A Seeq Add-on built-in python to identify input and output relationships for the system to create digital twin models for various analytics and machine learning tasks. System dynamics are identified thereby allowing users to get dynamic predictions quickly. The Add-on is fully integrated with Seeq Workbench. Cleaned and contextualized data from Seeq workbench can be used to identify dynamic models; the models can be pushed back into Seeq workbench. This framework supports both ad-hoc investigations as well as streaming predictions. The system identification framework can be used for a variety of tasks including simulation, digital twin construction, advanced process control, real-time optimization, etc.
The System Identification Add-on supports the construction of a variety of dynamic models. White box models are primarily based on physics-based principles such as conservation laws and reaction kinetics for the chemical process. Development of these models requires extensive domain knowledge and is typically more expensive to build and maintain. Machine learning models are largely data-driven. Greybox models combine the best of both; they simplify the white-box model by lumping several parameters into fewer parameters that can be identified from data with higher degrees of confidence. These models are capable of capturing the primary dynamics of the system but are valid over smaller ranges of operation. The SysID Add-on allows users to choose a modeling option based on the application.
- Grey-box model identification (ARX, Transfer Function, Subspace models)
- Complex model identification (Neural Networks-based models)
- Hybrid Physics and Machine learning model identification
ARX model is a system identification model that uses the linear correlation between previous and future values. ARX model consists of previous output terms (y) and previous input (u) terms multiplied by the linear coefficients (a, b). The linear combination of past input and output value computes the one-step-ahead prediction of output value(yk+1).
Multiple iterations of the one-step-ahead prediction return the multi-step prediction (from yk+1 to yk+n). The time window of the past input and output terms is shifted toward the next segment for every iteration for multi-step prediction.
Here is an example formula with and
for the single input and single output system,
: Auto-Regressive with eXogenous input
("Auto" indicates the past 'y' values, and "Exogenous" indicates the past 'u' values serving as model inputs)
: ARX coefficient for the past output value
: ARX coefficient for the past input value
