参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!
链表操作中,可以使用原链表来直接进行删除操作,也可以设置一个虚拟头结点再进行删除操作,接下来看一看哪种方式更方便。
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1: 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2: 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3: 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
《代码随想录》算法视频公开课:链表基础操作| LeetCode:203.移除链表元素,相信结合视频再看本篇题解,更有助于大家对本题的理解。
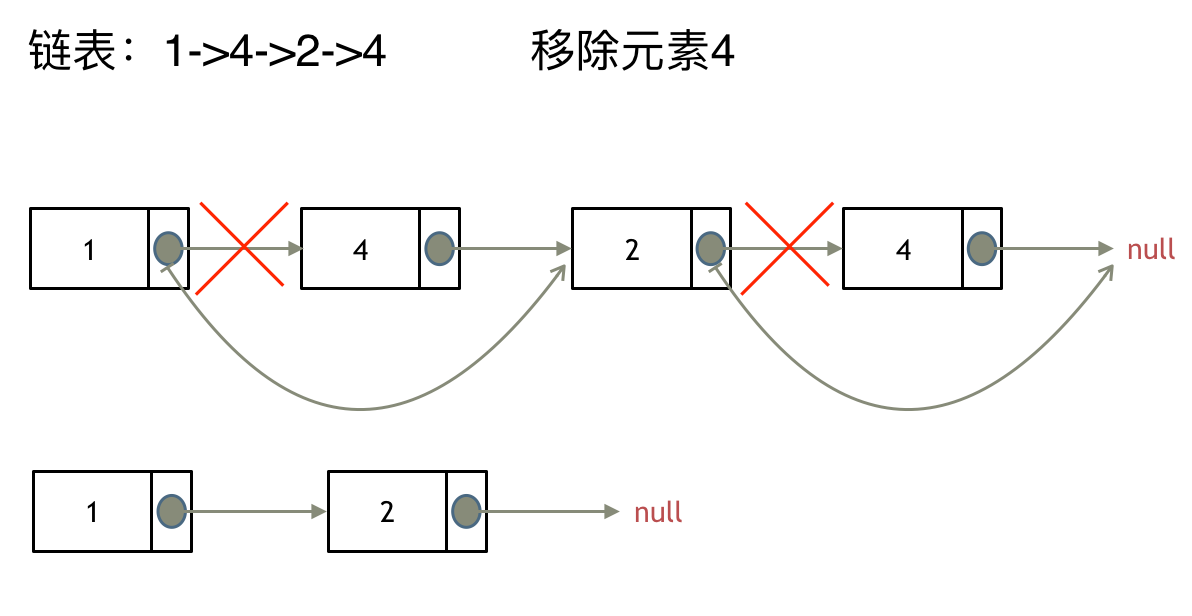
这里以链表 1 4 2 4 来举例,移除元素4。
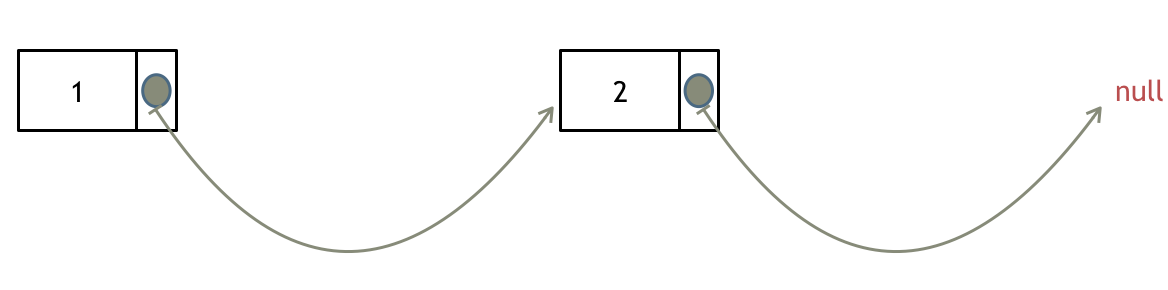
如果使用C,C++编程语言的话,不要忘了还要从内存中删除这两个移除的节点, 清理节点内存之后如图:
当然如果使用java ,python的话就不用手动管理内存了。
还要说明一下,就算使用C++来做leetcode,如果移除一个节点之后,没有手动在内存中删除这个节点,leetcode依然也是可以通过的,只不过,内存使用的空间大一些而已,但建议依然要养成手动清理内存的习惯。
这种情况下的移除操作,就是让节点next指针直接指向下下一个节点就可以了,
那么因为单链表的特殊性,只能指向下一个节点,刚刚删除的是链表的中第二个,和第四个节点,那么如果删除的是头结点又该怎么办呢?
