-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 32
Health Check with WatchDogs
Health checks are an essential aspect of microservices architecture.
A health check is a procedure that helps to determine if a microservice is functioning correctly or not.
It involves checking various aspects of the microservice, such as the network connectivity, dependencies,
and resources that the microservice uses.
There is more than one reason to use health checks in a microservice environment.
-
Improved Reliability:
Health checks enable the microservices to be more reliable by providing real-time information
about the health of the microservices. When a microservice fails, the health check can quickly
detect the failure and notify the relevant parties, allowing them to take corrective measures. -
Better Monitoring:
Health checks can offer comprehensive data on how the microservices perform.
This data can be used to track and evaluate the microservices' functionality over time
and spot problems before they get out of hand. -
Faster Issue Resolution:
By identifying problems with the microservices rapidly, health checks can help shorten the time
it takes to fix problems. As a result of the development teams' ability to identify problems in real time,
downtime can be avoided and the effect on users is minimized.
Health checking can be installed using the following Docker files. More information about the installation is here:
Getting Started
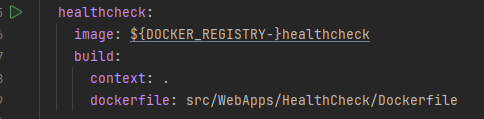
https://github.com/ebubekirdinc/SuuCat/blob/master/docker-compose.yml
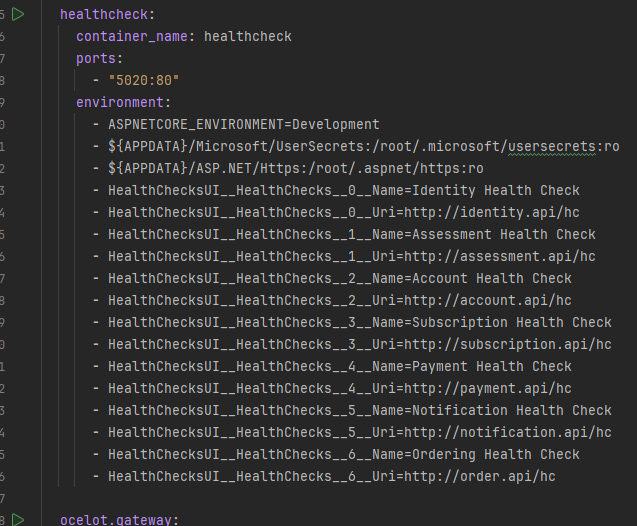
https://github.com/ebubekirdinc/SuuCat/blob/master/docker-compose.override.yml
.
Note that, as can be seen under the environment section, each microservices must be set separately.
In our project, we have implemented health checks for each microservice.
For example, the following is the health check of the Identity microservice, which is obtained by sending a GET request to the following URL:
{
"status": "Healthy",
"totalDuration": "00:00:00.0017412",
"entries": {
"masstransit-bus": {
"data": {
"Endpoints": {
"rabbitmq://localhost/EBU_Identity_bus_wbdyyyn5mqyxwpmkbdp184fzb9?temporary=true": {
"status": "Healthy",
"description": "ready (not started)"
}
}
},
"description": "Ready",
"duration": "00:00:00.0015457",
"status": "Healthy",
"tags": [
"ready",
"masstransit"
]
}
}
}The health check of each microservice can be accessed similarly.
But in order to see the health status of all microservices at once, we have implemented a health check project.
endpoints.MapHealthChecksUI(); is added to the Startup.cs file of the HealthCheck project.
