Kotlin+MVVM+Retrofit+协程+ViewBinding+EventBus
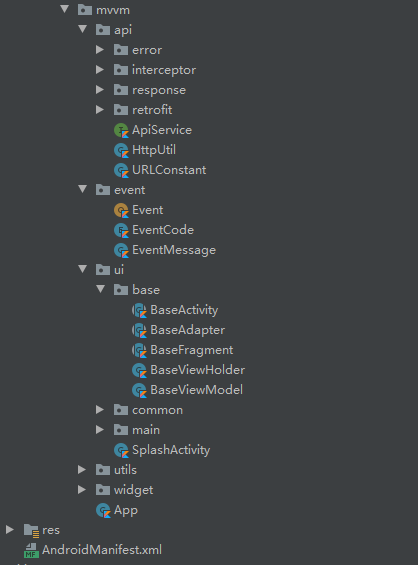
项目框架整体架构图:
-
使用 Kotlin 语言;
-
使用 MVVM + 协程开发模式,相较于常用的 MVP+RxJava 开发模式,会减省大量的 MvpView 的创建及大量的接口回调,并且不再需要 Presenter 的注册和注销,减少内存泄漏风险;
-
ViewBinding(根据 xml 自动生成),你将不再需要进行 findViewById 的繁琐工作,比 ButterKnife 更加方便;
-
关于消息传递,GitHub 上有基于 LiveData 的 LiveEventBus,优点是具有生命周期感知能力,不需要主动注册和注销,但缺点是书写相对麻烦,且无法统一配置,衍生版 SmartEventBus 虽然支持定制,但配置依然麻烦,而本项目选择继续使用 EventBus 的原因,则是因为 EventBus 的强大以及它的稳定性和灵活性,且方便统一配置(下面有讲到);
只需要传入对应的 ViewModel 和 ViewBinding 即可。
class TestActivity : BaseActivity<TestViewModel, ActivityTestBinding>() {
override fun initView() {
}
override fun initClick() {
}
override fun initData() {
}
}无对应的 ViewModel,传入 BaseViewModel 即可。
Fragment 同!
只需要传入数据 model 类型和 item 的 ViewBinding 即可。
class ArticleListAdapter(context: Activity, listDatas: ArrayList<ArticleBean>) :
BaseAdapter<ItemArticleBinding, ArticleBean>(context, listDatas) {
override fun convert(v: ItemArticleBinding, t: ArticleBean, position: Int) {
Glide.with(mContext).load(t.envelopePic).into(v.ivCover)
v.tvTitle.text = t.title
v.tvDes.text = t.desc
}
}@GET("test")
suspend fun test(@QueryMap options: HashMap<String, String?>): BaseResult<TestModel>注意:suspend 不可缺少!
class MainViewModel : BaseViewModel() {
var articlesData = MutableLiveData<ArticleListBean>()
fun getArticleList(page: Int, isShowLoading: Boolean) {
launch({ httpUtil.getArticleList(page) }, articlesData, isShowLoading)
}
}在 Activity 或 Fragment 中直接通过传入的 ViewModel 调用:
vm.getArticleList()//调用接口
vm.articlesData.observe(this, Observer {//返回结果
})本项目中,像 EventBus 的注册与注销,以及消息接收全部放在了 BaseActivity 中,并提供了一个对外的消息处理方法,利用消息 Code 来区分不同消息,在需要使用消息的界面,重写该方法即可:
// 发送消息:
Event.post(EventMessage(EventCode.REFRESH))
/**
* 接收消息
*/
override fun handleEvent(msg: EventMessage) {
super.handleEvent(msg)
if (msg.code == EventCode.REFRESH) {
showMessage("主页:刷新")
page = 0
vm.getArticleList(page, false)
}
}这样做的好处是:
-
不再需要你去手动在每个界面去注册和注销 EventBus,你只用关心什么时候 post 消息,和什么时间接收消息即可,大大减少出错几率,并提高代码可读性;
-
可以随时更换消息传递框架,方便快捷;
当然,缺点,只有一个,就是发送消息所有活动界面都会收到,但这个缺点并未有任何影响,相对于上面提到的优点,完全可以忽略!
该框架已应用到自己公司项目中,运行良好,如果后续发现有坑的地方,会及时更新!
1.使用协程请求接口时,不再需要 withContext-IO,有 suspend 关键字即可;
2.将 UI 更新部分,放在了 viewModel 中进行,在 ui 中仅调用接口请求方法即可,例:
class MainActivityViewModel : BaseViewModel() {
var articlesData = MutableLiveData<ArticleListBean>()
fun getArticleList(page: Int, isShowLoading: Boolean = false) {
launch({ httpUtil.getArticleList(page) }, articlesData, isShowLoading)
}
override fun observe(activity: Activity, owner: LifecycleOwner, viewBinding: ViewBinding) {
val mContext = activity as MainActivity
val vb = viewBinding as ActivityMainBinding
articlesData.observe(owner, Observer {
vb.refreshLayout.finishRefresh()
vb.refreshLayout.finishLoadMore()
if (mContext.page == 0) mContext.list?.clear()
it.datas?.let { it1 -> mContext.list?.addAll(it1) }
mContext.adapter?.notifyDataSetChanged()
})
errorData.observe(owner, Observer {
vb.refreshLayout.finishRefresh()
vb.refreshLayout.finishLoadMore()
})
}
}observe 方法在 BaseActivity 和 BaseFragment 中调用,子 ViewModel 中重写即可,重点是有两个强制转化:
val mContext = activity as MainActivity
val vb = viewBinding as ActivityMainBindingmContext 也可以是 Fragment,即获取该 ui 界面声明的变量,vb 则是当前 ui 的 ViewBinding!
当然,这不是强制的,你也可以选择不使用这种方式,依然在 ui 界面更新 ui!
第二种方式:在 BaseViewModel 中传入 VB 泛型,这样就不需要再传入 ViewBinding 强转了(可以对比一下第一种和第二种写法):
abstract class BaseActivity<VM : BaseViewModel<VB>, VB : ViewBinding> : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var mContext: FragmentActivity
lateinit var vm: VM
lateinit var vb: VB
private var loadingDialog: ProgressDialog? = null
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
initResources()
var pathfinders = ArrayList<GenericParadigmUtil.Pathfinder>()
pathfinders.add(GenericParadigmUtil.Pathfinder(0, 0))
val clazzVM = GenericParadigmUtil.parseGenericParadigm(javaClass, pathfinders) as Class<VM>
vm = ViewModelProvider(this).get(clazzVM)
pathfinders = ArrayList()
pathfinders.add(GenericParadigmUtil.Pathfinder(0, 1))
val clazzVB = GenericParadigmUtil.parseGenericParadigm(javaClass, pathfinders)
val method = clazzVB.getMethod("inflate", LayoutInflater::class.java)
vb = method.invoke(null, layoutInflater) as VB
vm.binding(vb)
vm.observe(this, this)
setContentView(vb.root)
...
open class BaseViewModel<VB : ViewBinding> : ViewModel() {
lateinit var vb: VB
fun binding(vb: VB) {
this.vb = vb
}
open fun observe(activity: Activity, owner: LifecycleOwner) {
}
open fun observe(fragment: Fragment, owner: LifecycleOwner) {
}
class MainActivityViewModel : BaseViewModel<ActivityMainBinding>() {
var articlesData = MutableLiveData<ArticleListBean>()
fun getArticleList(page: Int, isShowLoading: Boolean = false) {
launch({ httpUtil.getArticleList(page) }, articlesData, isShowLoading)
}
override fun observe(activity: Activity, owner: LifecycleOwner) {
val mContext = activity as MainActivity
articlesData.observe(owner, Observer {
vb.refreshLayout.finishRefresh()
vb.refreshLayout.finishLoadMore()
if (mContext.page == 0) mContext.list?.clear()
it.datas?.let { it1 -> mContext.list?.addAll(it1) }
mContext.adapter?.notifyDataSetChanged()
})
errorData.observe(owner, Observer {
vb.refreshLayout.finishRefresh()
vb.refreshLayout.finishLoadMore()
})
}
}子 Adapter 继承 BaseAdapter,不需要再强转 ViewBinding 了:
BaseAdapter:
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: BaseViewHolder, position: Int) {
convert(holder.v as VB, listDatas[position], position)
}
abstract fun convert(v: VB, t: T, position: Int)子类 Adapter:
override fun convert(v: ItemArticleBinding, t: ArticleBean, position: Int) {
Glide.with(mContext).load(t.envelopePic).into(v.ivCover)
v.tvTitle.text = t.title
v.tvDes.text = t.desc
}直接传入 item 对应的 ViewBinding 对象,更加简单便捷!
关于 BaseAdapter,这里解释下原来的说明,为什么 recycleview 的 item 高度要设置为 wrap?
由于 item 的 ViewBinding 也是通过反射得到,但得到后 itemView 的宽高会自动被系统设为 wrap,所以这里需要重新赋值宽高,之前的做法是将父容器宽高给了 item,这里有问题,item 的父容器就是 RecyclerView,所以如果 RecyclerView 设置了宽高后,item 显示就出问题了,因此,现在修改为 item 重置自身宽高,宽度 match_parent,高度 wrap_content,此时就要注意,item 的最外层父布局的的宽高同样为 match_parent 和 wrap_content,这适用于大多数 item 的布局,如果确实有需求要对 item 设置固定宽高,建议在子 Adapter 中通过代码动态设置宽高!
vb.root.layoutParams = RecyclerView.LayoutParams(
RecyclerView.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
RecyclerView.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT
)在使用 viewpager+fragment 过程中发现,某些机型应用在按返回键退出时,fragment 中的 contentView 未销毁:
if (null == contentView) {
contentView = v.root
//...
}
return contentView导致再次打开 App 时,fragment 并未重建,直接用的原来缓存在内存中的 View 致使页面出现问题。对于这种情况,目前的解决办法是在 Fragment 销毁时,将 contentView = null:
override fun onDestroyView() {
super.onDestroyView()
contentView = null
}接口调用流程简化,新增接口只需要在 ApiService 中添加后,即可直接在 ViewModel 中通过 httpUtil 调用,一步到位!
另附上文件上传案例代码,需要时以作参考:
fun uploadFile(path: String) {
val file = File(path)
val map: HashMap<String, RequestBody> = LinkedHashMap()
val requestBody: RequestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("image/*"), file)
map["file\"; filename=\"" + file.name] = requestBody//file为后台规定参数
map["name"] = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("text/plain"), file.name)
map["arg1"] = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("text/plain"), "arg1")//普通参数
map["arg2"] = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("text/plain"), "arg2")
//签名(根据服务器规则)
val params = LinkedHashMap<String, String?>()
params["name"] = file.name
params["arg1"] = "arg1"
params["arg2"] = "arg2"
val sign: String = getSign(params)
map["sign"] = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("text/plain"), sign)
launch({ httpUtil.upLoadFile(map) }, uploadData)
}ApiService:
@Multipart
@POST("/upload")
suspend fun upLoadFile(@PartMap map: HashMap<String, RequestBody>): BaseResult<UploadModel>