| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
You are given an n x n integer matrix grid where each value grid[i][j] represents the elevation at that point (i, j).
The rain starts to fall. At time t, the depth of the water everywhere is t. You can swim from a square to another 4-directionally adjacent square if and only if the elevation of both squares individually are at most t. You can swim infinite distances in zero time. Of course, you must stay within the boundaries of the grid during your swim.
Return the least time until you can reach the bottom right square (n - 1, n - 1) if you start at the top left square (0, 0).
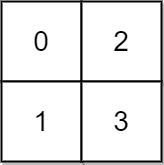
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]] Output: 3 Explanation: At time 0, you are in grid location (0, 0). You cannot go anywhere else because 4-directionally adjacent neighbors have a higher elevation than t = 0. You cannot reach point (1, 1) until time 3. When the depth of water is 3, we can swim anywhere inside the grid.
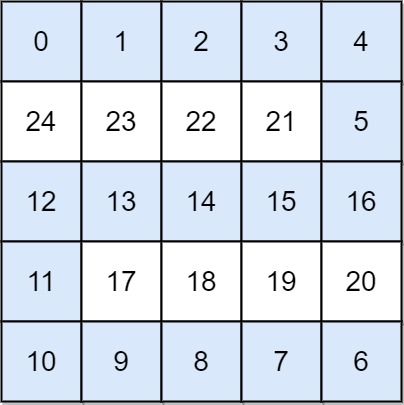
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]] Output: 16 Explanation: The final route is shown. We need to wait until time 16 so that (0, 0) and (4, 4) are connected.
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2- Each value
grid[i][j]is unique.
class Solution:
def swimInWater(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def find(x):
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
n = len(grid)
p = list(range(n * n))
hi = [0] * (n * n)
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, h in enumerate(row):
hi[h] = i * n + j
for t in range(n * n):
i, j = hi[t] // n, hi[t] % n
for a, b in [(0, -1), (0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]:
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] <= t:
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(hi[t])
if find(0) == find(n * n - 1):
return t
return -1class Solution {
private int[] p;
public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
p = new int[n * n];
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
int[] hi = new int[n * n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
hi[grid[i][j]] = i * n + j;
}
}
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int t = 0; t < n * n; ++t) {
int i = hi[t] / n;
int j = hi[t] % n;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k];
int y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] <= t) {
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j);
}
if (find(0) == find(n * n - 1)) {
return t;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> p;
int swimInWater(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
p.resize(n * n);
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) p[i] = i;
vector<int> hi(n * n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
hi[grid[i][j]] = i * n + j;
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int t = 0; t < n * n; ++t) {
int i = hi[t] / n, j = hi[t] % n;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] <= t)
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(hi[t]);
if (find(0) == find(n * n - 1)) return t;
}
}
return -1;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
};func swimInWater(grid [][]int) int {
n := len(grid)
p := make([]int, n*n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
hi := make([]int, n*n)
for i, row := range grid {
for j, h := range row {
hi[h] = i*n + j
}
}
var find func(x int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
for t := 0; t < n*n; t++ {
i, j := hi[t]/n, hi[t]%n
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] <= t {
p[find(x*n+y)] = find(hi[t])
}
if find(0) == find(n*n-1) {
return t
}
}
}
return -1
}function swimInWater(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length,
n = grid[0].length;
let visited = Array.from({ length: m }, () => new Array(n).fill(false));
let ans = 0;
let stack = [[0, 0, grid[0][0]]];
const dir = [
[0, 1],
[0, -1],
[1, 0],
[-1, 0],
];
while (stack.length) {
let [i, j] = stack.shift();
ans = Math.max(grid[i][j], ans);
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) break;
for (let [dx, dy] of dir) {
let x = i + dx,
y = j + dy;
if (x < m && x > -1 && y < n && y > -1 && !visited[x][y]) {
visited[x][y] = true;
stack.push([x, y, grid[x][y]]);
}
}
stack.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
}
return ans;
}const DIR: [(i32, i32); 4] = [
(-1, 0),
(1, 0),
(0, -1),
(0, 1),
];
impl Solution {
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn swim_in_water(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = grid.len();
let m = grid[0].len();
let mut ret_time = 0;
let mut disjoint_set: Vec<usize> = vec![0; n * m];
// Initialize the disjoint set
for i in 0..n * m {
disjoint_set[i] = i;
}
loop {
if Self::check_and_union(&grid, &mut disjoint_set, ret_time) {
break;
}
// Otherwise, keep checking
ret_time += 1;
}
ret_time
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn check_and_union(grid: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>, cur_time: i32) -> bool {
let n = grid.len();
let m = grid[0].len();
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..m {
if grid[i][j] != cur_time {
continue;
}
// Otherwise, let's union the square with its neighbors
for (dx, dy) in DIR {
let x = dx + (i as i32);
let y = dy + (j as i32);
if
Self::check_bounds(x, y, n as i32, m as i32) &&
grid[x as usize][y as usize] <= cur_time
{
Self::union(i * m + j, (x as usize) * m + (y as usize), d_set);
}
}
}
}
Self::find(0, d_set) == Self::find(n * m - 1, d_set)
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn find(x: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) -> usize {
if d_set[x] != x {
d_set[x] = Self::find(d_set[x], d_set);
}
d_set[x]
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn union(x: usize, y: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) {
let p_x = Self::find(x, d_set);
let p_y = Self::find(y, d_set);
d_set[p_x] = p_y;
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
fn check_bounds(i: i32, j: i32, n: i32, m: i32) -> bool {
i >= 0 && i < n && j >= 0 && j < m
}
}