这里就涉及如下链表操作的两种方式:
- 直接使用原来的链表来进行删除操作。
- 设置一个虚拟头结点在进行删除操作。
来看第一种操作:直接使用原来的链表来进行移除。
移除头结点和移除其他节点的操作是不一样的,因为链表的其他节点都是通过前一个节点来移除当前节点,而头结点没有前一个节点。
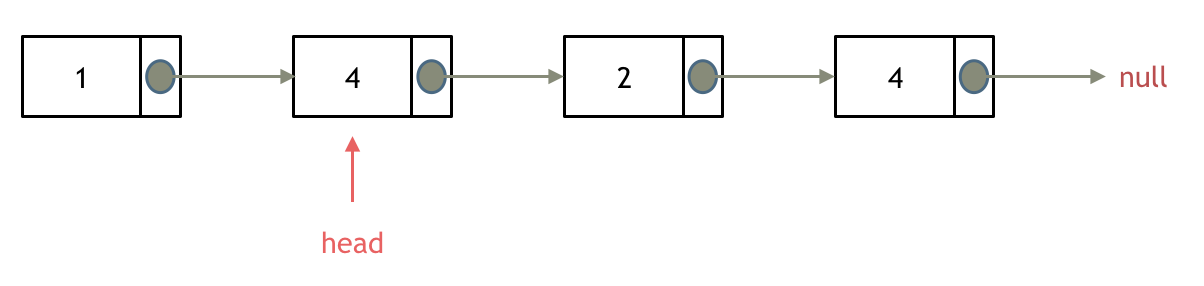
所以头结点如何移除呢,其实只要将头结点向后移动一位就可以,这样就从链表中移除了一个头结点。
这样移除了一个头结点,是不是发现,在单链表中移除头结点 和 移除其他节点的操作方式是不一样,其实在写代码的时候也会发现,需要单独写一段逻辑来处理移除头结点的情况。
