K-fold cross validation framework of tensorflow-based time series forecasting models for problems with hourly frequency and daily seasonality (e.g. Energy Prices, Solar Energy Production, Energy Load, etc...)
These instructions are valid for Linux Ubuntu 18.04 OS, but it should work on other OS with proper modifications.
After cloning or downloading this repository in a directory (DIR_MAIN, e.g. ~/Desktop/Projects) I strongly suggest to install virtualenv if not already present on your machine: it will help you setting up a project-specific python interpreter without installing packages system-wide. In order to install it, execute in a terminal (Ctrl-Alt-t):
sudo apt-get install virtualenv # install virtualenv
cd DIR_MAIN # cd to the repository directory
virtualenv venv # create the virtual environment
source ./venv/bin/activate # activate it
pip install -r requirements.txt # install the required packages
and you're all set.
This repository uses the CPU version of Tenforslow 2.1.0. but the GPU accelerated package tensorflow-gpu can be interchangeably used (the installation guide can be found here).
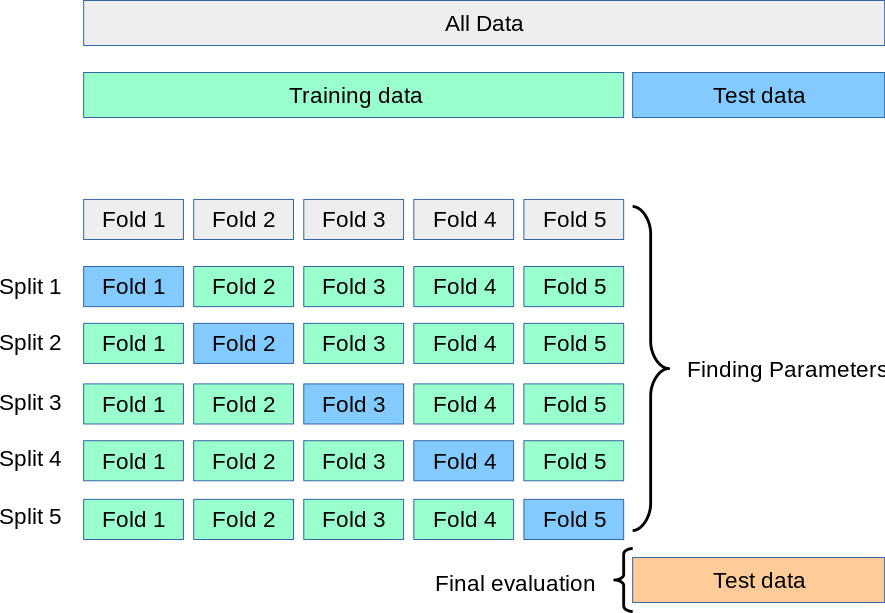
K-fold cross validation is a technique that allows to tune ML models' hyperparameters by splitting
- the dataset in a training and in a test set
- the training set in K equally sized sub-sets
Of the k sub-sets, one is retained as the validation data, and the remaining k − 1 are used as training data. The cross-validation process is then repeated k times, with each of the k sub-sets used exactly once as the validation data.
Once the process is completed, the performances of the selected combination of hyperparameters is given by the average of the performances on the k validation folds (one should also check that the variance of the performances on the k validation sets aren't too high, in order to confirm that the data is indipendent and identically distributed i.i.d).
This procedure allows to identify the best model architecture, and the overall model performances can be eventually evaluated on the test set. If overfitting of the validation sets didn't occur, the performances of the (k) validation and test sets should be similar.
When dealing with time series, a standard k-split of the training set would lead to the injection of informations from future time steps into the training set, leading to biased performance in all folds (except for the k-th one that uses past data in the training phase). Therefore an additional split in the training set is applied:
- The fraction of the dataset containing the least recent samples is identified and used for training
- The remaining dataset is sliced in k equally sized sub-sets and validation is performed on them starting from the least recent data. For every fold after the first one, the precedent fold is added to the training set.
From this point the process is similar to the standard one, with the evaluation of the average fold and test performances.
(I found this good and self-explanatory image here)
The current framework allows to perform time series k-fold crossvalidation on data with hourly frequency and daily seasonality.
In order to better unfold the hourly-specific dynamics, 24 hourly independent models are trained and validated on 6 validation folds following the procedure described in the previous subsection.
After setting the desired set of hyperparameters in the globals.py file, open a terminal and type:
cd DIR_MAIN
source ./venv/bin/activate
python main.py
A dedicated folder for every run is created in the ./run folder, and data such as learning curves, metrics (MSE, MAE and MAPE)and weights are stored in it.
The training phase of every model saved in ./runs/RUN_DIR/HOUR_DIR can be monitored through Tensorboard, just open a terminal and type:
cd DIR_MAIN
source ./venv/bin/activate
tensorboard -logdir=DIR_MAIN/runs/RUN_DIR/HOUR_DIR
then open a browser and in the url box type localhost:6006.
Hour-wise and overall metrics for every combination of hyperparameter are evaluated and stored in the metrics.csv files
that can be found in ./runs/RUN_DIR_NAME and ./runs/RUN_DIR/HOUR_DIR.