- 支持单数据读写,多数据读写,大数据量自动分包读写
- 支持序列化批量多地址且地址不连续的读写
- 支持读写DB区,I区,Q区,M区,V区
- 支持读写西门子S1500,S1200,S400,S300,S200Smart,西门子机床828D
- 支持PLC自动重连
- 如果你不熟悉S7协议可以查看这个地址
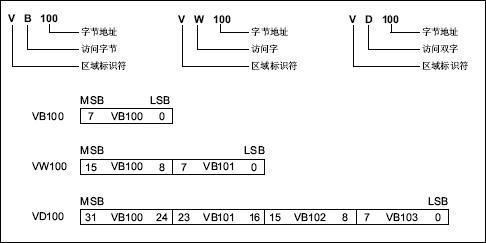
- 对于200smartPLC的V区,就是DB1.X,例如,V1=DB1.1,V100=DB1.100
知识点1:地址的格式以及对应含义,兼容大小写
| 简写 | 区域 | 字节索引 | 位索引 | PLC类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB1.1.2 | DB1区 | 1 | 2 | S1200/S1500 |
| DB2 | DB2区 | 0 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| DB3.3 | DB3区 | 3 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| D1.1.2 | DB1区 | 1 | 2 | S1200/S1500 |
| Q1.6 | Q区 | 1 | 6 | S1200/S1500 |
| Q1 | Q区 | 1 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| I2.5 | I区 | 2 | 5 | S1200/S1500 |
| I2 | I区 | 2 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| M3.2 | M区 | 3 | 2 | S1200/S1500 |
| M3 | M区 | 3 | 0 | S1200/S1500 |
| V2.1 | V区 | 2 | 1 | S200Smart |
| V2 | V区 | 2 | 0 | S200Smart |
知识点2:访问数据类型与JAVA数据类型和PLC数据类型对应关系
| 访问数据类型 | 数据类型名称 | 数据大小[位] | 数据大小[字节] | JAVA数据类型 | PLC数据类型 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 布尔类型 | 1 | 1/8 | Boolean | BOOL | true |
| byte | 字节类型 | 8 | 1 | Byte | BYTE | 0x11 |
| uint16 | 无符号2字节整型 | 16 | 2 | Integer | WORD/UINT | 65535 |
| int16 | 有符号2字节整型 | 16 | 2 | Short | WORD/INT | -32760 |
| uint32 | 无符号4字节整型 | 32 | 4 | Long | DWORD/UDINT | 70000 |
| int32 | 有符号4字节整型 | 32 | 4 | Integer | DWORD/DINT | -70000 |
| float32 | 4字节浮点型 | 32 | 4 | Float | REAL | 3.14 |
| float64 | 8字节浮点型 | 64 | 8 | Double | LREAL | 3.14 |
| string | 字符型 | 8 | 1 | String | String | ABC |
| time | 时间/耗时 | 32 | 4 | Long | Time | 100ms |
| date | 日期 | 16 | 2 | LocalDate | Date | 2023-04-03 |
| timeOfDay | 一天中的时间 | 32 | 4 | LocalTime | TimeOfDay | 10:22:11 |
| dtl | 日期+时间 | 96 | 12 | LocalDateTime | DTL | 2023-04-03 10:22:11 |
知识点3:PLC地址与本项目地址和数据类型的对应关系
| PLC地址 | 位大小 | 字节大小 | 访问地址 | 访问数据类型 | PLC类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB100.DBX0.0 | 1 | 1/8 | DB100.0.0 | boolean | S1200/S1500 |
| DB100.DBB5 | 8 | 1 | DB100.5 | byte | S1200/S1500 |
| DB100.DBW6 | 16 | 2 | DB100.6 | uint16/int16 | S1200/S1500 |
| DB100.DBD3 | 32 | 4 | DB100.3 | uint32/int32/float32 | S1200/S1500 |
| VB100 | 8 | 1 | V100 | byte | S200Smart |
| VW100 | 16 | 2 | V100 | uint16/int16 | S200Smart |
| VD100 | 32 | 4 | V100 | uint32/int32/float32 | S200Smart |
| MB1 | 8 | 1 | M1 | byte | - |
| MW1 | 16 | 2 | M1 | uint16/int16 | - |
| MD1 | 32 | 4 | M1 | uint32/int32/float32 | - |
如果想知道通信过程中的实际输入输出报文内容,可以添加报文信息打印
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// 报文输出设置
this.s7PLC.setComCallback((tag, bytes) -> System.out.printf("%s[%d] %s%n", tag, bytes.length, HexUtil.toHexString(bytes)));
s7PLC.readByte("DB2.1");
s7PLC.close();
}
}- PLC默认采用长连接的方式,不用的时候需要手动关闭;
- 若需要短连接,则需要手动设置;
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 长连接方式,即持久化为true
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.readByte("DB2.1");
// 需要手动关闭,若一直要使用,则不需要关闭
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 短连接
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// 设置短连接模式,即持久化为false
s7PLC.setPersistence(false);
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.readByte("DB2.1");
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// read boolean
boolean boolData = s7PLC.readBoolean("DB1.2.0");
List<Boolean> boolDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("DB1.2.0", "DB1.2.1", "DB1.2.7");
List<Boolean> iDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("I0.0", "I0.1", "I0.2", "I0.3", "I0.4", "I0.5");
List<Boolean> qDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("Q0.0", "Q0.1", "Q0.2", "Q0.3", "Q0.4", "Q0.5", "Q0.6", "Q0.7");
List<Boolean> mDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("M1.0", "M1.1", "M1.2", "M1.3", "M1.4", "M1.5", "M1.6", "M1.7");
List<Boolean> vDatas = s7PLC.readBoolean("V1.0", "V1.1", "V1.2", "V1.3", "V1.4", "V1.5", "V1.6", "V1.7"); // 200smart有V区
// read byte
byte byteData = s7PLC.readByte("DB14.0");
byte[] byteDatas = s7PLC.readByte("DB14.0", 4);
byte iByteData = s7PLC.readByte("I0");
byte qByteData = s7PLC.readByte("Q0");
