An interactive, code-first tour of Transformer inference created for developers who have never opened a machine learning textbook.
Hover, scrub, and step through a real model to see exactly what happens between a keystroke and the next predicted token.
🚀 https://decoding-attention.opsbr.dev/
(Note: This environment will be offline sometime.)
- Install uv
- Check out this repository
uv python install 3.12
uv sync
uv run task start
- Build a Transformer model architecture using PyTorch and existing functions
- Infer the next token using pre-trained model weights
- Interactively visualize each step so you can intuitively understand how Transformers work
- Training models — We focus on inference to understand the core logic (we'll skip backpropagation, loss functions, optimization, etc.)
- Implementing from scratch — We use existing implementations of complex parts (RMSNorm, SwiGLU, RoPE, etc.) and focus on concepts instead
- If you feel this course is boring, you already know about Transformers! Go to other advanced courses like those in the Acknowledgements section.
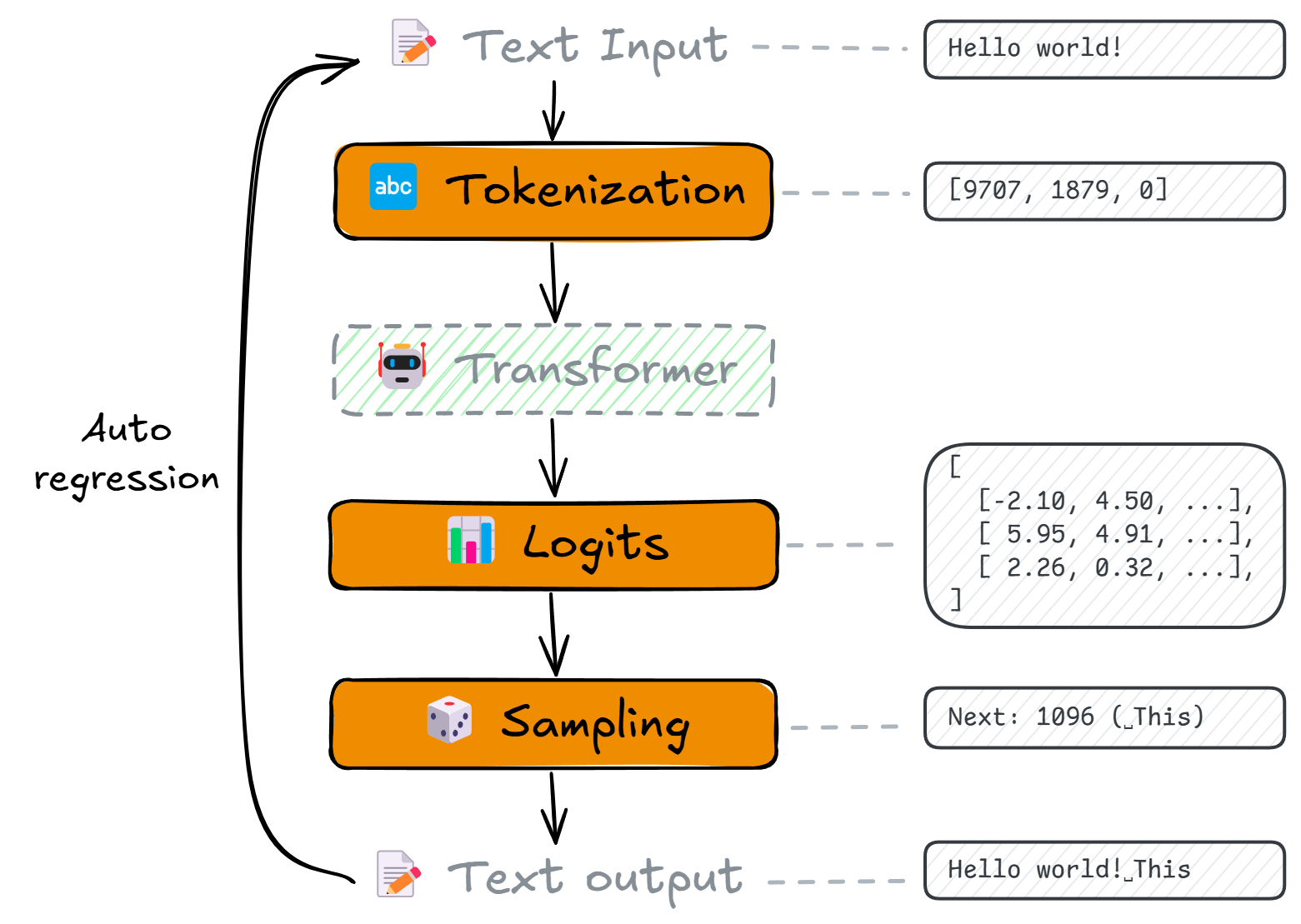
- What is tokenization and why do we need it? (BPE)
- How does a Transformer work at a high level?
