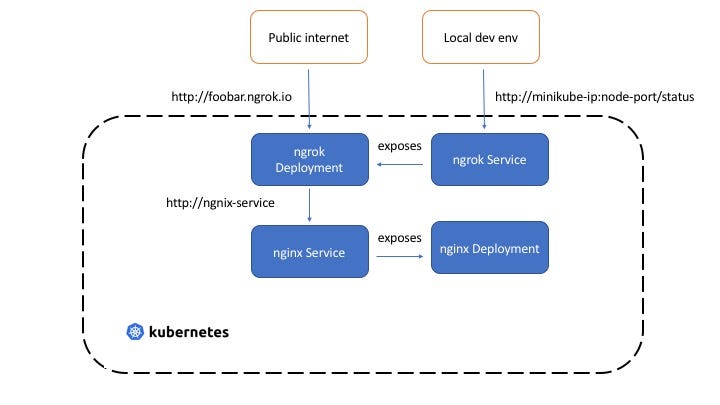
Kubexpose makes it easy to access a Kubernetes Deployment over a public URL. It's a Kubernetes Operator backed by a Custom Resource Definition.
Kubexposeis an experimental project built using kubebuilder
Any Kubernetes cluster will work (minikube, kind, Docker Desktop, on the cloud, whatever...).
To deploy the operator and required components:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/kubexpose-all-in-one.yaml
# check CRD
kubectl get crdMake sure Operator is up and running:
export OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=kubexpose-operator-system
# check Pods
kubectl get pods -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE
# check logs
kubectl logs -f $(kubectl get pods --namespace $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -c manager -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACECreate nginx Deployment (this is the one you want to expose over the internet using a public URL) and kubexpose resource (which will help you do that!):
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/quickstart/nginx.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/quickstart/kubexpose.yaml
Wait for a few seconds and check the public URL at which the Nginx Deployment can be accessed:
kubectl get kubexpose/kubexpose-test -o=jsonpath='{.status.url}'Access the publlic URL using your browser or test it using
curl
Confirm that the Service and Deployment have been created as well:
kubectl get svc/nginx-test-svc-kubexpose-test
kubectl get deployment/nginx-test-expose-kubexpose-testYou can try out other scenarios such as trying to
Deploymentand/orService- the Operator will reconcile or bring things back to the state as specified in the resource.
To delete the kubexpose resource:
kubectl delete kubexpose/kubexpose-testThis will also delete the
ServiceandDeploymentwhich were created for this resource
Delete the Nginx deployment:
kubectl delete deployment/nginx-testTo uninstall the Operator:
kubectl delete -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operator/master/kubexpose-all-in-one.yamlThis will delete the CRD,
kubexposeoperator and other resources.
Behind the scenes, Kubexpose uses the awesome ngrok project to get the job done!
When you create a kubexpose resource, the operator:
- Creates a
ClusterIPtypeServicefor theDeploymentyou want to access (naming format:<deployment name>-svc-<kubexpose resource name>) - Creates a
Deployment(using this ngrok Docker image) that runsngrok- which is configured to point to theService(naming format:<deployment name>-expose-<kubexpose resource name>). It's equivalent to startingngrokas such:ngrok http foo-svc-bar 80
The
DeploymentandServiceand owned and managed by the Kubexpose resource instance.
You need to have kubebuilder installed on your machine. If you don't want to do that, simply leverage the devcontainer config that comes with the project to setup the entire environment in just a few clicks.
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/abhirockzz/kubexpose-operatorFirst, build a Docker image and push it to a registry of your choice:
export IMG=<enter docker image e.g. my-docker-repo/kubexpose>
docker login
make docker-build docker-push IMG=$IMGYou can now setup the operator and associated resources on the Kubernetes cluster:
export IMG=<enter docker image e.g. my-docker-repo/kubexpose>
make deploy IMG=$IMGThis single command will create a bunch of resources, such as the Kubexpose Custom Resource Definition (CRD), Kubexpose Operator Deployment, RBAC policies etc.
Check the output for details:
/workspaces/kubexpose-operator/bin/controller-gen "crd:trivialVersions=true,preserveUnknownFields=false" rbac:roleName=manager-role webhook paths="./..." output:crd:artifacts:config=config/crd/bases
cd config/manager && /workspaces/kubexpose-operator/bin/kustomize edit set image controller=abhirockzz/kubexpose
/workspaces/kubexpose-operator/bin/kustomize build config/default | kubectl apply -f -
namespace/kubexpose-operator-system created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubexposes.kubexpose.kubexpose.io created
serviceaccount/kubexpose-operator-controller-manager created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-leader-election-role created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-manager-role created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-metrics-reader created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-proxy-role created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-leader-election-rolebinding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-manager-rolebinding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubexpose-operator-proxy-rolebinding created
configmap/kubexpose-operator-manager-config created
service/kubexpose-operator-controller-manager-metrics-service created
deployment.apps/kubexpose-operator-controller-manager createdThe operator runs in a different namespace -
kubexpose-operator-system
To check the operator Deployment:
export OPERATOR_NAMESPACE=kubexpose-operator-system
# wait for Pod to come up
kubectl get pods -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE -w
# check logs
kubectl logs -f $(kubectl get pods --namespace $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE -o=jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -c manager -n $OPERATOR_NAMESPACE