byte mByteData = s7PLC.readByte("M0");
byte vByteData = s7PLC.readByte("V0"); // 200smart有V区
// read UInt16
int intData = s7PLC.readUInt16("DB14.0");
List<Integer> intDatas = s7PLC.readUInt16("DB1.0", "DB1.2");
// read UInt32
long int32Data = s7PLC.readUInt32("DB1.0");
List<Long> int32Datas = s7PLC.readUInt32("DB1.0", "DB1.4");
// read float32
float float32Data = s7PLC.readFloat32("DB1.0");
List<Float> float32Datas = s7PLC.readFloat32("DB1.0", "DB1.4");
// read float64
double float64Data = s7PLC.readFloat64("DB1.0");
List<Double> float64Datas = s7PLC.readFloat64("DB1.0", "DB1.4");
// read String
String strData = s7PLC.readString("DB14.4");
String strData1 = s7PLC.readString("DB14.4", 10);
// read time
long timeData = s7PLC.readTime("DB1.0");
// read date
LocalDate localDateData = s7PLC.readDate("DB1.0");
// read time of day
LocalTime localTimeOfDayData = s7PLC.readTimeOfDay("DB1.0");
// read DTL
LocalDateTime dateTime = s7PLC.readDTL("DB1.0");
// read multi address
MultiAddressRead addressRead = new MultiAddressRead();
addressRead.addData("DB1.0", 1)
.addData("DB1.2", 3)
.addData("DB1.3", 5);
List<byte[]> multiByte = s7PLC.readMultiByte(addressRead);
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// write boolean
s7PLC.writeBoolean("DB2.0.7", true);
s7PLC.writeBoolean("Q0.7", true);
s7PLC.writeBoolean("M1.4", true);
// write byte
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.writeByte("M1", (byte) 0x11);
s7PLC.writeByte("V1", (byte) 0x11); // 200smart有V区
// write UInt16
s7PLC.writeUInt16("DB2.0", 0x2222);
// write UInt32
s7PLC.writeUInt32("DB2.0", 0x11111122);
// write float32
s7PLC.writeFloat32("DB2.0", 12);
// write float64
s7PLC.writeFloat64("DB2.0", 12.02);
// write String
s7PLC.writeString("DB14.4", "demo");
// write time
s7PLC.writeTime("DB1.0", 1000);
// write date
s7PLC.writeDate("DB1.0", LocalDate.now());
// write time of day
s7PLC.writeTimeOfDay("DB1.0", LocalTime.now());
// write DTL
s7PLC.writeDTL("DB1.0", LocalDateTime.now());
// write multi address
MultiAddressWrite addressWrite = new MultiAddressWrite();
addressWrite.addByte("DB2.0", (byte) 0x11)
.addUInt16("DB2.2", 88)
.addBoolean("DB2.1.0", true);
s7PLC.writeMultiData(addressWrite);
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// hot restart
s7PLC.hotRestart();
// cold restart
s7PLC.coldRestart();
// plc stop
s7PLC.plcStop();
// copy ram to rom
s7PLC.copyRamToRom();
// compress
s7PLC.compress();
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S200_SMART, "127.0.0.1");
//********************************* upload ***************************************/
// upload file data, PLC -> PC, success in 200Smart
byte[] bytes = s7PLC.uploadFile(EFileBlockType.OB, 1);
//******************************** download **************************************/
// 1. create mc7 file
Mc7File mc7 = Mc7File.fromBytes(bytes);
// 2. plc stop, stop plc before download file
s7PLC.plcStop();
// 3. download file data, PC -> PLC, success in 200Smart
s7PLC.downloadFile(mc7);
// 4. insert new filename
s7PLC.insert(mc7.getBlockType(), mc7.getBlockNumber());
// 5. hot restart, restart plc after download and insert file
s7PLC.hotRestart();
s7PLC.close();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// bit数据读写
byte[] expect = new byte[]{(byte) 0x00};
s7PLC.writeRaw(EParamVariableType.BIT, 1, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 0, 3,
EDataVariableType.BIT, expect);
byte[] actual = s7PLC.readRaw(EParamVariableType.BIT, 1, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 0, 3);
// byte数据读写
expect = new byte[]{(byte) 0x02, (byte) 0x03};
s7PLC.writeRaw(EParamVariableType.BYTE, 2, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 1, 0,
EDataVariableType.BYTE_WORD_DWORD, expect);
byte[] actual1 = s7PLC.readRaw(EParamVariableType.BYTE, 2, EArea.DATA_BLOCKS, 1, 1, 0);
// 对象形式发送
RequestNckItem item = new RequestNckItem(ENckArea.C_CHANNEL, 1, 23, 1, ENckModule.S, 1);
S7Data s7Data = NckRequestBuilder.creatNckRequest(item);
S7Data ackData = s7PLC.readFromServerByPersistence(s7Data);
// 裸报文发送
byte[] sendByteArray = new byte[]{
// tpkt
