你被请来给一个要举办高尔夫比赛的树林砍树。树林由一个 m x n 的矩阵表示, 在这个矩阵中:
0表示障碍,无法触碰1表示地面,可以行走比 1 大的数表示有树的单元格,可以行走,数值表示树的高度
每一步,你都可以向上、下、左、右四个方向之一移动一个单位,如果你站的地方有一棵树,那么你可以决定是否要砍倒它。
你需要按照树的高度从低向高砍掉所有的树,每砍过一颗树,该单元格的值变为 1(即变为地面)。
你将从 (0, 0) 点开始工作,返回你砍完所有树需要走的最小步数。 如果你无法砍完所有的树,返回 -1 。
可以保证的是,没有两棵树的高度是相同的,并且你至少需要砍倒一棵树。
示例 1:
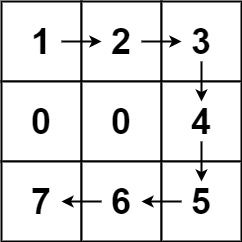
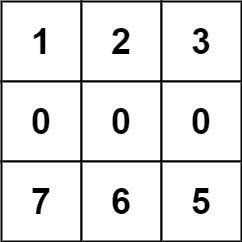
输入:forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,4],[7,6,5]] 输出:6 解释:沿着上面的路径,你可以用 6 步,按从最矮到最高的顺序砍掉这些树。
示例 2:
输入:forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,0],[7,6,5]] 输出:-1 解释:由于中间一行被障碍阻塞,无法访问最下面一行中的树。
示例 3:
输入:forest = [[2,3,4],[0,0,5],[8,7,6]] 输出:6 解释:可以按与示例 1 相同的路径来砍掉所有的树。 (0,0) 位置的树,可以直接砍去,不用算步数。
提示:
m == forest.lengthn == forest[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500 <= forest[i][j] <= 109
方法一:BFS + 优先队列(A* 算法)
题目的一个关键信息是“所有树的高度都不同”,要按照从小到大的顺序依次砍树,因此,我们先遍历树林,找出所有树及对应的坐标点。然后将树按照高度升序排列。
接下来就是找相邻两个点之间的最短距离。可以用 BFS,A* 算法优化搜索。
A* 算法主要思想如下:
- 将 BFS 队列转换为优先队列(小根堆);
- 队列中的每个元素为
(dist[state] + f(state), state),dist[state]表示从起点到当前 state 的距离,f(state)表示从当前 state 到终点的估计距离,这两个距离之和作为堆排序的依据; - 当终点第一次出队时,说明找到了从起点到终点的最短路径,直接返回对应的 step;
f(state)是估价函数,并且估价函数要满足f(state) <= g(state),其中g(state)表示 state 到终点的真实距离;- A* 算法只能保证终点第一次出队时,即找到了一条从起点到终点的最小路径,不能保证其他点出队时也是从起点到当前点的最短路径。
class Solution:
def cutOffTree(self, forest: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def f(i, j, x, y):
return abs(i - x) + abs(j - y)
def bfs(i, j, x, y):
q = [(f(i, j, x, y), i, j)]
dist = {i * n + j: 0}
while q:
_, i, j = heappop(q)
step = dist[i * n + j]
if (i, j) == (x, y):
return step
for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]:
c, d = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= c < m and 0 <= d < n and forest[c][d] > 0:
if c * n + d not in dist or dist[c * n + d] > step + 1:
dist[c * n + d] = step + 1
heappush(q, (dist[c * n + d] + f(c, d, x, y), c, d))
return -1
m, n = len(forest), len(forest[0])
trees = [
(forest[i][j], i, j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n) if forest[i][j] > 1
]
trees.sort()
i = j = 0
ans = 0
for _, x, y in trees:
t = bfs(i, j, x, y)
if t == -1:
return -1
ans += t
i, j = x, y
return ansclass Solution {
private int[] dist = new int[3600];
private List<List<Integer>> forest;
private int m;
private int n;
public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) {
this.forest = forest;
m = forest.size();
n = forest.get(0).size();
List<int[]> trees = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (forest.get(i).get(j) > 1) {
trees.add(new int[] {forest.get(i).get(j), i * n + j});
}
}
}
trees.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int ans = 0;
int start = 0;
for (int[] tree : trees) {
int end = tree[1];
int t = bfs(start, end);
if (t == -1) {
return -1;
}
ans += t;
start = end;
}
return ans;
}
private int bfs(int start, int end) {
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
q.offer(new int[] {f(start, end), start});
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dist[start] = 0;
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int state = q.poll()[1];
if (state == end) {
return dist[state];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = state / n + dirs[k];
int y = state % n + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && forest.get(x).get(y) > 0) {
if (dist[x * n + y] > dist[state] + 1) {
dist[x * n + y] = dist[state] + 1;
q.offer(new int[] {dist[x * n + y] + f(x * n + y, end), x * n + y});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private int f(int start, int end) {
int a = start / n;
int b = start % n;
int c = end / n;
int d = end % n;
return Math.abs(a - c) + Math.abs(b - d);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int m;
int n;
vector<int> dist;
