Extensions for Microsoft.Agents.AI and Microsoft.Extensions.AI.
To ensure the long-term sustainability of this project, users of this package who generate revenue must pay an Open Source Maintenance Fee. While the source code is freely available under the terms of the License, this package and other aspects of the project require adherence to the Maintenance Fee.
To pay the Maintenance Fee, become a Sponsor at the proper OSMF tier. A single fee covers all of Devlooped packages.
Extensions for Microsoft.Agents.AI, such as configuration-driven auto-reloading agents.
Microsoft.Agents.AI (aka Agent Framework is a comprehensive API for building AI agents. Its programatic model (which follows closely the Microsoft.Extensions.AI approach) provides maximum flexibility with little prescriptive structure.
This package provides additional extensions to make developing agents easier and more declarative.
Tweaking agent options such as description, instructions, chat client to use and its options, etc. is very common during development/testing. This package provides the ability to drive those settings from configuration (with auto-reload support). This makes it far easier to experiment with various combinations of agent instructions, chat client providers and options, and model parameters without changing code, recompiling or even restarting the application:
Note
This example shows integration with configurable chat clients feature from the
Devlooped.Extensions.AI package, but any IChatClient registered in the DI container
with a matching key can be used.
{
"AI": {
"Agents": {
"MyAgent": {
"Description": "An AI agent that helps with customer support.",
"Instructions": "You are a helpful assistant for customer support.",
"Client": "Grok",
"Options": {
"ModelId": "grok-4",
"Temperature": 0.5,
}
}
},
"Clients": {
"Grok": {
"Endpoint": "https://api.grok.ai/v1",
"ModelId": "grok-4-fast-non-reasoning",
"ApiKey": "xai-asdf"
}
}
}
}var host = new HostApplicationBuilder(args);
host.Configuration.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json, optional: false, reloadOnChange: true);
// 👇 implicitly calls AddChatClients
host.AddAIAgents();
var app = host.Build();
var agent = app.Services.GetRequiredKeyedService<AIAgent>("MyAgent");Agents are also properly registered in the corresponding Microsoft Agent Framework AgentCatalog:
var catalog = app.Services.GetRequiredService<AgentCatalog>();
await foreach (AIAgent agent in catalog.GetAgentsAsync())
{
var metadata = agent.GetService<AIAgentMetadata>();
Console.WriteLine($"Agent: {agent.Name} by {metadata.ProviderName}");
}Extensions for Microsoft.Extensions.AI
Since tweaking chat options such as model identifier, reasoning effort, verbosity and other model settings is very common, this package provides the ability to drive those settings from configuration (with auto-reload support), both per-client as well as per-request. This makes local development and testing much easier and boosts the dev loop:
{
"AI": {
"Clients": {
"Grok": {
"Endpoint": "https://api.grok.ai/v1",
"ModelId": "grok-4-fast-non-reasoning",
"ApiKey": "xai-asdf"
}
}
}
}var host = new HostApplicationBuilder(args);
host.Configuration.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json, optional: false, reloadOnChange: true);
host.AddChatClients();
var app = host.Build();
var grok = app.Services.GetRequiredKeyedService<IChatClient>("Grok");Changing the appsettings.json file will automatically update the client
configuration without restarting the application.
Full support for Grok Live Search and Reasoning model options.
// Sample X.AI client usage with .NET
var messages = new Chat()
{
{ "system", "You are a highly intelligent AI assistant." },
{ "user", "What is 101*3?" },
};
var grok = new GrokChatClient(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("XAI_API_KEY")!, "grok-3-mini");
var options = new GrokChatOptions
{
ModelId = "grok-3-mini-fast", // 👈 can override the model on the client
Temperature = 0.7f,
ReasoningEffort = ReasoningEffort.High, // 👈 or Low
Search = GrokSearch.Auto, // 👈 or On/Off
};
var response = await grok.GetResponseAsync(messages, options);Search can alternatively be configured using a regular ChatOptions
and adding the HostedWebSearchTool to the tools collection, which
sets the live search mode to auto like above:
var messages = new Chat()
{
{ "system", "You are an AI assistant that knows how to search the web." },
{ "user", "What's Tesla stock worth today? Search X and the news for latest info." },
};
var grok = new GrokChatClient(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("XAI_API_KEY")!, "grok-3");
var options = new ChatOptions
{
Tools = [new HostedWebSearchTool()] // 👈 equals setting GrokSearch.Auto
};
var response = await grok.GetResponseAsync(messages, options);We also provide an OpenAI-compatible WebSearchTool that can be used to restrict
the search to a specific country in a way that works with both Grok and OpenAI:
var options = new ChatOptions
{
Tools = [new WebSearchTool("AR")] // 👈 search in Argentina
};This is equivalent to the following when used with a Grok client:
var options = new ChatOptions
{
// 👇 search in Argentina
Tools = [new GrokSearchTool(GrokSearch.On) { Country = "AR" }]
};To configure advanced live search options, beyond the On|Auto|Off settings
in GrokChatOptions, you can use the GrokSearchTool instead, which exposes
the full breath of live search options
available in the Grok API.
var options = new ChatOptions
{
Tools = [new GrokSearchTool(GrokSearch.On)
{
FromDate = new DateOnly(2025, 1, 1),
ToDate = DateOnly.FromDateTime(DateTime.Now),
MaxSearchResults = 10,
Sources =
[
new GrokWebSource
{
AllowedWebsites =
[
"https://catedralaltapatagonia.com",
"https://catedralaltapatagonia.com/parte-de-nieve/",
"https://catedralaltapatagonia.com/tarifas/"
]
},
]
}]
};Tip
You can configure multiple sources including GrokWebSource, GrokNewsSource,
GrokRssSource and GrokXSource, each containing granular options.
The support for OpenAI chat clients provided in Microsoft.Extensions.AI.OpenAI fall short in some scenarios:
- Specifying per-chat model identifier: the OpenAI client options only allow setting
a single model identifier for all requests, at the time the
OpenAIClient.GetChatClientis invoked. - Setting reasoning effort: the Microsoft.Extensions.AI API does not expose a way to set reasoning
effort for reasoning-capable models, which is very useful for some models like
o4-mini.
So solve both issues, this package provides an OpenAIChatClient that wraps the underlying
OpenAIClient and allows setting the model identifier and reasoning effort per request, just
like the above Grok examples showed:
var messages = new Chat()
{
{ "system", "You are a highly intelligent AI assistant." },
{ "user", "What is 101*3?" },
};
IChatClient chat = new OpenAIChatClient(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OPENAI_API_KEY")!, "gpt-5");
var options = new ChatOptions
{
ModelId = "gpt-5-mini", // 👈 can override the model on the client
ReasoningEffort = ReasoningEffort.High, // 👈 or Medium/Low/Minimal, extension property
};
var response = await chat.GetResponseAsync(messages, options);Tip
We provide support for the newest Minimal reasoning effort in the just-released
GPT-5 model family.
Similar to the Grok client, we provide the WebSearchTool to enable search customization
in OpenAI too:
var options = new ChatOptions
{
// 👇 search in Argentina, Bariloche region
Tools = [new WebSearchTool("AR")
{
Region = "Bariloche", // 👈 Bariloche region
TimeZone = "America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires", // 👈 IANA timezone
ContextSize = WebSearchToolContextSize.High // 👈 high search context size
}]
};Note
This enables all features supported by the Web search feature in OpenAI.
If advanced search settings are not needed, you can use the built-in M.E.AI HostedWebSearchTool
instead, which is a more generic tool and provides the basics out of the box.
The underlying HTTP pipeline provided by the Azure SDK allows setting up policies that can observe requests and responses. This is useful for monitoring the requests and responses sent to the AI service, regardless of the chat pipeline configuration used.
