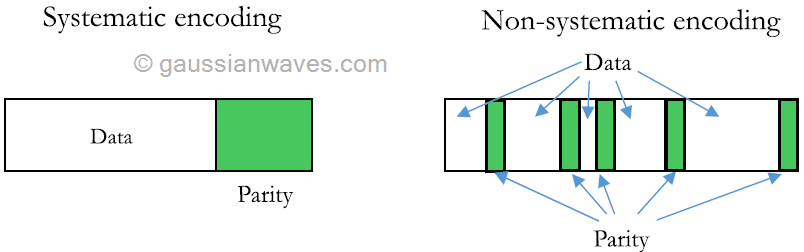
Bit errors occur when data bits are undesirably flipped during transfer. Causes include network interference, hardware failure/deterioration, etc. Hamming codes are error-correcting codes capable of reversing single-bit errors by padding messages with parity bits. In addition, non-systematic encoding allows Hamming codes' efficiency to grow exponentially as message length increases.
| Data Bits ( 2m - m - 1 ) | 1 | 4 | 11 | 26 | 57 | 120 | 247 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency (Data vs. Total Bits) | 33% | 57% | 73% | 84% | 91% | 95% | 97% |
An autoscaling Hamming encoder/decoder to correct single-bit errors while maximizing storage efficiency. Errors are simulated over a TCP transmission and rectified by the receiver. Note: we establish an upper bound of 247 data-bits per chunk (97% efficient) to prevent 2-bit chunk errors.