Building AI agents should feel like assembling a dream team, not wrestling with complex code.
ArcheAI is a lightweight Python framework designed to make AI agent development intuitive, flexible, and downright fun! 🎉
"Another AI agent framework? What makes ArcheAI different?" 🤔
Let's break it down:
- Simplicity First 🧘
- Strip away unnecessary complexity
- Clean and elegant API
- Unleash Your Creativity 🎨
- Modular design for experimentation
- Support for various LLMs (Gemini, Groq, Cohere, OpenAI, Anthropic)
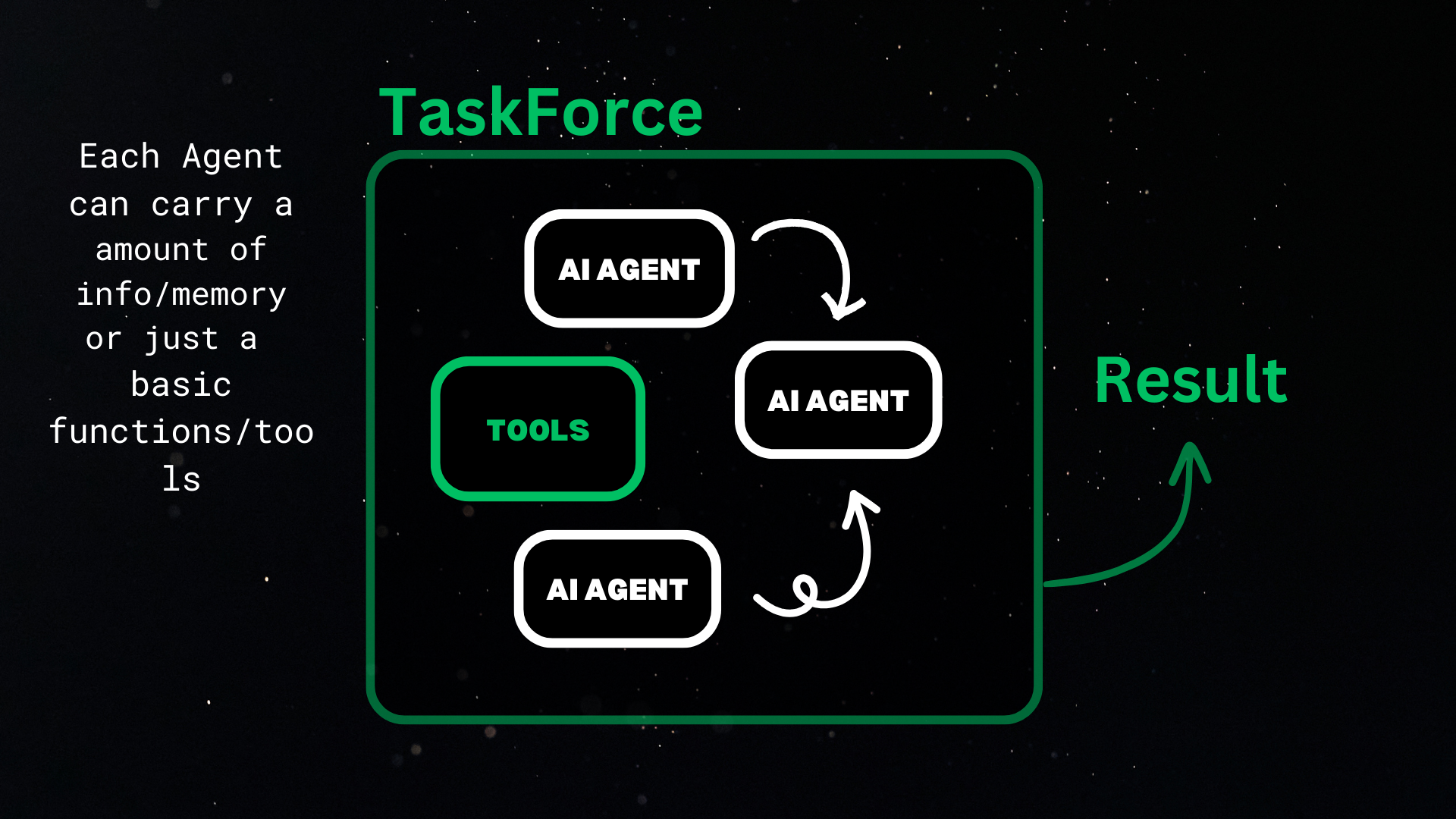
- Power in Collaboration 🤝
- TaskForce feature for seamless agent orchestration
- Built for Exploration 🔭
- Flexible foundation ready to adapt to new technologies
- large-scale AI agent networks 🌐
- Scalable architecture for complex workflows
Get started with ArcheAI in just one line:
pip install archeaiThe Agent class is the heart of ArcheAI. It represents an individual AI agent within your system.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
llm |
An instance of the LLM (Large Language Model) class that the agent will use for language processing and decision-making. |
tools |
A list of Tool objects that define the actions the agent can perform. |
identity |
A string representing the agent's name or identifier. |
description |
A brief description of the agent's role or purpose. |
expected_output |
A string describing the expected format or style of the agent's responses. |
ask_user |
A boolean value indicating whether the agent should ask the user for input when generating responses. Defaults to True. |
max_iterations |
The maximum number of iterations the agent will attempt to generate a valid response. Defaults to 3. |
check_response_validity |
A boolean value indicating whether the agent should check the validity of the response before it is returned. Defaults to False. |
output_file |
The name of the file where the agent's responses will be saved. Defaults to None. |
verbose |
A boolean value indicating whether the agent should print verbose output during execution. Defaults to False. |
rollout(): Execute the agent's main workflow
Tools are actions or capabilities that an agent can perform.
from archeai import Tool
def get_weather(city: str):
"""Fetches the current weather for a given city."""
# Implementation...
return weather_data
weather_tool = Tool(
func=get_weather,
description="Gets the current weather for a specified city.",
