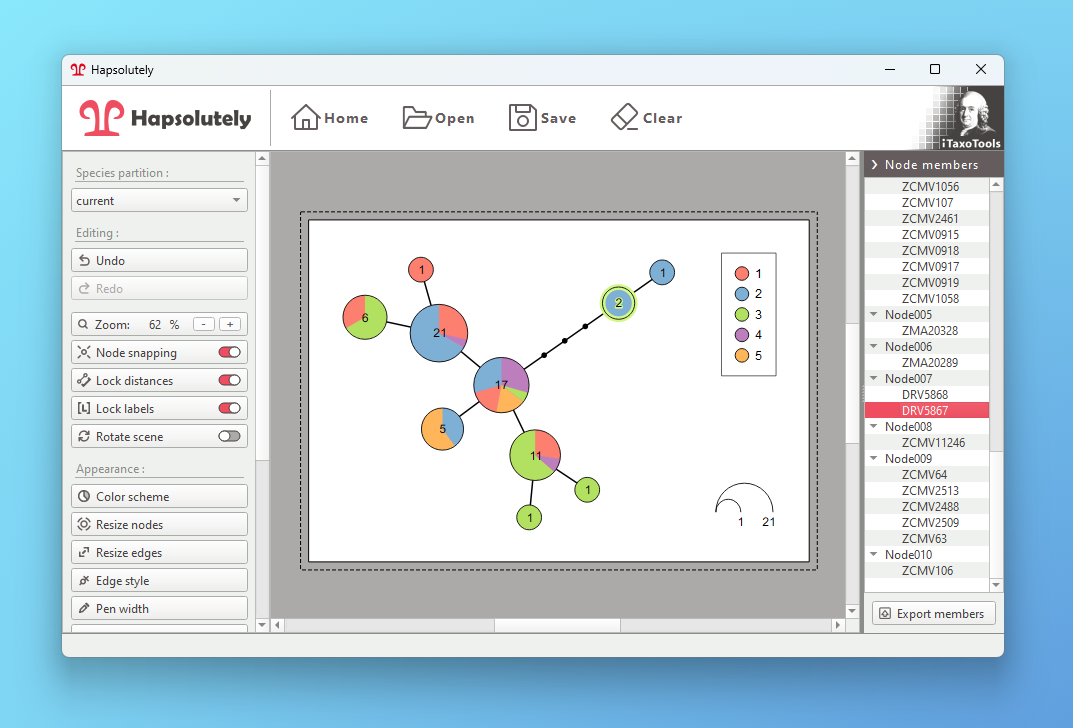
Reconstruct haplotypes and produce genealogy graphs from population data.
- Phase sequences: Reconstruct haplotypes from sequence data
- Haplotype visualization: Generate haplotype networks, genealogies and haplowebs
- Haplotype statistics: Detect fields for recombination and subset overlap
Hapsolutely is a comprehensive program that integrates ConvPhase, haplodemo, popart_networks and haplostats.
Input files can be in TSV, FASTA or SPART/XML format.
Download and run the standalone executables without installing Python.
Hapsolutely is available on PyPI. You can install it through pip:
pip install itaxotools-hapsolutely
hapsolutely
Please refer to the Hapsolutely manual for information on how to use the program.
Hapsolutely was developed in the framework of the iTaxoTools project:
Vences M. et al. (2021): iTaxoTools 0.1: Kickstarting a specimen-based software toolkit for taxonomists. - Megataxa 6: 77-92.
Sequences are phased using PHASE and SeqPHASE:
Stephens, M., Smith, N., and Donnelly, P. (2001). A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. American Journal of Human Genetics, 68, 978--989.
Stephens, M., and Donnelly, P. (2003). A comparison of Bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population genotype data. American Journal of Human Genetics, 73:1162-1169.
Flot, J.F. (2010) seqphase: a web tool for interconverting phase input/output files and fasta sequence alignments. Mol. Ecol. Resour., 10, 162–166.
Networks are generated using either of Fitchi or popart_networks:
Matschiner M (2015) Fitchi: Haplotype genealogy graphs based on the Fitch algorithm. Bioinformatics, 32:1250-252.
Leigh, JW, Bryant D (2015). PopART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol Evol 6(9):1110-1116.
Bandelt H, Forster P, Röhl A (1999). Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16(1):37-48.
Clement M, Snell Q, Walke P, Posada D, Crandall, K (2002). TCS: estimating gene genealogies. Proc 16th Int Parallel Distrib Process Symp 2:184.
Doyle, J. J. (1995) The irrelevance of allele tree topologies for species delimitation, and a non-topological alternative. Syst. Bot., 20, 574-588.
BioPython is used to create ML/NJ trees if needed. networkx is used for laying out the initial graph.
Cock, P.J. et al., 2009. Biopython: freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 25(11), pp.1422-1423.
Hagberg, A., Swart, P. & S Chult, D., 2008. Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX.