Synchronizes recordings from a BlackVue dashcam with a local directory over a LAN.
BlackVue dashcams expose an HTTP server that can be used to download all recordings. This project downloads only recordings that are not already downloaded, optionally limiting downloads in a local directory to a date range.
A typical setup would be a periodic cron job or a Docker container running on a local server.
- Portable runtimes:
- A single, self-contained Python script with no third-party dependencies. It can be copied and run anywhere, either manually or periodically.
- A docker image that runs periodically via an internal cron job.
- Smart: Only downloads recordings that haven't already been downloaded.
- Resilient: If a download interrupts for whatever reason, the script resumes where it left off the next time it runs. This is especially useful for possibly unreliable Wi-Fi connections from a garage.
- Hands-off: Optionally retains recordings for a set amount of time. Outdated recordings are automatically removed.
- Cron-friendly: Only one process is allowed to run at any given time for a specific download destination.
- Safe: Stops executing if the destination disk is almost full.
- Friendly error reporting: Communicates a range of known error conditions with sensible verbosity.
- Python 3.5+ or Docker.
- Sufficient disk space on a file system local to the script. Plan for about 5GB/hr per camera.
- BlackVue Viewer or a media player to view the recordings.
A cloud-enabled BlackVue dashcam must be connected via Wi-Fi to the local network with a static IP address.
The dashcam must be kept powered for some time after the vehicle is turned off. BlackVue offers these accessories to draw power from the vehicle for a configurable amount of time:
- Power Magic EZ: Plugs into the OBD port.
- Hardwiring Kit: Plugs into the fuse box.
The power-on timer should be set to a duration sufficient for recordings to be downloaded. Consult the dashcam manual for the bit rate for your chosen image quality, and compare it with the download speed reported by BlackVue Sync.
Example with a DR750S-2CH recording with two cameras at the highest quality setting and a good but conservative download speed:
# dashcam bitrates
dashcam_bitrate_front = 12Mbps
dashcam_bitrate_back = 10Mbps
dashcam_bitrate = dashcam_bitrate_front + dashcam_bitrate_back
download_speed = 20Mbps
# hours on the timer for every hour of recording
ratio = dashcam_bitrate / download_speed => 1.1
For illustration purposes, all examples assume that the camera is reachable at the dashcam.example.net address. A static numeric IP address works just as well.
A quick way to verify that the dashcam is online is by using curl.
$ curl http://dashcam.example.net/blackvue_vod.cgi
v:1.00
n:/Record/20181026_135003_PF.mp4,s:1000000
n:/Record/20181026_140658_PF.mp4,s:1000000
n:/Record/20181026_140953_PF.mp4,s:1000000
...
$Another way is by browsing to: http://dashcam.example.net/blackvue_vod.cgi.
The dashcam address is the only required parameter. The --dry-run option makes it so that the script communicates what it would do without actually doing anything. Example:
blackvuesync.py dashcam.example.net --dry-runIt's also possible to specify a destination directory other than the current directory with --destination:
blackvuesync.py dashcam.example.net --destination /data/dashcam --dry-runA retention period can be indicated with the -keep option. Recordings prior to the retention period will be removed from the destination directory. Accepted units are d for days and w for weeks. If no unit is indicated, days are assumed.
blackvuesync.py dashcam.example.net --destination /data/dashcam --keep 2w --dry-runA typical invocation would be:
blackvuesync.py dashcam.example.net --destination /data/dashcam --keep 2wOther options:
--grouping: Groups downloaded recordings in directories according to different schemes. Grouping speeds up loading recordings in the BlackVue Viewer app. The supported groupings are:daily: By day, e.g. 2018-10-26;weekly: By week, with the directory indicating the date of that week's monday, e.g. 2018-10-22;monthly: By month, e.g. 2018-10;yearly: By year, e.g. 2018;none: No grouping, the default.