This is added to the OpenAIClientOptions (or more properly, any
ClientPipelineOptions-derived options) using the Observe method:
var openai = new OpenAIClient(
Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OPENAI_API_KEY")!,
new OpenAIClientOptions().Observe(
onRequest: request => Console.WriteLine($"Request: {request}"),
onResponse: response => Console.WriteLine($"Response: {response}"),
));You can for example trivially collect both requests and responses for payload analysis in tests as follows:
var requests = new List<JsonNode>();
var responses = new List<JsonNode>();
var openai = new OpenAIClient(
Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OPENAI_API_KEY")!,
new OpenAIClientOptions().Observe(requests.Add, responses.Add));We also provide a shorthand factory method that creates the options and observes is in a single call:
var requests = new List<JsonNode>();
var responses = new List<JsonNode>();
var openai = new OpenAIClient(
Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OPENAI_API_KEY")!,
OpenAIClientOptions.Observable(requests.Add, responses.Add));Given the following tool:
MyResult RunTool(string name, string description, string content) { ... }You can use the ToolFactory and FindCall<MyResult> extension method to
locate the function invocation, its outcome and the typed result for inspection:
AIFunction tool = ToolFactory.Create(RunTool);
var options = new ChatOptions
{
ToolMode = ChatToolMode.RequireSpecific(tool.Name), // 👈 forces the tool to be used
Tools = [tool]
};
var response = await client.GetResponseAsync(chat, options);
// 👇 finds the expected result of the tool call
var result = response.FindCalls<MyResult>(tool).FirstOrDefault();
if (result != null)
{
// Successful tool call
Console.WriteLine($"Args: '{result.Call.Arguments.Count}'");
MyResult typed = result.Result;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Tool call not found in response.");
}If the typed result is not found, you can also inspect the raw outcomes by finding
untyped calls to the tool and checking their Outcome.Exception property:
var result = response.FindCalls(tool).FirstOrDefault();
if (result.Outcome.Exception is not null)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Tool call failed: {result.Outcome.Exception.Message}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"Tool call succeeded: {result.Outcome.Result}");
}Important
The ToolFactory will also automatically sanitize the tool name
when using local functions to avoid invalid characters and honor
its original name.
Additional UseJsonConsoleLogging extension for rich JSON-formatted console logging of AI requests
are provided at two levels:
- Chat pipeline: similar to
UseLogging. - HTTP pipeline: lowest possible layer before the request is sent to the AI service,
can capture all requests and responses. Can also be used with other Azure SDK-based
clients that leverage
ClientPipelineOptions.
Note
Rich JSON formatting is provided by Spectre.Console
The HTTP pipeline logging can be enabled by calling UseJsonConsoleLogging on the
client options passed to the client constructor:
var openai = new OpenAIClient(
Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OPENAI_API_KEY")!,
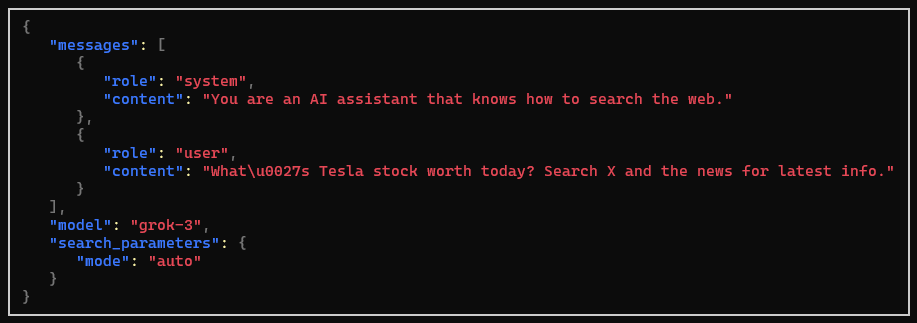
new OpenAIClientOptions().UseJsonConsoleLogging());For a Grok client with search-enabled, a request would look like the following:
Both alternatives receive an optional JsonConsoleOptions instance to configure
the output, including truncating or wrapping long messages, setting panel style,
and more.
The chat pipeline logging is added similar to other pipeline extensions:
IChatClient client = new GrokChatClient(Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("XAI_API_KEY")!, "grok-3-mini")
.AsBuilder()
.UseOpenTelemetry()
// other extensions...
.UseJsonConsoleLogging(new JsonConsoleOptions()
{
// Formatting options...
Border = BoxBorder.None,
WrapLength = 80,
})
.Build();