- How to convert Transformer outputs (logits) to token probabilities? (Temperature, Top-K, Top-P, Min-P, Softmax)
- How to sample the next token from probabilities?
- How does autoregressive generation create new text?
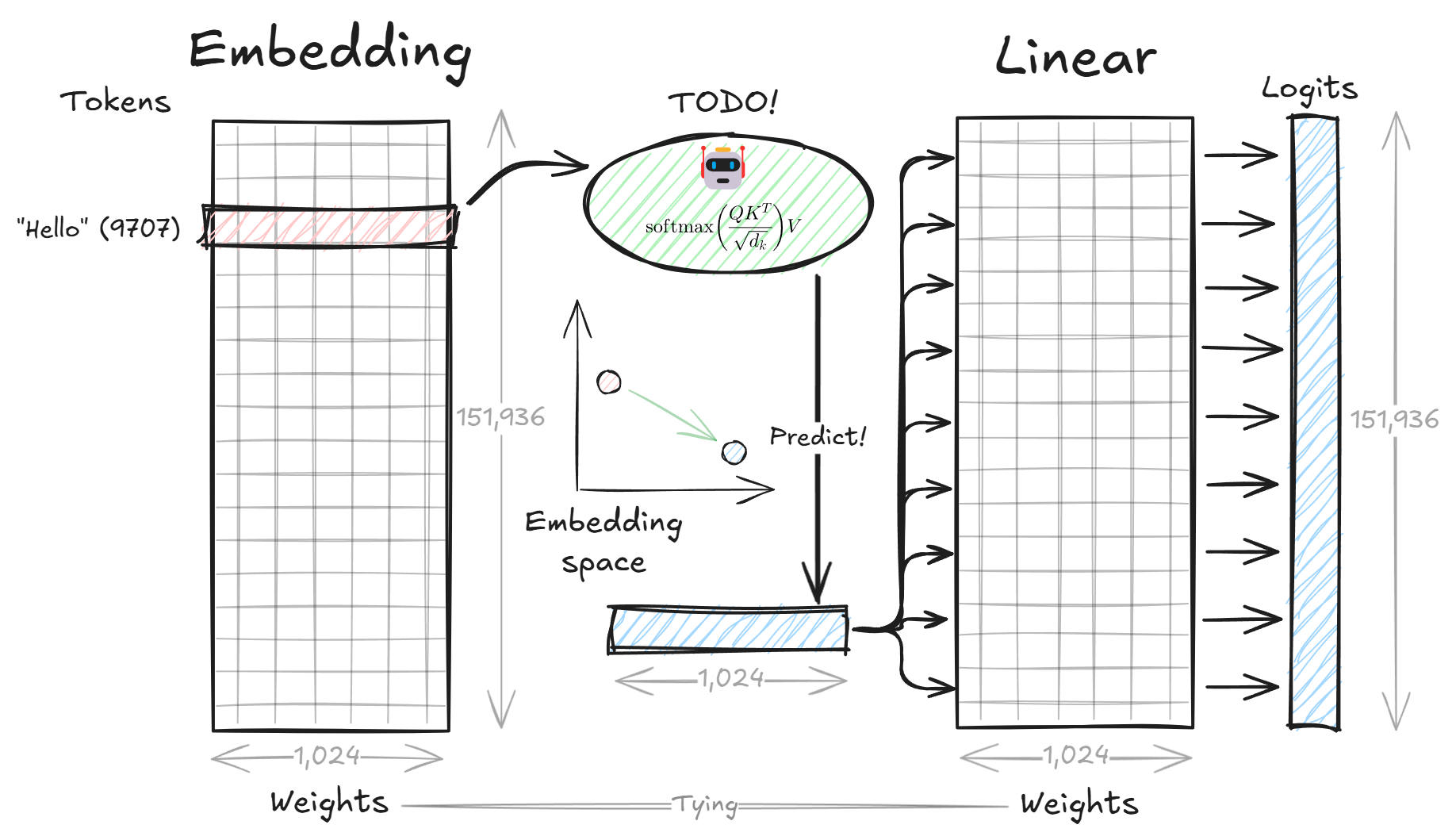
- What are embeddings and why are they important?
