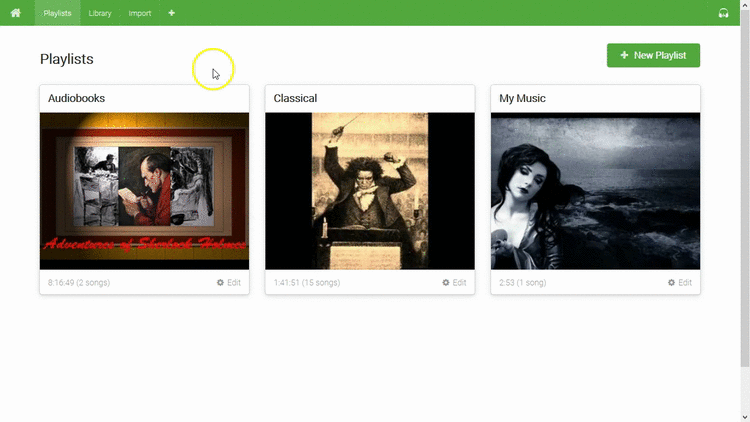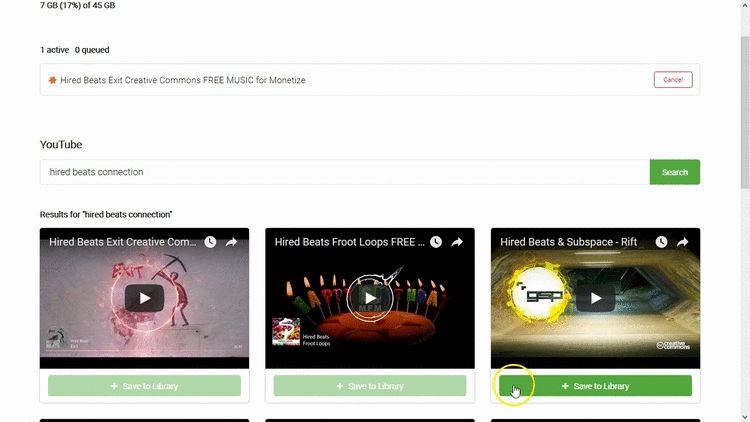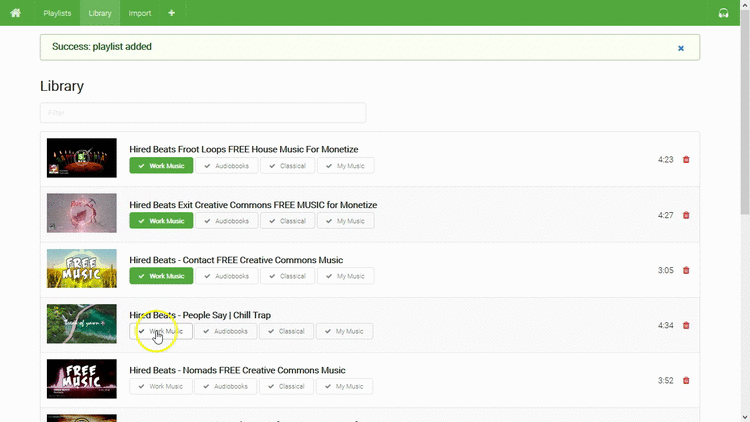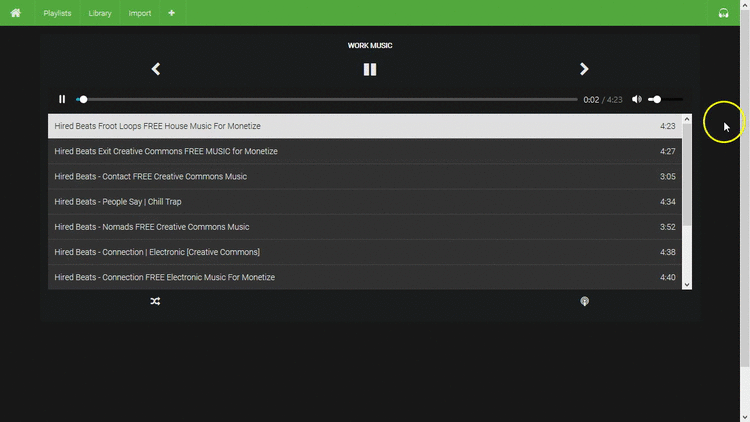
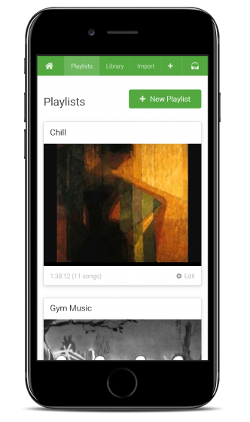
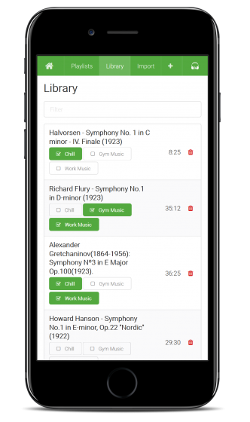
- Playlists
- Create unlimited playlists from your library
- Shareable link for each playlist
- Library
- Filter your media by title and description
- Add to playlists with one button
- Import
- YouTube search and download
- Built in search with queueing downloader
- Cancel downloading/transcode jobs
- HTTP Streaming to any device
- Transcodes to streamable MP4.
- Converts any source to AAC-encoded MP4 (.m4a) audio files using ffmpeg
- Plays in all modern web browsers, media players, and podcast apps
- Private Podcast URLs
- Each Playlist has its own private podcast URL
- Works with any podcast app on desktop or mobile
- Enables downloading for offline access
- Lightweight player
- Uses browser-native player with minimal additions
- Keyboard shortcuts
space(play/pause)p(previous)n(next)m(mute)-/+(volume)- Remembers your volume setting
- Simple self-hosting
- Public Docker image
- Single static Go binary with assets bundled
- Automatic TLS using Let's Encrypt
- Redirects http to https
Recommended Specs
- Type: VPS or dedicated
- Distribution: Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial)
- Memory: 512MB
- Storage: 10GB+
Recommended Providers
Create a DNS A record in your domain pointing to your server's IP address.
Example: music.example.com A 172.16.1.1
When enabled with the --letsencrypt flag, streamlist runs a TLS ("SSL") https server on port 443. It also runs a standard web server on port 80 to redirect clients to the secure server.
Requirements
- Your server must have a publicly resolvable DNS record.
