A collection of basic algorithms and data structures (algodat)
- AvlTree
- BstTree
- The graphs datastructure with it vertices and edges is implemented as "linked list".
- The idea is that it is not neccessary to load the entire graph to execute an algorithm.
- Each vertex can save a generic
Value. - The graph is fully (de)serializeable.
- LinkedList (will be reimplemented see)
- Documentation
| nuget.org |
|---|
| Abstract.DataStructures |
| Abstract.DataStructures.Algorithms |
| Abstract.DataStructures.Algorithms.Graph |
| Abstract.DataStructures.UI |
| Azure DevOps |
|---|
| Pipeline |
| Doc Release Pipeline |
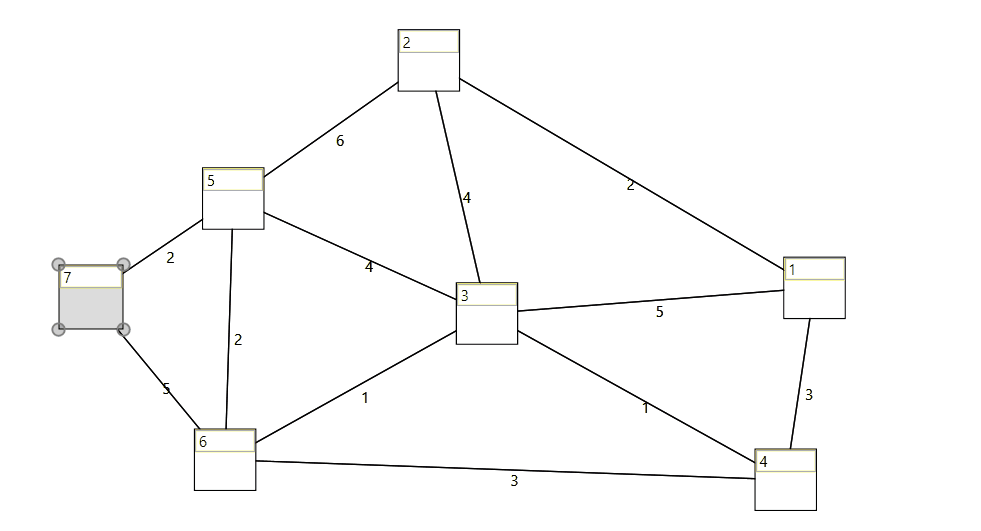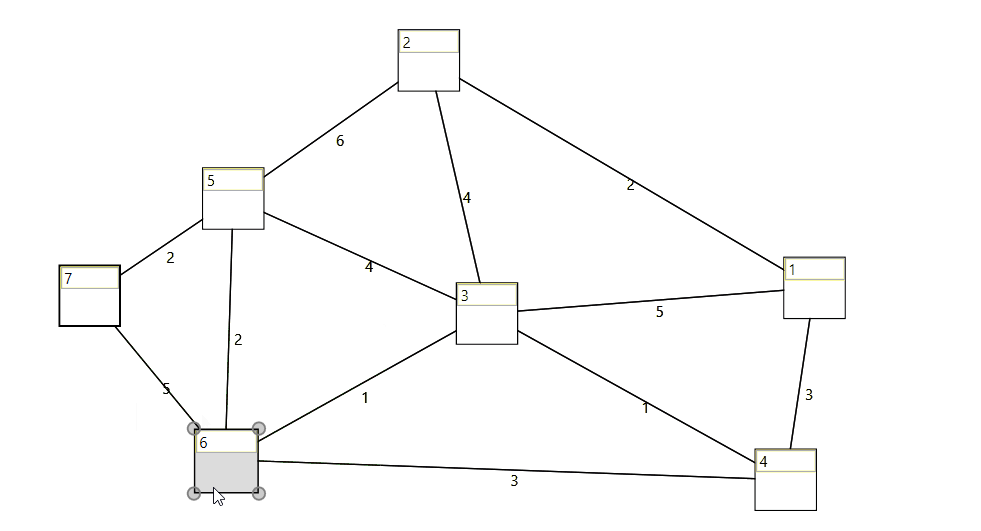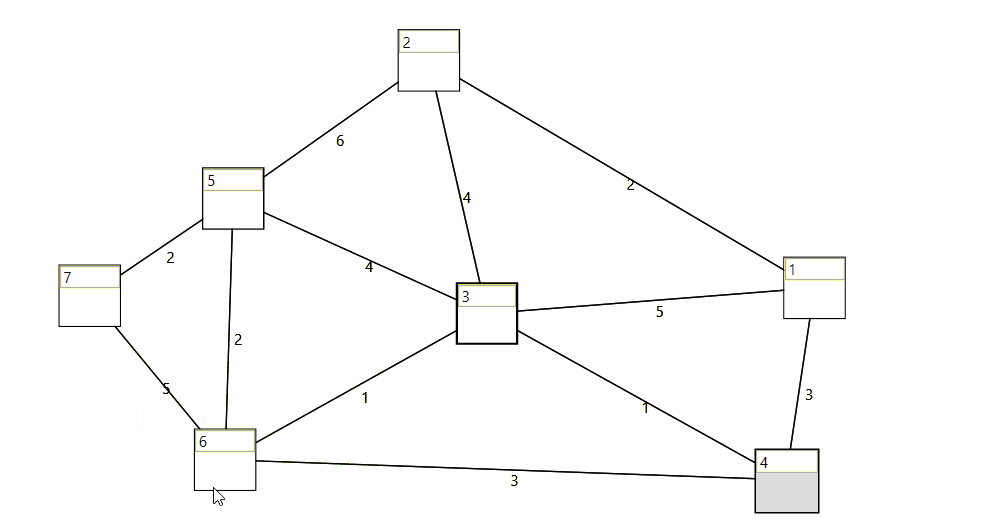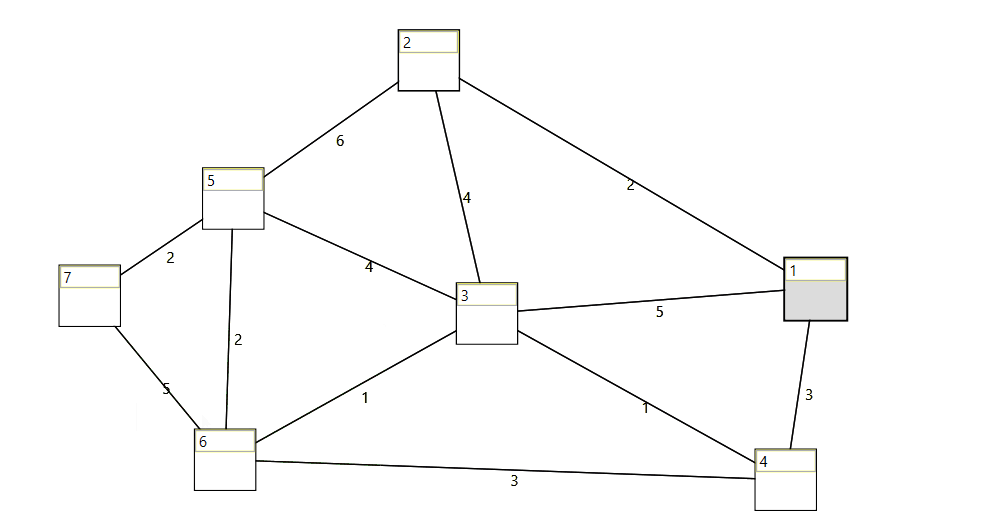