(byte) 0x03, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x1D,
// cotp DT Data
(byte) 0x02, (byte) 0xF0, (byte) 0x80,
// header
(byte) 0x32, (byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x13, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x0C, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x00,
// parameter
(byte) 0x04, (byte) 0x01,
// request item
(byte) 0x12, (byte) 0x08, (byte) 0x82, (byte) 0x41, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x03, (byte) 0x00, (byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x7f, (byte) 0x01
};
byte[] recByteArray = s7PLC.readFromServerByPersistence(sendByteArray);
s7PLC.close();
}
}支持BOOL,UINT16,INT16,UINT32,INT32,FLOAT32,FLOAT64,STRING,TIME,DATE,TIME_OF_DAY,DTL等数据类型读写
构建数据量比较小的数据类
@Data
public class DemoBean {
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.0.1", type = EDataType.BOOL)
private Boolean bitData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.4", type = EDataType.UINT16)
private Integer uint16Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.6", type = EDataType.INT16)
private Short int16Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.8", type = EDataType.UINT32)
private Long uint32Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.12", type = EDataType.INT32)
private Integer int32Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.16", type = EDataType.FLOAT32)
private Float float32Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.20", type = EDataType.FLOAT64)
private Double float64Data;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.28", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 3)
private byte[] byteData;
// 注意:实际总长度为12,不是10,31 + 12 = 43, 如果字符串后面还有其他字段,需要多预留2个字节数据
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.31", type = EDataType.STRING, count = 10)
private String stringData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.43", type = EDataType.TIME)
private Long timeData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.47", type = EDataType.DATE)
private LocalDate dateData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.49", type = EDataType.TIME_OF_DAY)
private LocalTime timeOfDayData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.53", type = EDataType.DTL)
private LocalDateTime dateTimeData;
}对于大数据量建议采用字节数组的方式,后续采用字节数据解析
构建数据量比较大的数据类
@Data
public class DemoLargeBean {
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.0.1", type = EDataType.BOOL)
private boolean bitData;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.10", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 50)
private byte[] byteData1;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.60", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 65)
private byte[] byteData2;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.125", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 200)
private byte[] byteData3;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.325", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 322)
private byte[] byteData4;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.647", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 99)
private byte[] byteData5;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.746", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 500)
private byte[] byteData6;
@S7Variable(address = "DB1.1246", type = EDataType.BYTE, count = 44)
private byte[] byteData7;
}数据读写
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建PLC对象
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// 构建序列化对象
S7Serializer s7Serializer = S7Serializer.newInstance(s7PLC);
// 小数据量的读写
DemoBean bean = new DemoBean();
bean.setBitData(true);
bean.setUint16Data(42767);
bean.setInt16Data((short) 32767);
bean.setUint32Data(3147483647L);
bean.setInt32Data(2147483647);
bean.setFloat32Data(3.14f);
bean.setFloat64Data(4.15);
bean.setByteData(new byte[]{(byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x02, (byte) 0x03});
bean.setStringData("1234567890");
bean.setTimeData(12L);
bean.setDateData(LocalDate.of(2023, 5, 15));