那么可不可以 以一种统一的逻辑来移除 链表的节点呢。
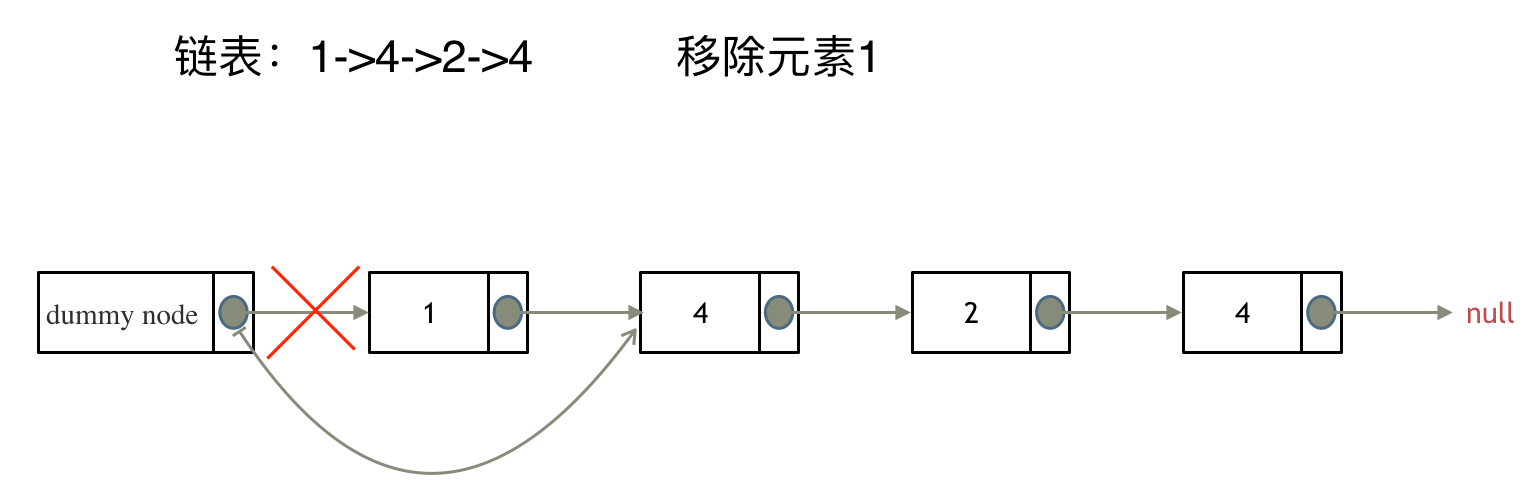
其实可以设置一个虚拟头结点,这样原链表的所有节点就都可以按照统一的方式进行移除了。
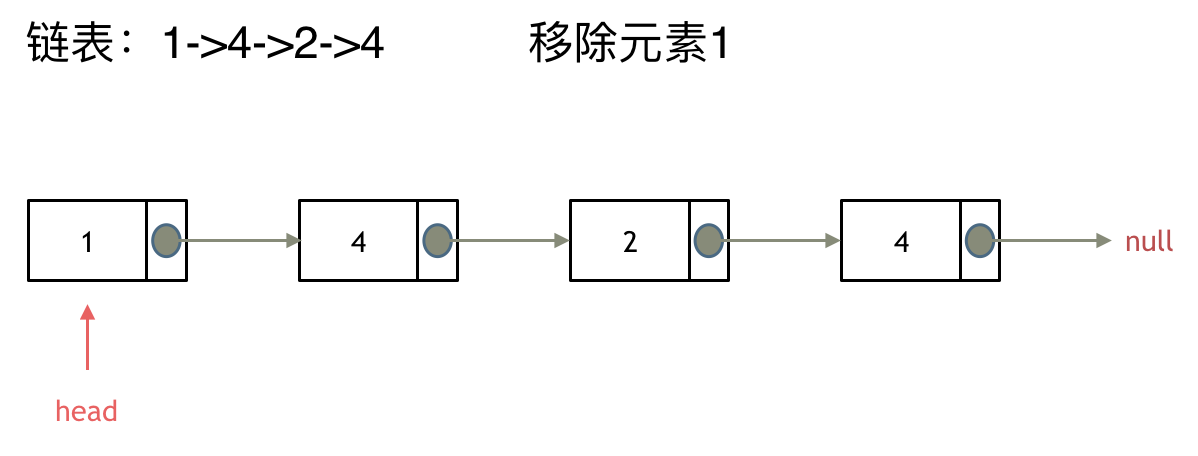
来看看如何设置一个虚拟头。依然还是在这个链表中,移除元素1。
这里来给链表添加一个虚拟头结点为新的头结点,此时要移除这个旧头结点元素1。
这样是不是就可以使用和移除链表其他节点的方式统一了呢?
