SedonaDB is an open-source single-node analytical database engine with geospatial as a first-class citizen. It aims to deliver the fastest spatial analytics query speed and the most comprehensive function coverage available.
SedonaDB is perfect for processing smaller to medium datasets on local machines or cloud instances. For distributed workloads, you can leverage the power of SedonaSpark, SedonaFlink, or SedonaSnow.
-
Columnar in-memory datasets
- Spatial indexing
- Spatial statistics
- CRS tracking
- Arrow format and zero serialization overhead
-
Spatial query optimization
- Spatial-aware heuristic based optimization
- Spatial-aware cost based optimization
-
Spatial query processing
- Spatial range query, KNN query, spatial join query, KNN join query
- Map algebra, NDVI, mask, zonal statistics
Raster functions are coming soon. We expect SedonaDB Raster will match all raster functions provided in SedonaSpark.
SedonaDB has several advantages:
- High Performance: Built in Rust for exceptional speed and memory efficiency
- Comprehensive Spatial Toolkit: Supports both vector and raster functions in a single library
- CRS Propagation: Always maintains coordinate reference system information
- Format Flexibility: Supports legacy and modern file formats including GeoParquet, Shapefile, GeoJSON
- Dual APIs: Python and SQL interfaces for seamless workflow integration
- Extensible: Easily customizable and extensible architecture
- Ecosystem Integration: Interoperable with PyArrow-compatible libraries like GeoPandas, DuckDB, and Polars
- Active Community: Great maintainers and contributors who encourage external contributions
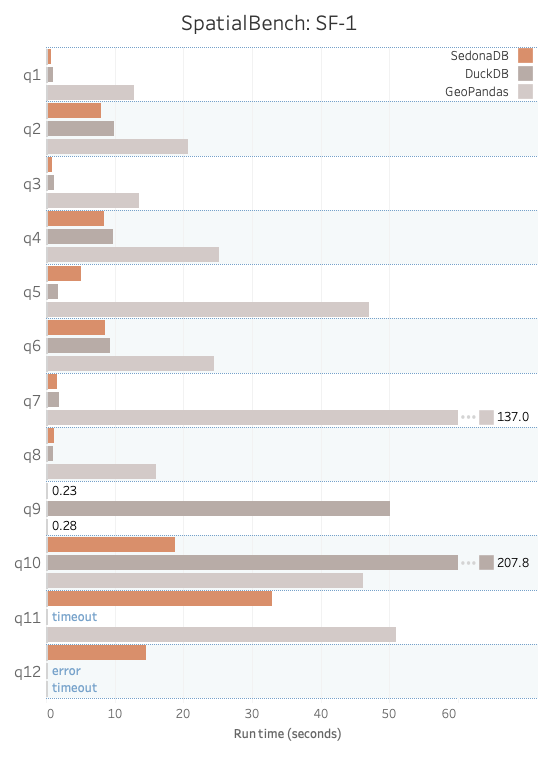
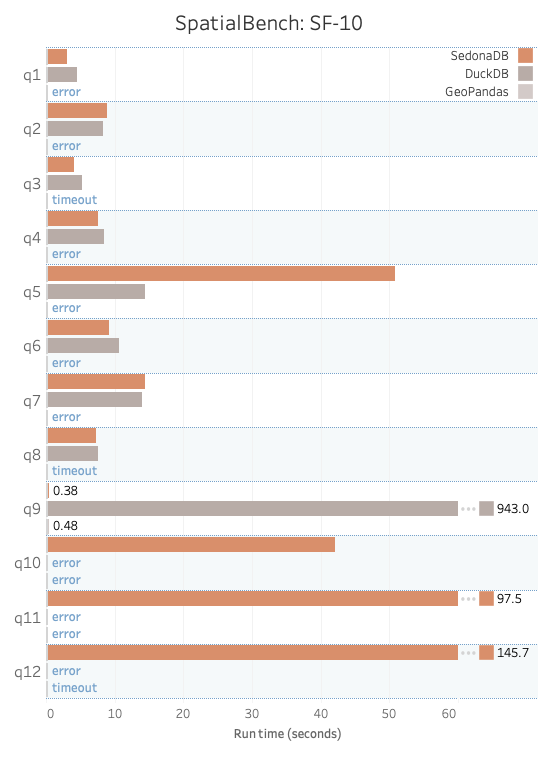
This is a performance benchmark comparing SedonaDB 0.1.0, DuckDB 1.4.0, and GeoPandas 1.1.1 using SpatialBench Queries 1-12 at Scale Factors 1 and 10. Details can be found at Apache Sedona SpatialBench.