 https://github.com/ebubekirdinc/SuuCat/blob/master/src/WebApps/HealthCheck/Program.cs
https://github.com/ebubekirdinc/SuuCat/blob/master/src/WebApps/HealthCheck/Program.cs
And appsettings.json file:
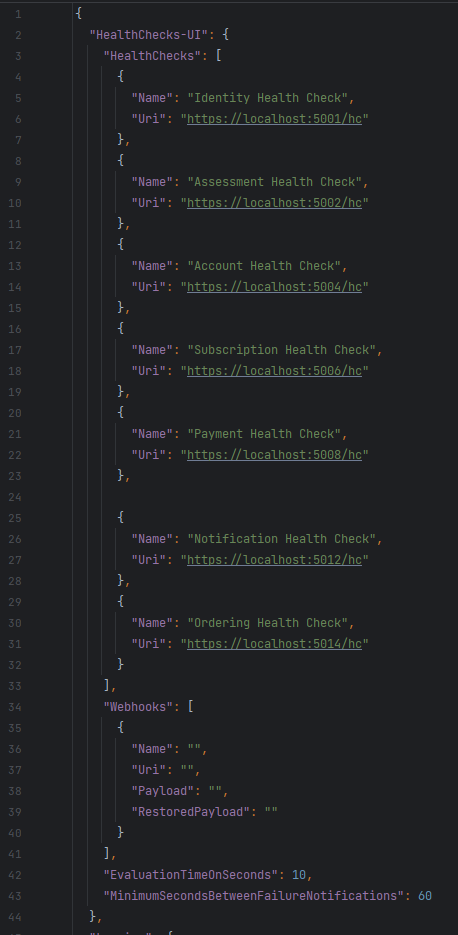 https://github.com/ebubekirdinc/SuuCat/blob/master/src/WebApps/HealthCheck/appsettings.json
https://github.com/ebubekirdinc/SuuCat/blob/master/src/WebApps/HealthCheck/appsettings.json
Use the following URL to access the health check page of all microservices:
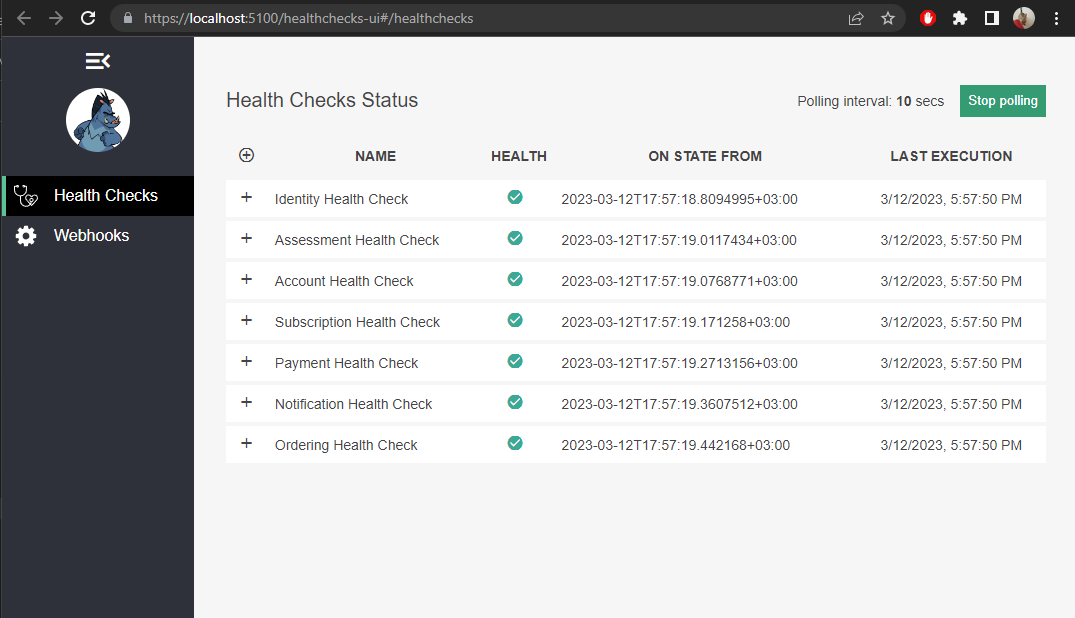 WatchDog Health Checks(Healthy status)
WatchDog Health Checks(Healthy status)
Here, we can see the health status of all microservices.
If you click on the Expand All button, you can see the details of the health check of each microservice. And you can see additional information like Db connection, or RabbitMq connection.