来看一下,如何移除元素1 呢,还是熟悉的方式,然后从内存中删除元素1。
最后呢在题目中,return 头结点的时候,别忘了 return dummyNode->next;, 这才是新的头结点
直接使用原来的链表来进行移除节点操作:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
// 删除头结点
while (head != NULL && head->val == val) { // 注意这里不是if
ListNode* tmp = head;
head = head->next;
delete tmp;
}
// 删除非头结点
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL && cur->next!= NULL) {
if (cur->next->val == val) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
设置一个虚拟头结点在进行移除节点操作:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); // 设置一个虚拟头结点
dummyHead->next = head; // 将虚拟头结点指向head,这样方便后面做删除操作
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while (cur->next != NULL) {
if(cur->next->val == val) {
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
head = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return head;
}
};
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
也可以通过递归的思路解决本题:
基础情况:对于空链表,不需要移除元素。
递归情况:首先检查头节点的值是否为 val,如果是则移除头节点,答案即为在头节点的后续节点上递归的结果;如果头节点的值不为 val,则答案为头节点与在头节点的后续节点上递归得到的新链表拼接的结果。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
// 基础情况:空链表
if (head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
// 递归处理
if (head->val == val) {
ListNode* newHead = removeElements(head->next, val);
delete head;
return newHead;
} else {
head->next = removeElements(head->next, val);
return head;
}
}
};- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
用原来的链表操作:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode* temp;
// 当头结点存在并且头结点的值等于val时
while(head && head->val == val) {
temp = head;
// 将新的头结点设置为head->next并删除原来的头结点
head = head->next;
free(temp);
}
struct ListNode *cur = head;
// 当cur存在并且cur->next存在时
// 此解法需要判断cur存在因为cur指向head。若head本身为NULL或者原链表中元素都为val的话,cur也会为NULL
while(cur && (temp = cur->next)) {
// 若cur->next的值等于val
if(temp->val == val) {
// 将cur->next设置为cur->next->next并删除cur->next
cur->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
// 若cur->next不等于val,则将cur后移一位
else
cur = cur->next;
}
// 返回头结点
return head;
}设置一个虚拟头结点:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode *shead;
shead = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
shead->next = head;
ListNode *cur = shead;
while(cur->next != NULL){
if (cur->next->val == val){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
free(tmp);
}
else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
head = shead->next;
free(shead);
return head;
}用原来的链表操作:
/**
* 方法1
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while(head!=null && head.val==val) {
head = head.next;
}
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr!=null && curr.next !=null) {
if(curr.next.val == val){
curr.next = curr.next.next;
} else {
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return head;
}
/**
* 方法1
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
// 已经为null,提前退出
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 已确定当前head.val != val
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}设置一个虚拟头结点:
/**
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 设置一个虚拟的头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}递归
/**
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(n)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 假设 removeElements() 返回后面完整的已经去掉val节点的子链表
// 在当前递归层用当前节点接住后面的子链表
// 随后判断当前层的node是否需要被删除,如果是,就返回
// 也可以先判断是否需要删除当前node,但是这样条件语句会比较不好想
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
if (head.val == val) {
return head.next;
}
return head;
// 实际上就是还原一个从尾部开始重新构建链表的过程
}
}(版本一)虚拟头节点法
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: Optional[ListNode], val: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 创建虚拟头部节点以简化删除过程
dummy_head = ListNode(next = head)
# 遍历列表并删除值为val的节点
current = dummy_head
while current.next:
if current.next.val == val:
current.next = current.next.next
else:
current = current.next
return dummy_head.next直接使用原链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
//依旧是先定义逻辑
//如果原链表的头节点为val的话,head=head.next,且为持续过程,防止头节点后面的节点也为Val
//这里前置循环 并且要判定head 是否为nil,防止出错
for head != nil && head.Val == val {//由于leetcode代码运行方式,for循环条件判断前后顺序不能修改,下面的for循环也同样如此
head = head.Next
}
cur := head
for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil {
if cur.Next.Val == val {
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
} else {
cur = cur.Next
}
}
return head
}虚拟头节点方式:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func removeElements(head *ListNode, val int) *ListNode {
dummyHead := &ListNode{}
dummyHead.Next = head
cur := dummyHead
for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil {
if cur.Next.Val == val {
cur.Next = cur.Next.Next
} else {
cur = cur.Next
}
}
return dummyHead.Next
}/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} val
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeElements = function(head, val) {
const ret = new ListNode(0, head);
let cur = ret;
while(cur.next) {
if(cur.next.val === val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
continue;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return ret.next;
};版本一(在原链表上直接删除):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null {
// 删除头部节点
while (head !== null && head.val === val) {
head = head.next;
}
if (head === null) return head;
let pre: ListNode = head, cur: ListNode | null = head.next;
// 删除非头部节点
while (cur) {
if (cur.val === val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
//此处不加类型断言时:编译器会认为pre类型为ListNode, pre.next类型为ListNode | null
pre = pre.next as ListNode;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
};版本二(虚拟头节点):
function removeElements(head: ListNode | null, val: number): ListNode | null {
// 添加虚拟节点
const data = new ListNode(0, head);
let pre = data, cur = data.next;
while (cur) {
if (cur.val === val) {
pre.next = cur.next
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return data.next;
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public var val: Int
* public var next: ListNode?
