A new approach on Identification of Mesothelioma’s Disease using Logistic Regression - L1 regularization and Support Vector Machine
Jardel Santos (@jardsantos)
Venicius Ferreira (@veniciuss)
Identication of Cancer: Mesothelioma's Disease Using Logistic Regression and Association Rule
The Mesotheliona is a rare type of cancer that affects the mesothelium. The mesohtelium is the tissue that lines your lungs, stomach, heart, and other organs. It usually starts in the lungs, but can also start in the abdomen or other organs. It can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer.)
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare but serious type of cancer. This cances is usually assigned to people that work on jobs that exposed them to asbestos particles. After being exposed to asbestos, it usually takes a long time for the disease to form.
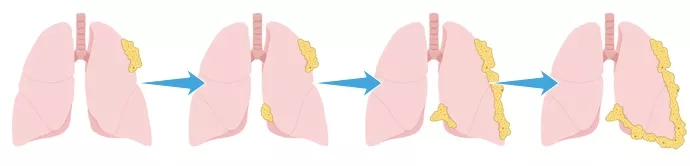
The asbestor particles become lodged in the pleura, a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered membranous pleural sac over the lungs. Over time, the asbestos fibers cause inflammation, scarring and eventually lead to mesothelioma cancer.
Asbestor particles lodged in the pleura over the time
This study uses the patient’s medical reports generated by Dicle University. The dataset contains 34 attributes, one binary response variable and 324 instances. The response variable is disposed in the following distribution:
| Values | # |
|---|---|
| 1 | 228 |
| 2 | 96 |
In the first phase of our model we partitioned the data into training and testing dataset, each one with 75% and 25% of the original data set, we applied the stratify option in order to maintain the balancing of the original dataset.
UCI Database - Mesothelioma Cancer
In this step, we separated the categorical features from the numerical and discretized them, creating dummies. After that all the features (dummmies + numerical) were normalized to zero mean and unit variance.
Logistic regression is the appropriate when we want to describe data and to explain the relationship between one dependent binary variable and one or more nominal, ordinal, interval or ratio-level independent variables. Also, we decided to use regularization in order to reduce generalization error without afects the training error, more than that we use regularization as a feature selection tool. The L1 regularization allow us to bring feature selection and generalizarion error reduce, so we decide to use this technique.
The sklearn library has few atributes that can improve the logistic regression perfomances. Besides the L1 regularization, we use 'liblinear' as optimization solver due the fact that our dataset is small. The C value, the inverse of regularization strength, is chosen by linear seach in the range 0 to 2.
| C | AUC | F1-Score | Features Eliminated |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 59 |
| 0.06 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 59 |
| 0.07 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 58 |
| 0.08 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 54 |
| 0.09 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 52 |
| 0.10 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 52 |
| 0.11 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 48 |
| 0.12 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 44 |
| 0.14 | 0.5274 | 0.1935 | 40 |
| 0.16 | 0.5186 | 0.1875 | 34 |
| 0.18 | 0.5186 | 0.1875 | 33 |
| 0.20 | 0.5636 | 0.3243 | 31 |
| 0.23 | 0.5724 | 0.3333 | 29 |
| 0.25 | 0.5932 | 0.3784 | 29 |
| 0.29 | 0.5932 | 0.3784 | 29 |
| 0.32 | 0.5932 | 0.3784 | 28 |
| 0.36 | 0.5932 | 0.3784 | 27 |
| 0.41 | 0.6140 | 0.4211 | 27 |
| 0.46 | 0.6173 | 0.4390 | 24 |
| 0.52 | 0.6086 | 0.4286 | 22 |
| 0.58 | 0.5910 | 0.4091 | 20 |
| 0.66 | 0.5910 | 0.4091 | 18 |
| 0.74 | 0.5910 | 0.4091 | 18 |
| 0.84 | 0.5822 | 0.4000 | 17 |
| 0.94 | 0.5822 | 0.4000 | 12 |
| 1.06 | 0.5822 | 0.4000 | 13 |
| 1.19 | 0.5822 | 0.4000 | 13 |
| 1.35 | 0.5822 | 0.4000 | 13 |
| 1.52 | 0.5822 | 0.4000 | 13 |
The best C choice is 0.46 that lead us to the bold line with AUC 0.6173, F1-Score 0.4390 and 24 dummies features eliminated. These dummies features represent 10 features in the original dataset.
Relevant Features remaining: 23
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | age | alkaline phosphatise (ALP) | cell count (WBC) | city |
| cytology | duration of asbestos exposure | duration of symptoms | dyspnoea | gender |
| habit of cigarette | hemoglobin (HGB) | keep side | performance status | platelet count (PLT) |
| pleural albumin | pleural glucose | pleural level of acidity (pH) | pleural thickness on tomography | sedimentation |
| total protein | type of MM | weakness |
Dropped features: 10
| ache on chest | albumin | asbestos exposure | blood lactic dehydrogenise (LDH) | dead or not |
| glucose | pleural effusion | pleural lactic dehydrogenise | pleural protein | white blood |
We performed a grid search on 3 of the SVM Classifier hyperparams on the data with the features selected on Logistic Regression and it was our final model.
- 'C': 1.5151515151515151
- 'class_weight': None
- 'kernel': 'rbf'
We also performed a SVM with Lasso Regression using cross-validation method in order to avoid overfitting and got the following results:
| Metric | Mean | CV 1 | CV 2 | CV 3 | CV 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 75.00% | 0.72839506 | 0.7654321 | 0.71604938 | 0.79012346 |
| ROC_AUC | 74.05% | 0.73464912 | 0.75584795 | 0.69005848 | 0.78143275 |
The results of SVM without Lasso Regression are the following:
| Metric | Mean | CV 1 | CV 2 | CV 3 | CV 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 74.38% | 0.71604938 | 0.75308642 | 0.71604938 | 0.79012346 |
| ROC_AUC | 67.73% | 0.6622807 | 0.70394737 | 0.62207602 | 0.72076023 |
The Logistic Regresion with Lasso Regression performance:
| Metric | Mean | CV 1 | CV 2 | CV 3 | CV 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 72.84% | 0.71604938 | 0.74074074 | 0.69135802 | 0.7654321 |
| ROC_AUC | 65.61% | 0.5994152 | 0.71710526 | 0.60233918 | 0.70540936 |