bean.setTimeOfDayData(LocalTime.of(20, 22, 13));
bean.setDateTimeData(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 5, 27, 12, 11, 22, 333225555));
s7Serializer.write(bean);
bean = s7Serializer.read(DemoBean.class);
// 大数据量的读写
DemoLargeBean largeBean = s7Serializer.read(DemoLargeBean.class);
largeBean.getByteData2()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData3()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData4()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData5()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData6()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData7()[0] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData2()[64] = (byte) 0x02;
largeBean.getByteData3()[199] = (byte) 0x03;
largeBean.getByteData4()[321] = (byte) 0x04;
largeBean.getByteData5()[98] = (byte) 0x05;
largeBean.getByteData6()[499] = (byte) 0x06;
largeBean.getByteData7()[43] = (byte) 0x07;
s7Serializer.write(bean);
s7PLC.close();
}
}数据读写
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建PLC对象
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200, "127.0.0.1");
// 构建序列化对象
S7Serializer s7Serializer = S7Serializer.newInstance(s7PLC);
byte[] byteData = new byte[]{(byte) 0x01, (byte) 0x02, (byte) 0x03};
List<S7Parameter> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.0.1", EDataType.BOOL, 1, true));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.4", EDataType.UINT16, 1, 42767));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.6", EDataType.INT16, 1, (short) 32767));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.8", EDataType.UINT32, 1, 3147483647L));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.12", EDataType.INT32, 1, 2147483647));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.16", EDataType.FLOAT32, 1, 3.14f));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.20", EDataType.FLOAT64, 1, 4.15));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.28", EDataType.BYTE, 3, byteData));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.31", EDataType.STRING, 10, "1234567890"));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.43", EDataType.TIME, 1, 12L));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.47", EDataType.DATE, 1, LocalDate.of(2023, 5, 15)));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.49", EDataType.TIME_OF_DAY, 1, LocalTime.of(20, 22, 13)));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.53", EDataType.DTL, 1, LocalDateTime.of(2023, 5, 27, 12, 11, 22, 333225555)));
s7Serializer.write(list);
list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.0.1", EDataType.BOOL));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.4", EDataType.UINT16));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.6", EDataType.INT16));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.8", EDataType.UINT32));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.12", EDataType.INT32));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.16", EDataType.FLOAT32));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.20", EDataType.FLOAT64));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.28", EDataType.BYTE, 3));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.31", EDataType.STRING, 10));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.43", EDataType.TIME));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.47", EDataType.DATE));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.49", EDataType.TIME_OF_DAY));
list.add(new S7Parameter("DB1.53", EDataType.DTL));
List<S7Parameter> actual = s7Serializer.read(list);
s7PLC.close();
}
}- 服务端支持默认支持I区,Q区,M区,T区,C区以及DB1区,每个区都包含65536个字节;
- 服务端可以自定义DB区,随意添加;
- 目前只支持读写操作;
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建服务端
S7PLCServer server = new S7PLCServer();
// 添加DB2,DB3,DB4
server.addDBArea(2, 3, 4);
// 服务端启动
server.start();
// 服务端停止
server.stop();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建服务端
S7PLCServer server = new S7PLCServer();
server.addDBArea(2, 3, 4);
server.start();
// 创建客户端
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.S1200);