--priority: Downloads recordings with different priorities:datedownloads oldest to newest;rdatedownloads newest to oldest;typedownloads manual, event (all types), normal and (non-event) parking recordings in that order. Defaults todate.--max-used-disk: Downloads stop once the specified used disk percentage threshold is reached. Defaults to90(i.e. 90%.)--timeout: Sets a timeout for establishing a connection to the dashcam, in seconds. Defaults to10.0seconds.--quiet: Quiets down output messages, except for unexpected errors. Takes precedence over--verbose.--verbose: Increases verbosity. Can be specified multiple times to indicate additional verbosity.
The script can run periodically by setting up a cron job on UNIX systems.
Simple example with crontab for a hypothetical media user:
*/15 * * * * /home/media/bin/blackvuesync.py dashcam.example.net --keep 2w --destination /data/dashcam --cronThe --cron option changes the logging level with the assumption that the output may be emailed. When this option is enabled, the script only produces logs when it downloads recordings and when it encounters unexpected errors. One would typically see an email only after driving or when something goes wrong.
Note that if the dashcam is unreachable for whatever reason, in --cron mode no output is generated, since this is an expected condition whenever the dashcam is away from the local network.
If cron jobs overlap, the script recognizes that another instance is currently running via a lock file on the destination directory. For the lock to work correctly, the destination directory must be on a local filesystem relative to the script.
Many NAS systems allow running commands periodically at set intervals.
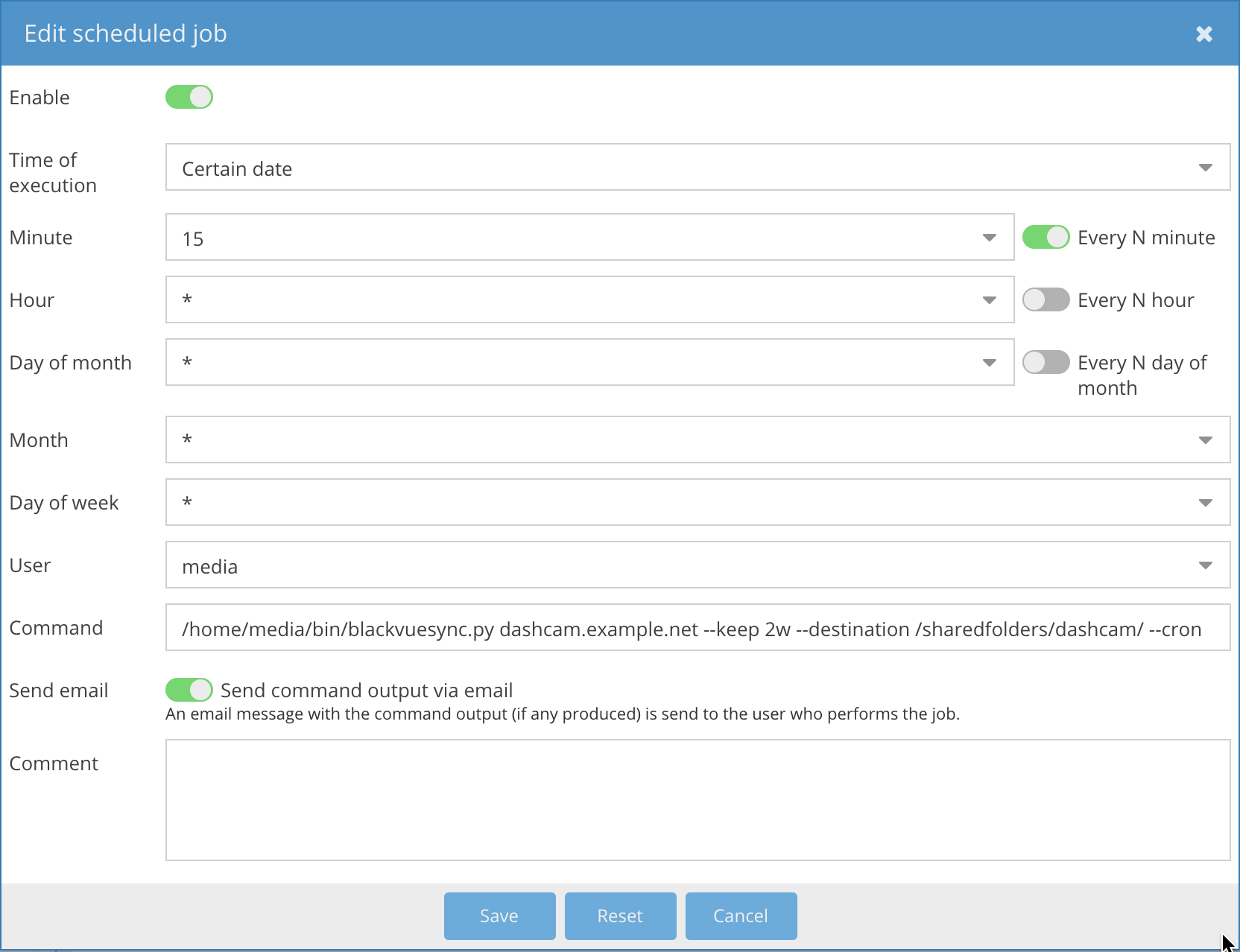
The openmediavault NAS solution allows running scheduled jobs with support for mail notifications.
