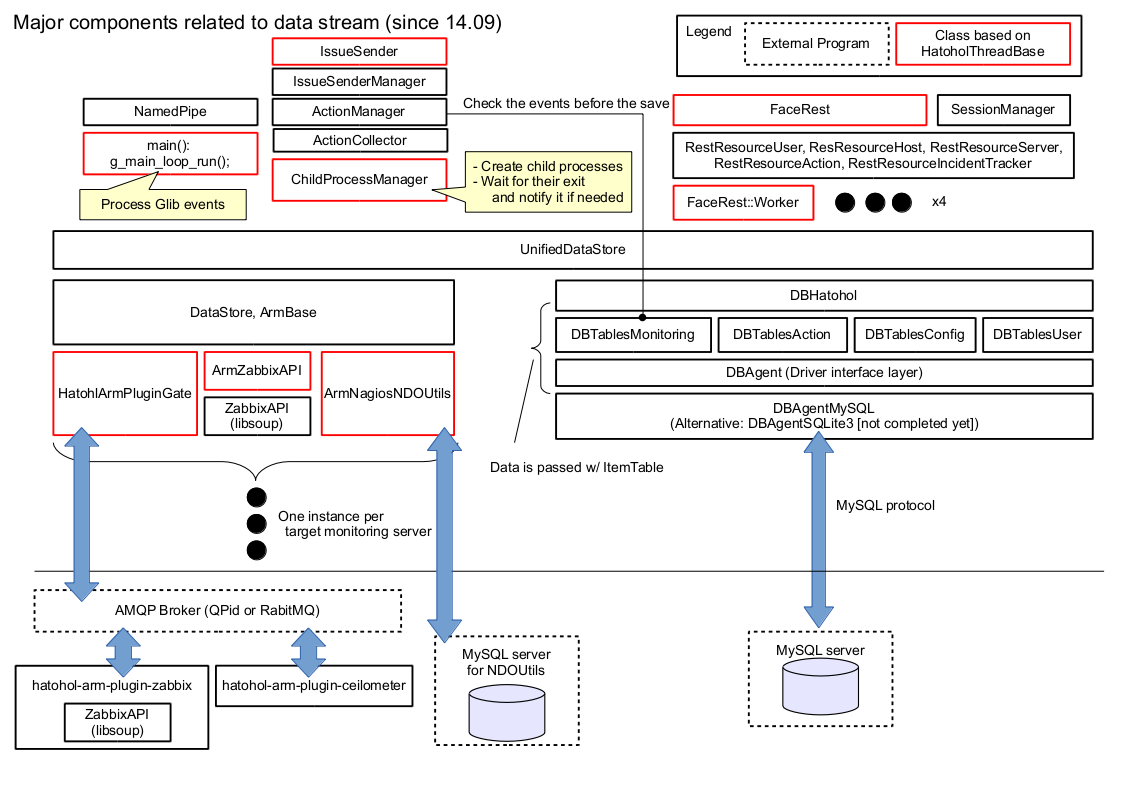
A REST interface to get unified data and configure Hatohol itself.
- Authentication and Generation of session IDs.
- Session IDs are on memory. So when hatohol server is restarted, all the session IDs are lost.
- MEMO: We may use Memcached or a similar program to keep the session ID and share them by multiple programs in the future.
- An expiration time of the session ID is 10 min from the last access with the ID.
A component to get monitoring data from monitoring servers such as Zabbix server.
- A base class to access DBs
- Actual Subclassess: DBAgentMySQL and DBAgentSQLite3
- The subclasses do the following things
- Provides C++ like API to access data in DB.
- manages one or more tables on DB.
- Convert data format: list or vector <==> ItemTable.
- A kind of connection pool for DB servers.
- A thread uses a same connection while it's alive.
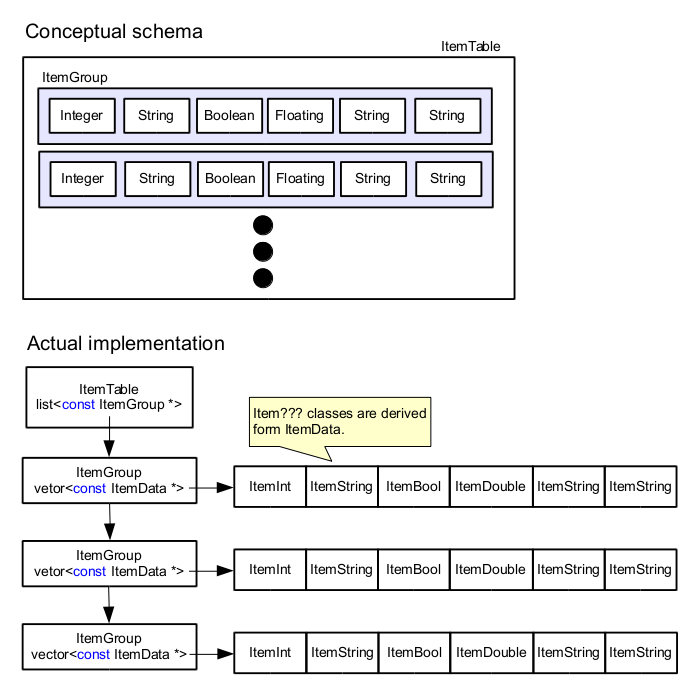
- A virtual base class to handle various type of value with the same interfaces.
- Implemented subclasses:
- ItemInt
- ItemBool
- ItemString
- ItemDouble
- ItemUint64
- A ItemData instance has the following information
- ItemID (can be SYSTEM_ITEM_ID_ANONYMOUS)
- Data type
- Null flag
- Value
- Used count (derived from UsedCountable class)
- Cannot modify the value once it is added to ItemGroup because it has ItemData as const. After that ItemData can be used multiple contexts on different threads.
- An instance is typically wrapped by ItemDataPtr that is a smart pointer for ItemData and increments (decrements) the used count at the constructor (destructor).
- Before newly obtained event data is passed to DBClientHatohol, it is compared with registered action conditions.
- If the event meets any of the conditions, all of the corresponding actions are executed.
- The execution process is asynchronous, so the caller thread may do the next task (typically saving the event to the DB) before the action finishes.
- There are two kinds of actions.
- Command
- Simply executes a specified command or script.
- The maximum number of command actions that can run concurrently: 10
- If the number of actions exceeds the above limit, a new action are queued.
- The queued action is executed soon after one of the running actions finishes.
- Resident
- Launched as a deamon process with a user specified shared library that contains the actual processing.
- After that the same kind of matched event is notified to the daemon (resident) via PIPE.
- Easily can use the previous action information or statistical information.
- Lighter than the command type action that is launched on every matched event.
- Command
- Automatically logs status of an action at several points and it is stored in DB via DBClientAction.
- start, success, fail, queued.
- failure reason
- Currently (14.06), there is no interface to see action logs. (Users can see them with MySQL command line tools)
- Methods of this class are called from various threads
- ArmZabbixAPI, ArmNagiosNDOUtils, and HatoholArmPluginGate
- execute an action if an event meets any conditions.
- ChildProcessManager
- Callback of the exit of actions.
- In the callback, following things are performed.
- Log the finish
- execute a queued actions if it is
- GLib's event loop
- Timeout callback
- Send KILL
- Receive or error callback of NamedPipe (Resident type)
- Deletion of related objects to avoid race.
- Timeout callback
- ArmZabbixAPI, ArmNagiosNDOUtils, and HatoholArmPluginGate
- Registers an issue to indent management system via IssueSender.
- Uses Action mechanism to check the condition.
- See [here](Incident management system integration) for more information