* public init() { self.val = 0; self.next = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.next = nil; }
* public init(_ val: Int, _ next: ListNode?) { self.val = val; self.next = next; }
* }
*/
func removeElements(_ head: ListNode?, _ val: Int) -> ListNode? {
let dummyNode = ListNode()
dummyNode.next = head
var currentNode = dummyNode
while let curNext = currentNode.next {
if curNext.val == val {
currentNode.next = curNext.next
} else {
currentNode = curNext
}
}
return dummyNode.next
}/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val = 0, $next = null) {
* $this->val = $val;
* $this->next = $next;
* }
* }
*/
//版本一(在原链表上直接删除):
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @param Integer $val
* @return ListNode
*/
function removeElements($head, $val)
{
if ($head == null) {
return null;
}
$now = $head;
while ($now->next != null) {
if ($now->next->val == $val) {
$now->next = $now->next->next;
} else {
$now = $now->next;
}
}
if ($head->val == $val) {
return $head->next;
}
return $head;
}
}
//版本二(虚拟头结点方式):
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @param Integer $val
* @return ListNode
*/
function removeElements($head, $val)
{
$dummyHead = new ListNode(0, $head);
$now = $dummyHead;
while ($now->next != null){
if ($now->next->val == $val) {
$now->next = $now->next->next;
} else {
$now = $now->next;
}
}
return $dummyHead->next;
}
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn remove_elements(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, val: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummyHead = Box::new(ListNode::new(0));
dummyHead.next = head;
let mut cur = dummyHead.as_mut();
// 使用take()替换std::mem::replace(&mut node.next, None)达到相同的效果,并且更普遍易读
while let Some(nxt) = cur.next.take() {
if nxt.val == val {
cur.next = nxt.next;
} else {
cur.next = Some(nxt);
cur = cur.next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
}
dummyHead.next
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(_x: Int = 0, _next: ListNode = null) {
* var next: ListNode = _next
* var x: Int = _x
* }
*/
object Solution {
def removeElements(head: ListNode, `val`: Int): ListNode = {
if (head == null) return head
var dummy = new ListNode(-1, head) // 定义虚拟头节点
var cur = head // cur 表示当前节点
var pre = dummy // pre 表示cur前一个节点
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.x == `val`) {
// 相等,就删除那么cur的前一个节点pre执行cur的下一个
pre.next = cur.next
} else {
// 不相等,pre就等于当前cur节点
pre = cur
}
// 向下迭代
cur = cur.next
}
// 最终返回dummy的下一个,就是链表的头
dummy.next
}
}/**
* Example:
* var li = ListNode(5)
* var v = li.`val`
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var next: ListNode? = null
* }
*/
class Solution {
fun removeElements(head: ListNode?, `val`: Int): ListNode? {
// 使用虚拟节点,令该节点指向head
var dummyNode = ListNode(-1)
dummyNode.next = head
// 使用cur遍历链表各个节点
var cur = dummyNode
// 判断下个节点是否为空
while (cur.next != null) {
// 符合条件,移除节点
if (cur.next.`val` == `val`) {
cur.next = cur.next.next
}
// 不符合条件,遍历下一节点
else {
cur = cur.next
}
}
// 注意:返回的不是虚拟节点
return dummyNode.next
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution
{
public ListNode RemoveElements(ListNode head, int val)
{
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode temp = dummyHead;
while(temp.next != null)
{
if(temp.next.val == val)
{
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
else
{
temp = temp.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}# 定义链表节点
class ListNode
attr_accessor :val, :next
def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
@val = val
@next = _next
end
end
# 删除链表中值为 val 的节点
def remove_elements(head, val)
# 创建一个虚拟头节点,这样可以简化删除头节点的处理
# 虚拟头节点的值为 0,指向当前链表的头节点
dummy = ListNode.new(0)
dummy.next = head
# 初始化当前节点为虚拟头节点
current = dummy
# 遍历链表,直到当前节点的下一个节点为空
while current.next
# 如果当前节点的下一个节点的值等于 val
if current.next.val == val
# 跳过该节点,即将当前节点的 next 指向下一个节点的 next
current.next = current.next.next
else
# 否则继续遍历,当前节点向前移动
current = current.next
end
end
# 返回删除 val 后的新链表的头节点,虚拟头节点的 next 就是新的头节点
dummy.next
end