: Number of terms for the past output value
: Number of terms for the past input value
: Delay between input and output
: present time step
Here is another example formula with delay ,
Although the ARX model can be more detailed by increasing the number of terms , it could result in an overfit. Thus, it could be an essential step to compare the training and validation set, ensuring the prediction for the validation set is as good as the training set. The model fitting can be quantified using different statistical methods such as MSE (Mean Squared Error) or SSE (Sum of Squared Error)
 |




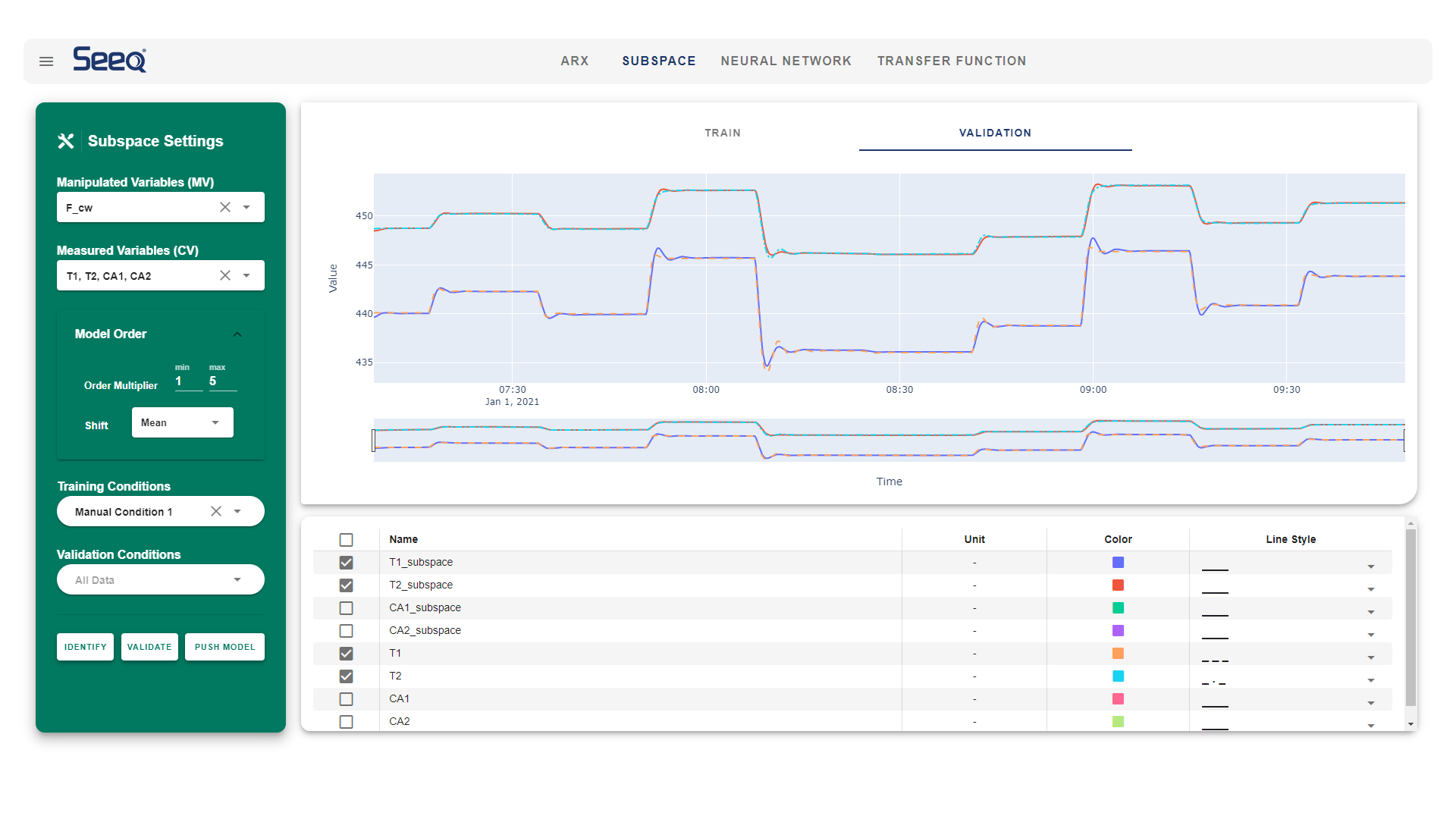
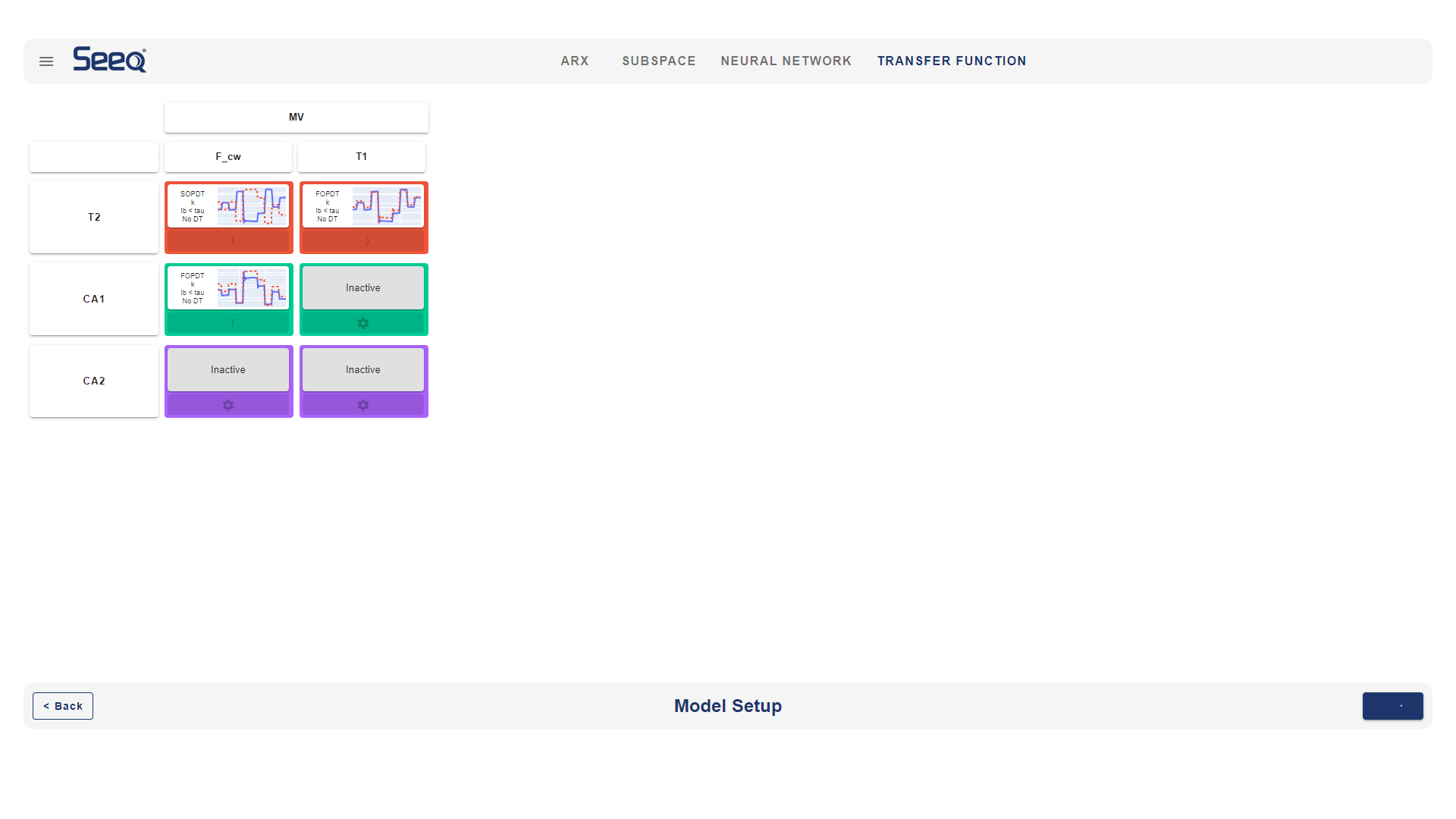
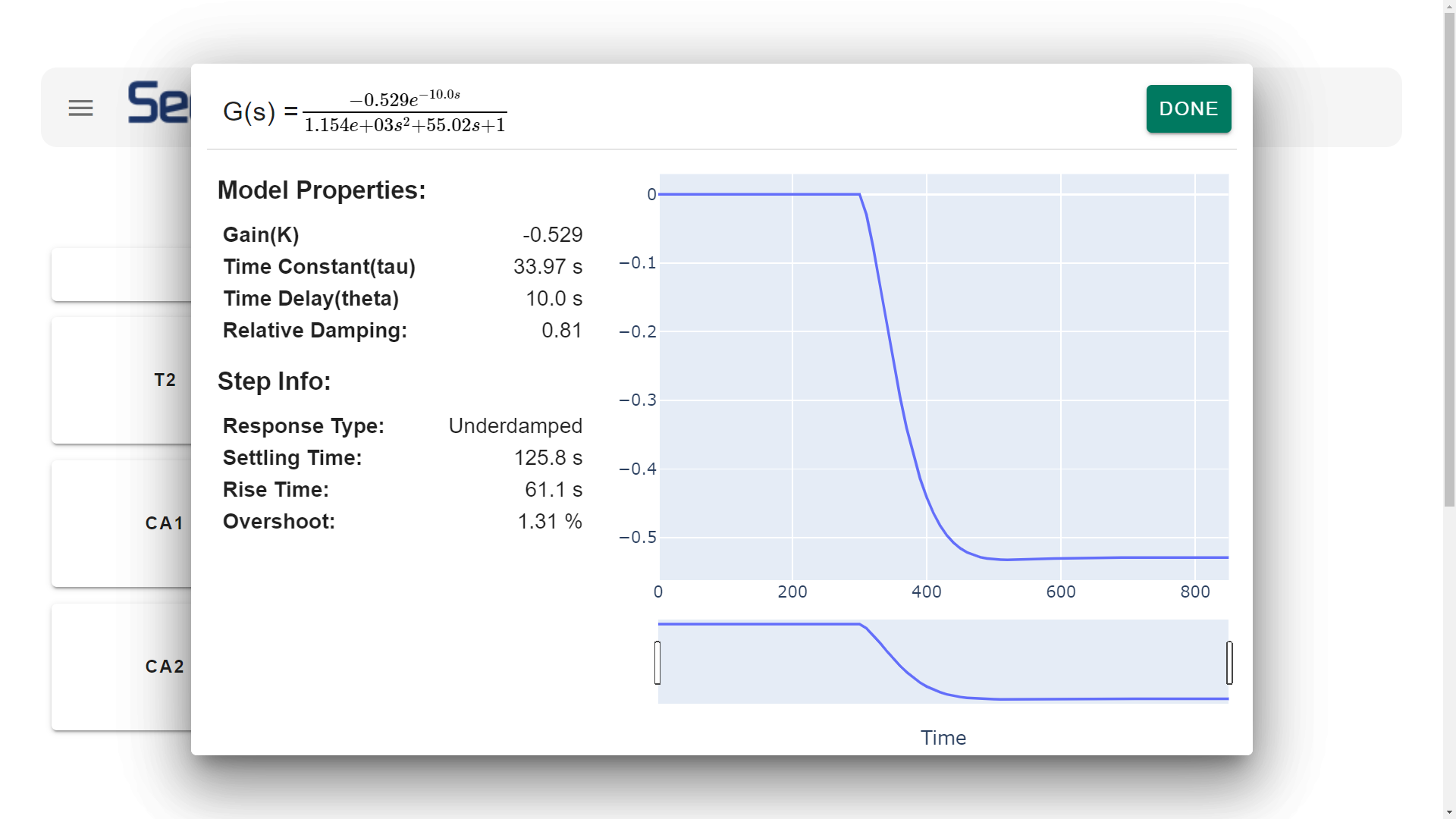
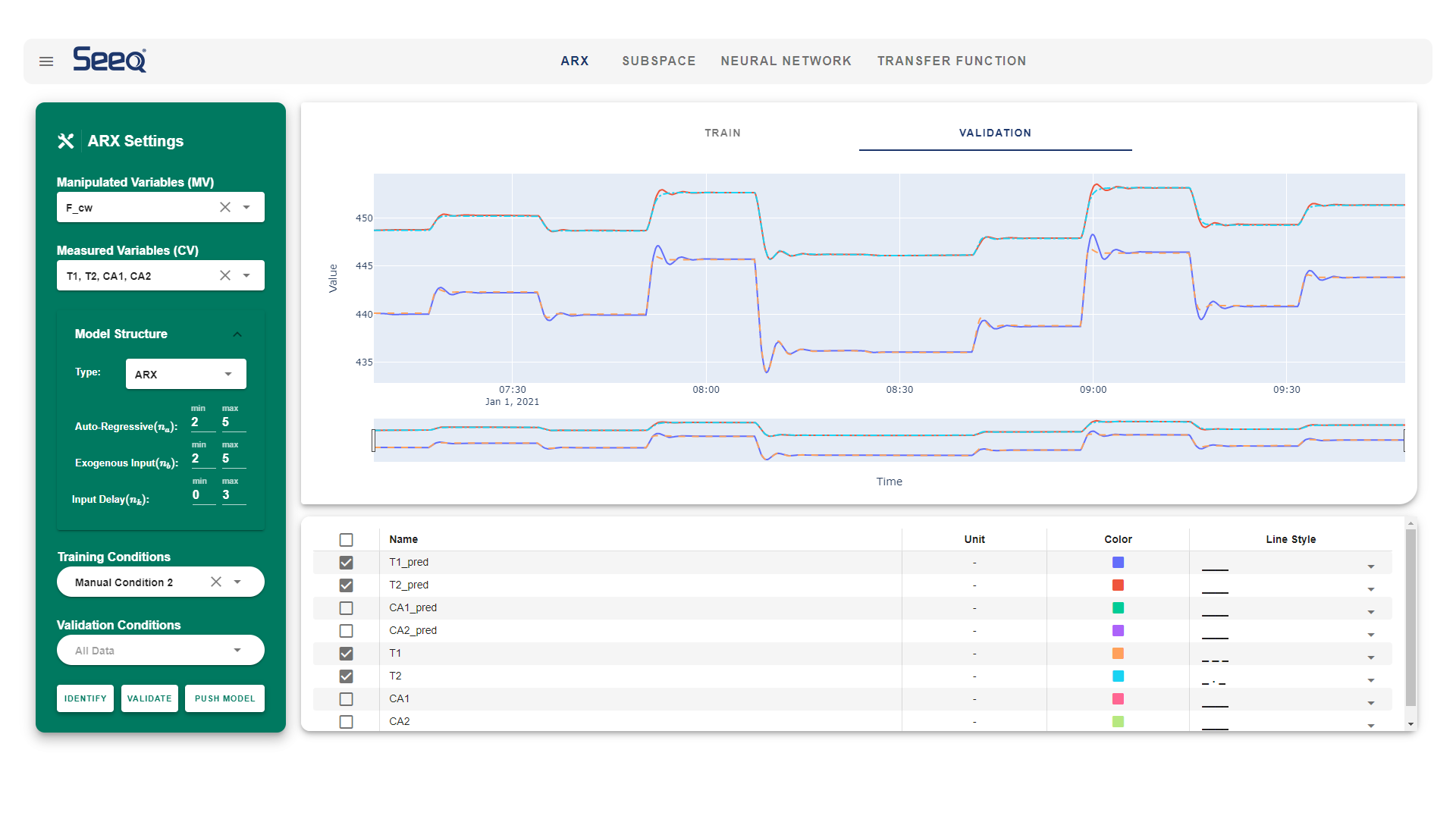
Sysid.Gui.mp4
SeeQ-System Identification User Guide provides a more in-depth explanation of System Identification and how seeq-sysid works.