- Your server must be reachable over the internet on ports 80 and 443.
Latest stable release: v0.0.2
Replace amd64 with arm64 or armv7 depending on your architecture.
# Install ffmpeg.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y wget ffmpeg
# Download the streamlist binary.
$ sudo wget -O /usr/bin/streamlist https://github.com/streamlist/streamlist/releases/download/v0.0.2/streamlist-linux-amd64
# Make it executable.
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/streamlist
# Allow it to bind to privileged ports 80 and 443 as non-root (this is also a potential risk).
$ sudo setcap cap_net_bind_service=+ep /usr/bin/streamlist
# Create your streamlist directory.
$ mkdir $HOME/Music
# (optional) Set a password (or one will be generated and printed in the log)
$ echo "mypassword" >$HOME/Music/.authsecret
# Run with Let's Encrypt enabled for automatic TLS setup (your server must be internet accessible).
$ streamlist --http-host music.example.com --http-username $USER --data-dir $HOME/Music --letsencrypt
1.503869865804371e+09 info Streamlist URL: https://music.example.com/streamlist/
1.503869865804527e+09 info Login credentials: <username> / <password>
# Create the htpassword file, setting a password.
$ sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/streamlist.htpasswd <username>
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user <username>
# Verify that you've created your htpasswd file correctly.
$ sudo cat /etc/nginx/streamlist.htpasswd
<username>:$apr1$9MuKubBu315eW3IjIy/Ci290dAtIac/
Run streamlist on localhost port 8000 with reverse proxy authentication, using Docker or not.
Note: You must specify --reverse-proxy-ip to disable basic auth and enable X-Authenticated-User header auth.