Example:
The acolomba/blackvuesync docker image sets up a cron job internal to the container that runs the synchronization operation every 15 minutes.
It's a good idea to do a single, interactive dry run first with verbose logging:
docker run -it --rm \
-e ADDRESS=dashcam.example.net \
-v $PWD:/recordings \
-e DRY_RUN=1 \
-e VERBOSE=1 \
-e RUN_ONCE=1 \
--name blackvuesync \
acolomba/blackvuesyncOnce that works, a typical invocation would be similar to:
docker run -d --restart unless-stopped \
-v /data/dashcam:/recordings \
-e ADDRESS=dashcam.example.net \
-e PUID=$(id -u) \
-e PGID=$(id -g) \
-e TZ="America/New_York" \
-e KEEP=2w \
--name blackvuesync \
acolomba/blackvuesyncDocker Compose may offer an easier, more repeatable and extensible option for running a BlackVueSync Docker container.
After downloading the Docker Compose file and editing its values as desired, BlackVueSync can be started with:
docker-compose up -dOR, depending on the Docker version:
docker compose up -dThese options are required for the docker image to operate correctly:
- The
/recordingsvolume mapped to the desired destination of the downloaded recordings. - The
ADDRESSparameter set to the dashcam address. - The
PUIDandPGIDparameters set to the desired destination directory's user id and group id. - The
TZparameter set to the same timezone as the dashcam. Note that BlackVue dashcams do not respect Daylight Savings Time, so their clock needs to be adjusted periodically.
Other parameters:
GROUPING: Groups downloaded recordings in directories,daily,weekly,monthly,yearlyandnoneare supported. (Default:none.)KEEP: Sets the retention period of downloaded recordings. Recordings prior to the retention period will be removed from the destination. Accepted units aredfor days andwfor weeks. If no unit is indicated, days are assumed. (Default: empty, meaning recordings are kept forever.)PRIORITY: Sets the priority to download recordings. Pickdateto download from oldest to newest; pickrdateto download from newset to oldest; picktypeto download manual, event (all types), normal and (non-event) parking recordings in that order. Defaults todate.MAX_USED_DISK: If set to a percentage value, stops downloading if the amount of used disk space exceeds the indicated percentage value. (Default:90, i.e. 90%.)TIMEOUT: If set to a float value, sets the timeout in seconds for connecting to the dashcam. (Default:10.0seconds.)VERBOSE: If set to a number greater than zero, increases logging verbosity. (Default:0.)QUIET: If set to any value, quiets down logs: only unexpected errors will be logged. (Default: empty.)CRON: Set by default, makes it so downloads of normal recordings and unexpected error conditions are logged. Can be set to""to disable.DRY_RUN: If set to any value, makes it so that the script communicates what it would do without actually doing anything. (Default: empty.)RUN_ONCE: If set to any value, the docker image runs the sync operation once and exits without setting up the cron job. (Default: empty. Not supported in Docker Compose.)
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the COPYING file for details
Copyright 2018-2022 Alessandro Colomba