You can install Python SedonaDB with PyPI:
pip install "apache-sedona[db]"Get started with SedonaDB in just a few lines:
import sedona.db
# Connect to SedonaDB
sd = sedona.db.connect()
# Run a simple spatial query
result = sd.sql("SELECT ST_Point(0, 1) as geom")
result.show()SedonaDB supports a wide range of geospatial file formats:
- Vector: GeoParquet, WKT, WKB, all formats supported by GeoPandas
- Raster: Coming soon with full SedonaSpark compatibility
This section shows how to query the Overture buildings data.
Start by establishing a connection:
import sedona.db
sd = sedona.db.connect()Read the dataset into a Python SedonaDB DataFrame. This is lazy: even though the Overture buildings table contains millions of rows, SedonaDB will only fetch the data required for the query.
df = sd.read_parquet(
"s3://overturemaps-us-west-2/release/2026-02-18.0/theme=buildings/type=building/",
options={"aws.skip_signature": True, "aws.region": "us-west-2"},
)
df.to_view("buildings")Now run a query to compute the centroids of tall buildings (above 20 meters) in New York City:
nyc_bbox_wkt = (
"POLYGON((-74.2591 40.4774, -74.2591 40.9176, -73.7004 40.9176, -73.7004 40.4774, -74.2591 40.4774))"
)
sd.sql(f"""
SELECT
id,
height,
num_floors,
roof_shape,
ST_Centroid(geometry) as centroid
FROM
buildings
WHERE
is_underground = FALSE
AND height IS NOT NULL
AND height > 20
AND ST_Intersects(geometry, ST_GeomFromText('{nyc_bbox_wkt}', 4326))
LIMIT 5;
""").show()Here's the query output:
┌─────────────────────────┬────────────────────┬────────────┬────────────┬─────────────────────────┐
│ id ┆ height ┆ num_floors ┆ roof_shape ┆ centroid │
│ utf8 ┆ float64 ┆ int32 ┆ utf8 ┆ geometry │
╞═════════════════════════╪════════════════════╪════════════╪════════════╪═════════════════════════╡
│ 1b9040c2-2e79-4f56-aba… ┆ 22.4 ┆ ┆ ┆ POINT(-74.230407502993… │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ 1b5e1cd2-d697-489e-892… ┆ 21.5 ┆ ┆ ┆ POINT(-74.231451103592… │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ c1afdf78-bf84-4b8f-ae1… ┆ 20.9 ┆ ┆ ┆ POINT(-74.232593032240… │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ 88f36399-b09f-491b-bb6… ┆ 24.5 ┆ ┆ ┆ POINT(-74.231878209597… │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ df37a283-f5bd-4822-a05… ┆ 24.154542922973633 ┆ ┆ ┆ POINT(-74.241910239840… │
└─────────────────────────┴────────────────────┴────────────┴────────────┴─────────────────────────┘
- Discord: Join our Discord community for real-time chat and support
- GitHub Discussions: Start a GitHub Discussion with questions or ideas
- Documentation: Check out our comprehensive docs
We welcome contributions! Here's how you can get involved:
- Report Issues: Found a bug? Open an issue on GitHub
- Suggest Features: Have an idea? Start a GitHub Discussion
- Fix Issues: Comment "take" on any open issue to claim it
- Submit PRs: Brainstorm features with contributors and submit pull requests
- Join Meetings: Monthly contributor meetings - we'd love to have you!
SedonaDB is a subproject of Apache Sedona, an Apache Software Foundation project. The project is governed by the Apache Software Foundation and subject to all the rules and oversight requirements. SedonaDB is built on top of Apache Arrow and Apache DataFusion for fast query processing.
- Apache Sedona - The main Apache Sedona project for distributed spatial analytics
- Sedona SpatialBench - Comprehensive benchmarking suite for spatial analytics performance testing