params={'city': {'description': 'The city to check weather for', 'type': 'str', 'default': 'unknown'}}
)| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
func |
The Python function that defines the tool's action. |
name |
The name of the tool (automatically derived from the function name). |
description |
A brief description of what the tool does. This is used by the agent to understand the tool's purpose. |
returns_value |
A boolean indicating whether the tool returns a value that can be used by other tools or included in the response. Defaults to True. |
instance |
Optional instance of a class if the tool is a bound method. |
llm |
Optional LLM object for more advanced tool interactions (e.g., using the LLM to help determine tool parameters). |
verbose |
A boolean indicating whether the tool should print verbose output during execution. Defaults to False. |
params |
An Optional dictionary containing information about the tool's parameters (automatically extracted if not provided). |
Manage a group of Agent objects for collaboration and complex workflows.
agents: List of Agent objects in the task forcecaching_dir: Directory to store cached responses
start_force(): Begin the task force's workflowexecute_agent(agent, prompt): Execute a specific agent's workflowrecord_result(agent): Save the result of an agent's workflowexit_force(): End the task force's workflow also delete the cache
from archeai import Agent, Tool, TaskForce
from archeai.llms import Gemini
# Initialize your LLM
llm = Gemini()
# Define tools
def say_hello(name: str):
return f"Hello there, {name}! 👋"
def calculate(equation: str):
return eval(equation)
hello_tool = Tool(func=say_hello,
description="Greets the user by name.",
params={'name': {'description': 'The name to greet.', 'type': 'str', 'default': 'unknown'}})
calculate_tool = Tool(func=calculate,
description="Evaluates an equation.",
params={'equation': {'description': 'The equation to evaluate.', 'type': 'str', 'default': 'unknown'}})
# Create agents
greeter = Agent(llm=llm,
tools=[hello_tool],
identity="Friendly Greeter",
verbose=True)
math_magician = Agent(llm=llm,
tools=[calculate_tool],
identity="Math Magician",
verbose=True)
# Assemble your task force!
force = TaskForce(agents=[greeter, math_magician], caching_dir='cache')
force.start_force()
force.execute_agent(greeter, "Hi I am mervin")
force.execute_agent(math_magician, "2+2")
force.exit_force()This example demonstrates creating agents with tools and using a TaskForce to manage execution.