int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) {
m = forest.size();
n = forest[0].size();
dist.resize(3600);
vector<pair<int, int>> trees;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (forest[i][j] > 1)
trees.push_back({forest[i][j], i * n + j});
sort(trees.begin(), trees.end());
int ans = 0;
int start = 0;
for (auto& tree : trees) {
int end = tree.second;
int t = bfs(start, end, forest);
if (t == -1) return -1;
ans += t;
start = end;
}
return ans;
}
int bfs(int start, int end, vector<vector<int>>& forest) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> q;
q.push({f(start, end), start});
fill(dist.begin(), dist.end(), INT_MAX);
dist[start] = 0;
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (!q.empty()) {
int state = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if (state == end) return dist[state];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = state / n + dirs[k], y = state % n + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && forest[x][y] && dist[x * n + y] > dist[state] + 1) {
dist[x * n + y] = dist[state] + 1;
q.push({dist[x * n + y] + f(x * n + y, end), x * n + y});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int f(int start, int end) {
int a = start / n, b = start % n;
int c = end / n, d = end % n;
return abs(a - c) + abs(b - d);
}
};var dirs = [][]int{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}
type tree struct {
height int
pos int
}
func cutOffTree(forest [][]int) int {
row, col := len(forest), len(forest[0])
bfs := func(start, end int) int {
q := []int{start}
vis := make(map[int]bool)
vis[start] = true
step := 0
for n := len(q); n > 0; n = len(q) {
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
state := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if state == end {
return step
}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := state/col+dirs[k][0], state%col+dirs[k][1]
nxt := x*col + y
if x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col && forest[x][y] != 0 && !vis[nxt] {
q = append(q, nxt)
vis[nxt] = true
}
}
}
step++
}
return -1
}
var trees []tree
for i := 0; i < row; i++ {
for j := 0; j < col; j++ {
if forest[i][j] > 1 {
trees = append(trees, tree{forest[i][j], i*col + j})
}
}
}
sort.Slice(trees, func(i, j int) bool {
return trees[i].height < trees[j].height
})
ans, start := 0, 0
for _, t := range trees {
end := t.pos
step := bfs(start, end)
if step == -1 {
return -1
}
ans += step
start = end
}
return ans
}use std::collections::HashSet;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
const DIRS: [[i32; 2]; 4] = [
[-1, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, -1],
[0, 1],
];
impl Solution {
pub fn cut_off_tree(forest: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let (row, col) = (forest.len() as i32, forest[0].len() as i32);
let bfs = |start: i32, end: i32| -> i32 {
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
let mut vis = HashSet::new();
queue.push_back(start);
vis.insert(start);
let mut step = 0;
while !queue.is_empty() {
let n = queue.len();
for _ in 0..n {
let state = queue.pop_front().unwrap();
if state == end {
return step;
}
for k in 0..4 {
let x = state / col + DIRS[k][0];
let y = (state % col) + DIRS[k][1];
let nxt = x * col + y;
if
x >= 0 &&
x < row &&
y >= 0 &&
y < col &&
forest[x as usize][y as usize] != 0 &&
!vis.contains(&nxt)
{
queue.push_back(nxt);
vis.insert(nxt);
}
}
}
step += 1;
}
-1
};
let mut trees = Vec::new();
for i in 0..row {
for j in 0..col {
let height = forest[i as usize][j as usize];
if height > 1 {
trees.push((height, i * col + j));
}
}
}
trees.sort();
let (mut ans, mut start) = (0, 0);
for t in &trees {
let end = t.1;
let step = bfs(start, end);
if step == -1 {
return -1;
}
ans += step;
start = end;
}
ans
}
}