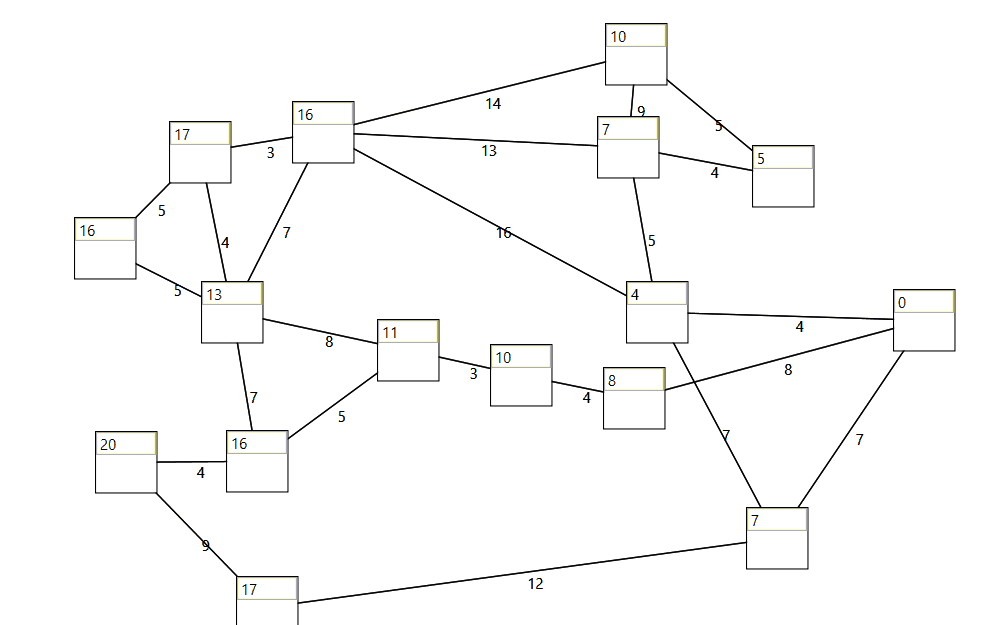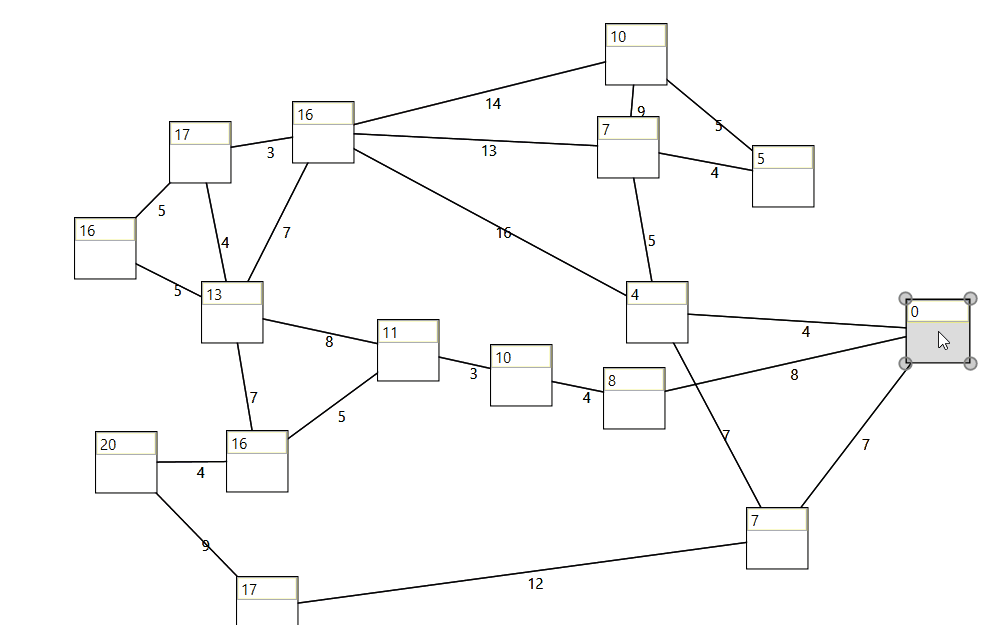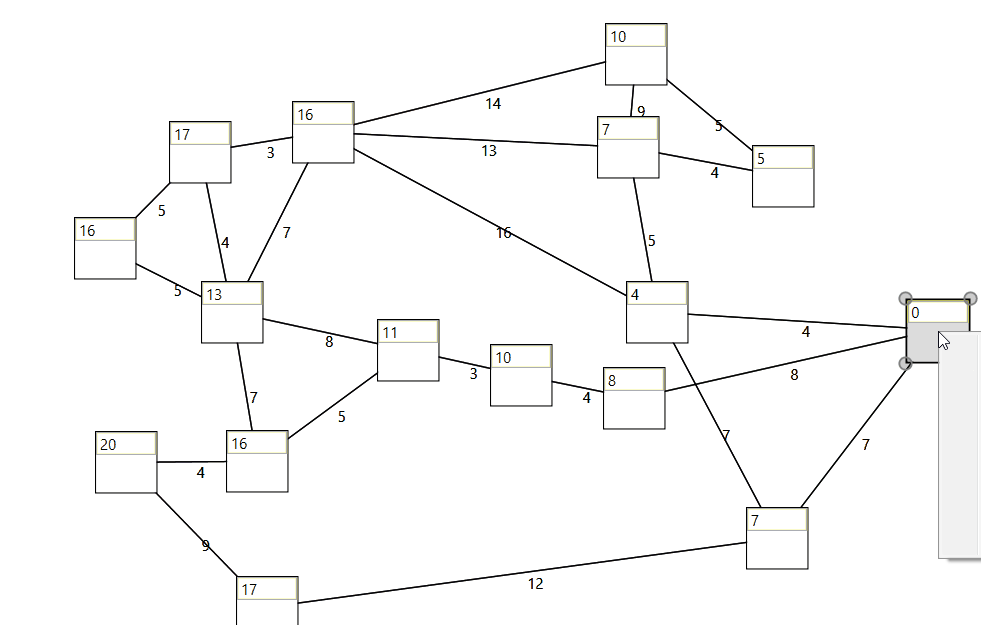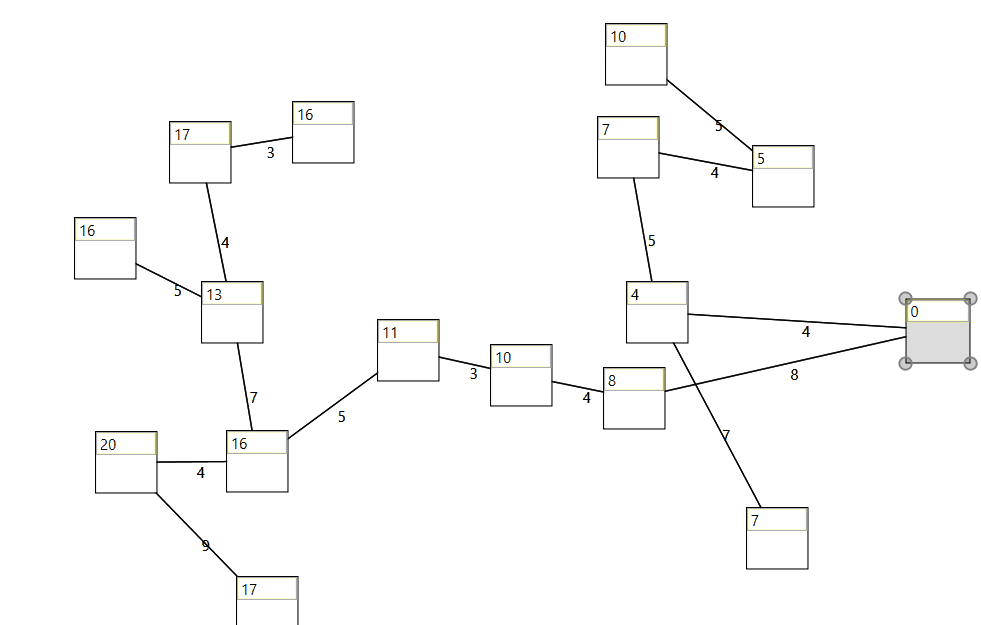
Wpf control to visualize, create and edit a graph. See here.
When taking a beginners class at the technical university of vienna, I started to implement and adopt some lessions from the algorithms and data structures course. I thought it would be fun to put my recently gained knowledge into practice.
Of course some frameworks regarding this topic already exist. For example linked list and various tree classes. When applying these I ran into several issues like limited extensibility, missing features and all of them came from diffrent sources. Therefore I wasn't able to combine the tree classes, especially the data structure classes.
So I started to create my own algorithms and data structures "framework".
With the old version of the framework I mainly focused on visually representing the graph data structure with wpf. (see UI\DataStructures.Demo)
- The Algorithm Design Manual
- A*Star https://www.codeguru.com/csharp/csharp/cs_misc/designtechniques/article.php/c12527/AStar-A-Implementation-in-C-Path-Finding-PathFinder.htm
- The Travelling salesman problem is one of the most well know NP-hard problem. Concorde’s solver can be used to solve exactly or approximately even large instances. http://www.math.uwaterloo.ca/tsp/index.html
- PRIM http://bioinfo.ict.ac.cn/~dbu/AlgorithmCourses/Lectures/Prim1957.pdf
When creating the graph with the ui (graph control) the proper model will be created in the background.
Another approach would be to overgive a graph data structure to the graph visualization control which created the proper ui graph. One of the benefits of the old implemention is that the kruskal algorithm creats a copy of the graph, therefore the vertices dont't stay in the same position.
When modifying a graph during runtime, the graph visualization control updates the ui.
The aforementioned features (graph visualization control) will be implemented into the new framework as well.