What does `record_result` func do?
The record_result function is used to save the result of an agent's workflow. This can be useful for passing one agent's response to another.
This concludes in the scalability and simplicity of the architecture.
- Multi-LLM Support: Seamlessly switch between different language models
- Custom Tool Creation: Easily create and integrate your own tools
- Response Validation: Ensure output quality with built-in validation
- Easy Passing of Information: Share information between agents with ease using the
record_resultfunction - Scalable Architecture: Build large-scale AI agent networks with the TaskForce class
ArcheAI is designed for efficiency:
- Lightweight core for minimal overhead
- Scalable architecture for complex agent networks
Actual Use Case:
from archeai.llms import Gemini
from archeai import Agent, Tool, TaskForce
from archeai.tools import get_current_time, web_search
import os
def list_dir():
"""Returns a list of items in the current working directory."""
try:
items = os.listdir()
return items
except OSError as e:
print(f"Error listing directory: {e}")
return []
def write_to_file(filename:str, content:str):
"""Writes the given content to a file with the specified filename.
Args:
filename (str): The name of the file to write to.
content (str): The content to write to the file.
"""
try:
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
f.write(content)
print(f"Successfully wrote to '{filename}'")
except OSError as e:
print(f"Error writing to file: {e}")
def gcd(a:int, b:int):
"""
Calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of two numbers using the Euclidean algorithm.
Parameters:
a (int): The first number.
b (int): The second number.
Returns:
int: The GCD of the two numbers.
"""
while b:
a, b = b, a % b
return a+b
llm_instance = Gemini()
# Define the tools using the OwnTool class
write_tool = Tool(
func=write_to_file,
description="Writes the given content to a file to the given filename in dir",
returns_value=False,
llm = llm_instance,
verbose=True
)
list_tool = Tool(
func=list_dir,
description="Provides the list of files and folders in current working dir.",
returns_value=True,
llm = llm_instance,
verbose=True
)
time_tool = Tool(
func=get_current_time,
description="Provides the current time.",
returns_value=True,
llm = llm_instance,
verbose=True
)
web_tool = Tool(
func=web_search,
description="Provides web search result on the given query.",
returns_value=True,
llm = llm_instance,
verbose=True
)
# Initialize the language model instance
content_saver = Agent(
llm=llm_instance,
identity="content_saver",
tools=[write_tool],
verbose=True,
description="A content saver which can save any content in markdown format to a given file.",
expected_output="In markdown format",
)
researcher = Agent(
llm=llm_instance,
identity="researcher",
tools=[time_tool, web_tool],
description="A researcher having access to web and can get info about any topic.",
expected_output="A summary of the research",
verbose=True,
)
writer = Agent(
llm=llm_instance,
identity="writer",
tools=[],
description="A writer which can write on any topic with information.",
expected_output="In markdown format",
verbose=True,
)
# Define the task force
task_force = TaskForce(
agents=[content_saver, researcher, writer],
caching_dir="cache",
)
# Run the task force
task_force.start_force()
task_force.execute_agent(researcher, "What are wormholes?")
researcher_result = task_force.record_result(researcher)
print(researcher_result)
task_force.execute_agent(writer, f"Write an article on wormholes. Here is the information: {researcher_result}")
writer_result = task_force.record_result(writer)
task_force.execute_agent(content_saver, f"Save this information in wormholes.md: {writer_result}")
task_force.exit_force()The Tools used from archeai in the use case are totally experimental and are not recommended to use.
We welcome contributions! Please feel free to:
Open an issue Submit a pull request
Check out our Contribution Guidelines for more information.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
If you find ArcheAI helpful, please give us a star on GitHub!