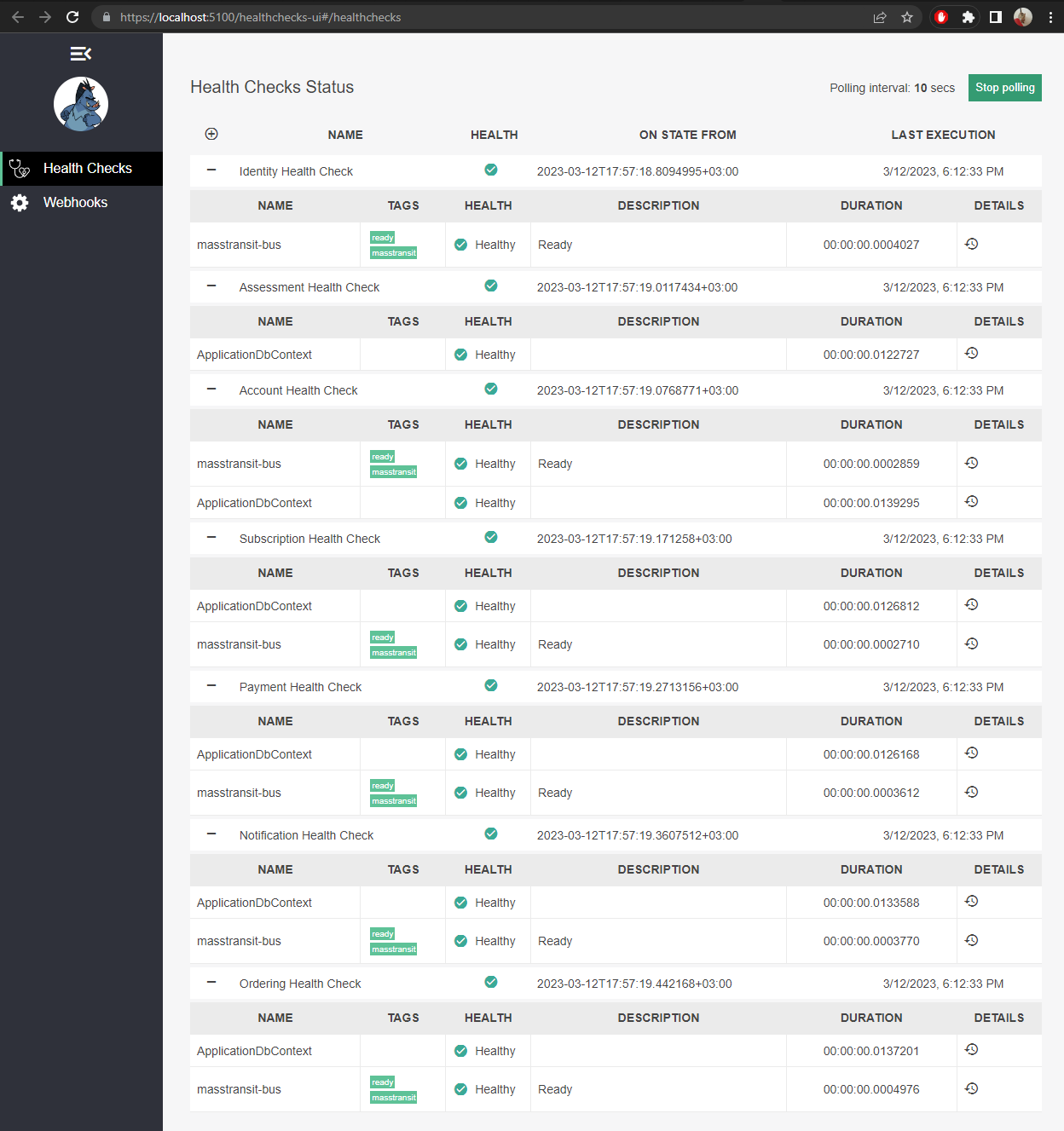 WatchDog Health Checks(Healthy status)
WatchDog Health Checks(Healthy status)
If any microservice is unhealthy, we can click on it to see the details of the problem. As you can see in the following image, the Assessment microservice is unhealthy because it is not running.
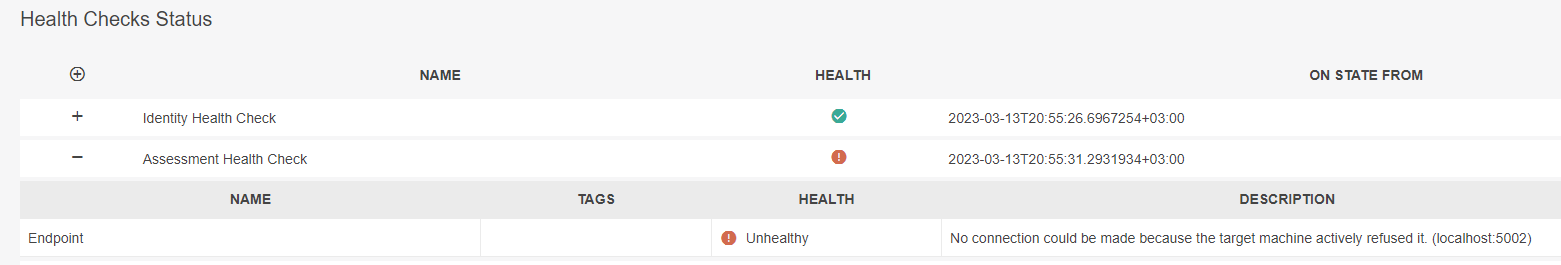 WatchDog Health Checks(Healthy status)
WatchDog Health Checks(Healthy status)