$ streamlist --http-addr 127.0.0.1:8000 --http-host music.example.com --reverse-proxy-ip 127.0.0.1
You might edit /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default or wherever your nginx config lives.
server {
server_name music.example.com;
listen 80;
# Using TLS (recommended)
# listen 443;
# ssl_certificate music.example.com.crt;
# ssl_certificate_key music.example.com.key;
# Redirect requests for "/" to "/streamlist/" (or use "location / {}" below)
# rewrite ^/$ /streamlist/ permanent;
location /streamlist/ {
auth_basic "Streamlist";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/streamlist.htpasswd;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Forwards username to Streamlist backend (required for auth)
proxy_set_header X-Authenticated-User $remote_user;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}
}
Probably the easiest way to run Streamlist is using the Docker image.
# Update apt
$ sudo apt-get update
# Remove old docker install.
$ sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io
# Ensure we have basics for apt-get.
$ sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
software-properties-common
# Add Docker's public key.
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
# Add Docker's apt repo
$ sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
# Update apt
$ sudo apt-get update
# Install Docker
$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce
# Run the hello-world test image
$ sudo docker run hello-world
The official image is streamlist/streamlist, which should run in any up-to-date Docker environment.
# Your download directory should be bind-mounted as `/data`
# inside the container using the `--volume` flag (see below).
$ mkdir $HOME/Music
# Set a password (default: a password is generated and printed in the log output)
$ echo "mypassword" >$HOME/Music/.authsecret
# Create the container.
$ sudo docker create \
--name streamlist \
--init \
--restart always \
--publish 80:80 \
--publish 443:443 \
--volume $HOME/Music:/data \
streamlist/streamlist:latest --http-host music.example.com --http-username $USER --letsencrypt
# Run the container
$ sudo docker start streamlist
# View logs for the container
$ sudo docker logs -f streamlist
1.503869865804371e+09 info Streamlist URL: https://music.example.com/streamlist/
1.503869865804527e+09 info Login credentials: <username> / <password>
Pull the latest image, remove the container, and re-create the container as explained above.
# Pull the latest image
$ sudo docker pull streamlist/streamlist
# Stop the container
$ sudo docker stop streamlist
# Remove the container (data is stored on the mounted volume)
$ sudo docker rm streamlist
# Re-create and start the container
$ sudo docker create ... (see above)
$ streamlist --help
Usage of streamlist:
-backlink string
backlink (optional)
-data-dir string
data directory (default "/data")
-debug
debug mode
-http-addr string
listen address (default ":80")
-http-host string
HTTP host
-http-prefix string
HTTP URL prefix (not actually supported yet!) (default "/streamlist")
-http-username string
HTTP basic auth username (default "streamlist")
-letsencrypt
enable TLS using Let's Encrypt
-reverse-proxy-header string
reverse proxy auth header (default "X-Authenticated-User")
-reverse-proxy-ip string
reverse proxy auth IP
The easiest way to build the static binary is using the Dockerfile.build file.
# Clone the git repo
$ git clone https://github.com/streamlist/streamlist.git
$ cd streamlist/
# Compile the code and create a Docker image for it.
$ sudo docker build --build-arg STREAMLIST_VERSION=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD) -t streamlist:build -f Dockerfile.build .
# Create a container based on the image we just built.
$ sudo docker create --name streamlistbuild streamlist:build
# Extract the binary from the image.
$ sudo docker cp streamlistbuild:/usr/bin/streamlist-linux-amd64 streamlist-linux-amd64
# armv7
# $ sudo docker cp streamlistbuild:/usr/bin/streamlist-linux-amd64 streamlist-linux-armv7
# arm64
# $ sudo docker cp streamlistbuild:/usr/bin/streamlist-linux-amd64 streamlist-linux-arm64
# We're done with the build container.
$ sudo docker rm streamlistbuild
# Inspect the binary.
$ file streamlist-linux-amd64
streamlist-linux-amd64: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), statically linked, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=c5a6f3a2e15c8ca511bec52c357ebf8f4g542233, stripped
# Run the binary.
$ ./streamlist-linux-amd64 --help
# Build a tiny alpine "runner" image.
# $ sudo docker build -t streamlist:latest .