The backend of seeq-sysid requires Python 3.7 or later.
See requirements.txt file for a list of
dependencies and versions. Additionally, you will need to install the seeq
module with the appropriate version that matches your Seeq server. For more
information on the seeq module see
seeq at pypi.
If you want to install seeq-sysid as a Seeq Add-on Tool, you will need:
-
Seeq Data Lab (>= R52.1.5, >=R53.0.2, or >=R54)
-
seeqmodule whose version matches the Seeq server version -
Seeq administrator access
-
Enable Add-on Tools (or External Tools) in the Seeq server
Note: For older versions of Seeq Data Lab you can find the installation guide `here``](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/55245976/137494969-43d93065-1e23-4e7c-952f-2397993eb269.mp4).
- Create a new Seeq Data Lab project and open the Terminal window
- Run
pip install seeq-sysid - Run
python -m seeq_sysid [--users <users_list> --groups <groups_list>]
For more information about adding this addon to the seeq workbench click here.
- Documentation for SysID Add-on
- Official source code repo
- System Identification with Industrial Data Webinar
You can get started by cloning the repository with the command:
git clone https://github.com/BYU-PRISM/Seeq.gitFor development work, it is highly recommended to create a python virtual environment and install the package in that working environment. If you are not familiar with python virtual environments, you can take a look here
Once your virtual environment is activated, you can install seeq-sysid from the source with:
Go to the setup.py directory (Seeq/'SysID Addon')
python setup.py install --userNote: Remember that the seeq module version in your local environment should match the Seeq server version
To test the UI, use the developer_notebook.ipynb in the root directory of this project.
This notebook can also be used while debugging from your IDE. You can also
create a whl first, install it on your virtual environment, and then
run developer_notebook.ipynb notebook there.
- Notebook extensions and requirements update
- Minor improvements
- Empty worksheet warning
- Performance improvements
- Hotfix: dependencies updated for R57>=
- Performance improvement in TF identification
- Progress bar added to TF identification
- Legends added to TF chipsets
- Bugs fixed for normalized plots in TF identification
- Minor bugs fixed
- MA model added
- Units switch added
- Version number added to the GUI
- Minor bugs fixed
- ARIMAX model added
- Minor improvements
- GUI object moved to app.py
- Display results after calculation (Default)
- Unit compatibility error fixed
- Workbook pull step bypassed
- Push functions improved
- Hotfix for R57+ (search, pull, push functions)
- Export ARX model (Gekko sysid outputs as a pickle)
- Data Editor Added
- Push formula added for Transfer Function
- ARX Seeq formula fixed
- Mistune package conflict resolved
- Transfer Function
- Documentation added
- Shift method added to SubSpace.
- Installation made easier.
- Open Worksheet moved to the Hamburger Menu.
- Minor improvements
- Neural Network Model (RNN) added
- FIR Model added
- Installation made easier
- N4SID method was removed temporarily.
Code-related issues (e.g. bugs, feature requests) can be created in the issue tracker
Please cite this work as:
seeq-sysid v1.0.1
BYU PRISM Group https://apm.byu.edu/prism/
https://github.com/BYU-PRISM/Seeq