- How to convert tokens to embedding vectors using the embedding layer?
- What is a linear layer and how does it work?
- How to convert embedding vectors back to token logits using the linear layer?
- How to combine embedding and linear layers for next token prediction?
- What is a neural network? (Perceptron and MLP)
- Activation functions (SwiGLU)
- Normalization (RMSNorm)
- Scaled dot-product attention mechanism
- Causal masks for autoregressive generation
- Multi-head attention (GQA)
- Positional encoding (RoPE)
- Residual connections
- Putting all the pieces together!
Found a bug or have suggestions? Please open an issue on GitHub.
ML experts: If you spot any incorrect explanations or understanding, please let us know!
Ryosuke Iwanaga / OpsBR Software Technology Inc.
Why am I building this course?
I've been working in the software industry for ~15 years, spanning datacenter operations, database administration, software engineering, and sales engineering. My expertise is in distributed systems, cloud computing, and DevOps/SRE, but I had barely touched machine learning or AI until very recently.
In 2025, I decided to switch my career to AI engineering completely. Luckily, I learned a bit about machine learning in college 20 years ago, so I was able to self-learn Transformers and related topics by watching the best online courses. See this blog post for more details.
During my self-learning, I found that most online courses are too difficult for beginners, especially those who have never opened a machine learning textbook—like software engineers who have no CS background. I believe most of them will start working with AI very soon, so I want to help them understand AI in some depth. Calling LLM APIs isn't enough to understand and predict what happens and what will change in the future. In my opinion, understanding the core logic of Transformers is key, just like understanding the core logic of operating systems or CPU, etc. is key to becoming a good software engineer.
This course is actually my re-learning journey of Transformers. I'll try to explain Transformers as simply as possible by re-implementing an existing model and providing many interactive visualizations. I hope this will help you understand Transformers and become a good AI engineer.
Other visualization contents of Transformer must help you to understand more details about Transformer. I highly recommend them to walkthrough.
I've been heavily inspired by this course, which is the best course for understanding Transformers and language modeling from scratch. I highly recommend it to anyone who wants to learn Transformers in depth.
Also, their Python-based lecture notes inspired me to create this course to be interactive and visual-heavy.
As I hadn't had any NLP experience before, I also watched this course to understand the basics of NLP. This course is great for understanding the foundations of NLP and how Transformers fit into the larger picture, including the history of NLP. If you need an NLP complement to CS336, I highly recommend this course as well.
This 3.5-hour video by the legendary Andrej Karpathy is a fantastic deep dive into LLMs, covering everything from the basics to advanced topics. It's a great resource for anyone who wants to understand the inner workings of LLMs in detail.
Qwen3 is an open-source language model that provides a great starting point for understanding Transformers. It has a well-documented architecture and is easy to use with PyTorch thanks to Hugging Face's Transformers library. I used Qwen3 as the base model for this course.
This project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License.
The source code is available on GitHub.
If you want, you can cite this work with:
@misc{Iwanaga2025DecodingAttention,
author = {Iwanaga, Ryosuke},
title = {Decoding Attention: An Interactive Guide of {Transformers} for Software Engineers},
url = {https://github.com/opsbr/decoding-attention},
year = {2025}
}