s7PLC.writeByte("DB2.0", (byte) 0x01);
byte b = s7PLC.readByte("DB2.0");
// 关闭
s7PLC.close();
server.stop();
}
}class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.SINUMERIK_828D, "127.0.0.1");
String cncId = s7PLC.readCncId();
String cncVersion = s7PLC.readCncVersion();
String cncType = s7PLC.readCncType();
String cncManufactureDate = s7PLC.readCncManufactureDate();
List<Double> machinePosition = s7PLC.readMachinePosition();
List<Double> readRelativePosition = s7PLC.readRelativePosition();
List<Double> readRemainPosition = s7PLC.readRemainPosition();
List<Double> tWorkPiecePosition = s7PLC.readTWorkPiecePosition();
int toolRadiusCompensationNumber = s7PLC.readToolRadiusCompensationNumber();
int toolNumber = s7PLC.readToolNumber();
double actSpindleSpeed = s7PLC.readActSpindleSpeed();
double feedRate = s7PLC.readFeedRate();
int workMode = s7PLC.readWorkMode();
double runTime = s7PLC.readRunTime();
double remainTime = s7PLC.readRemainTime();
String programName = s7PLC.readProgramName();
int alarmNumber = s7PLC.readAlarmNumber();
s7PLC.close();
}
}数据内容采用小端模式
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S7PLC s7PLC = new S7PLC(EPlcType.SINUMERIK_828D, "127.0.0.1");
// single request
RequestNckItem requestNckItem = new RequestNckItem(ENckArea.N_NCK, 1, 18040, 4, ENckModule.M, 1);
DataItem dataItem = s7PLC.readS7NckData(requestNckItem);
String cncType = ByteReadBuff.newInstance(dataItem.getData(), true).getString(dataItem.getCount()).trim();
System.out.println(cncType);
// multi request
List<RequestNckItem> requestNckItems = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4)
.mapToObj(x -> new RequestNckItem(ENckArea.C_CHANNEL, 1, 2, x, ENckModule.SMA, 1))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<DataItem> dataItems = s7PLC.readS7NckData(requestNckItems);
List<Double> positions = dataItems.stream().map(x -> ByteReadBuff.newInstance(x.getData(), true).getFloat64())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
positions.forEach(System.out::println);
s7PLC.close();
}
}1、为什么PLC能写入数据,但是checkConnected 却是false呢?
通信采用懒加载,读写的时候才会触发连接,将checkConnected放在write或read后就变成true。
2、在PLC关闭之后获取异常,在PLC重启之后自动连入该怎么处理?
内部支持断线重连,每次触发读写操作的时候,若PLC已经断线,则触发重连操作。
3、当反馈的报错信息为“未在模块上实现此服务或报告了帧错误”,原因是什么?
由于PLC没有该地址块数据,或者该地址数据不支持访问。
4、PLC通信过程中最大的读写数据字节大小?
PLC的网络通信,根据不同型号PLC的PDULength而定,S1200 = 240,S1500 = 960,总之有240, 480, 960。
最大读取字节数组大小是222 = 240 - 18, 462 = 480 - 18, 942 = 960 - 18。
目前PDULength默认都为240,可自行调整。
根据测试S1200[CPU 1214C],单次读多字节
发送:最大字节读取长度是 216 = 240 - 24, 24(请求报文的PDU)=10(header)+14(parameter)
接收:最大字节读取长度是 222 = 240 - 18, 18(响应报文的PDU)=12(header)+2(parameter)+4(dataItem)
根据测试S1200[CPU 1214C],单次写多字节
发送:最大字节写入长度是 212 = 240 - 28, 28(请求报文的PDU)=10(header)+14(parameter)+4(dataItem)
接收:最大字节写入长度是 225 = 240 - 15, 15(响应报文的PDU)=12(header)+2(parameter)+1(dataItem)
5、批量读写数据时,单次通信过程中,最多读写多少数据?
| PDU length | 数据类型 | 字节数量 | (写)最多个数 | (读)最多个数 | PLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 240 | boolean / byte | 1 | 12 | 18 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| 240 | uint16 / int16 | 2 | 12 | 18 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| 240 | uint32 / int32 / float32 | 4 | 11 | 18 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| 240 | float64 | 8 | 9 | 17 | S1200 / S200Smart |
| PDU length | 数据类型 | 字节数量 | (写)最多个数 | (读)最多个数 | PLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 480 | boolean / byte | 1 | 26 | 38 | S400 |
| 480 | uint16 / int16 | 2 | 24 | 38 | S400 |
| 480 | uint32 / int32 / float32 | 4 | 22 | 38 | S400 |
| 480 | float64 | 8 | 18 | 35 | S400 |
| PDU length | 数据类型 | 字节数量 | (写)最多个数 | (读)最多个数 | PLC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 960 | boolean / byte | 1 | 52 | 78 | S1500 |
| 960 | uint16 / int16 | 2 | 49 | 78 | S1500 |
| 960 | uint32 / int32 / float32 | 4 | 45 | 78 | S1500 |
| 960 | float64 | 8 | 38 | 72 | S1500 |
6、PLC初始化参数
| PLC | 最大 PDU length | Rack | Slot |
|---|---|---|---|
| S200_SMART | 240 | 0 | 1 |
| S300 | 240 | 0 | 2 |
| S400 | 480 | 0 | 3 |
| S1200 | 240 | 0 | 1 |
| S1500 | 960 | 0 | 1 |
7、一般PLC同时在线连接数量有限,切勿重复new S7PLC()!!!