-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Sigrok Protocol Decoder GPIB
For GPIB (General Purpose Interface Bus, or HPIB, or IEEE488; 16 bits parallel) protocol analysis with a Saleae Logic16 clone, I need a Sigrok decoder. It is planned, but I like to use it now. So, I tried to program it myself.
Not so easy, after the first look. The decoder HowTo describes it on a high level, but misses a lot of details. So, I am trying to understand the logic at the example ir_nec.
After some reading I found decoder parallel most suited as a guide.
On the right is a picture (click on the picture will expand it) of the GPIB connection. In order to make it easy, I used a 24 wire flat cable with a GPIB-DB24 plug on one end, and a 26 pin flat cable connector on the other side. A 26 pin pin-plug with wire-wrap pins is used to have an easy connection to the Saleae-Logic16 clone.

I made a sample session file hp1631ID.sr with an ID poll of a HP logic analyzer HP1631D.
In order to better understand the sequence of the commands, I made a State Analysis with an HP1652B Logic Analyser, with Inverse Assembler for the GPIB mnemonics. In this example the command ID was send to the Logic Analyser and the answer was HP1631D.
MACHINE 1 - STATE LISTING 2016-08-10
Label > ADDR ATN Mnemonic HEX EOI SRQ REN IFC STAT
Base > Hex Instructions Hex
+0000 ATN *UNL* 3F REN 1A
+0001 ATN *UNT* 5F REN 1A
+0002 ATN LAG_04 24 REN 1A
+0003 I 49 REN 1B
+0004 D 44 REN 1B
+0005 <LF > 0A EOI REN 19
+0006 ATN *UNL* 3F REN 1A
+0007 ATN *UNT* 5F REN 1A
+0008 ATN TAG_04 44 REN 1A
+0009 H 48 REN 9B
+0010 P 50 REN 9B
+0011 1 31 REN 9B
+0012 6 36 REN 9B
+0013 3 33 REN 9B
+0014 1 31 REN 9B
+0015 D 44 EOI REN 99
+0016 ATN *UNL* 3F REN 1A
+0017 ATN *UNT* 5F REN 1A
When you load the decoder GPIB in Pulseview the channel ATN must be set to pin 14, in order to decode the GPIB commands. Channel EOI is alread set to pin 8.
It will easier the handling, to connect the Logic Analyzer input bits with the same channel numbers (0..15), as shown in the protcol decoder.
The source code is named init.py and pd.py and can be viewed via mouse click, and downloaded.
The 2 files must be copied in, either:
# Ubuntu, user local
$ mkdir ~/.local/share/libsigrokdecode/decoders/gpib
or
# Ubuntu, in sigrok installation
$ sudo mkdir /usr/local/share/libsigrokdecode/decoders/gpib
Take care about the 2 underscores of the init file. It can happen, that the operating system will modify them, as it happened to me on Mac OS X. Then the decoder gpib will not load, and you get no error message.
For an easier installation (user local) you can also install via github.
The files must be placed in a new folder named gpib:
# path libsigrokdecode/decoders/gpib/
# a quick test for a good installation, and showing the parameters is:
$ sigrok-cli --protocol-decoders gpib --show
ID: gpib
Name: GPIB
Long name: General Purpose Interface Bus
Description: IEEE-488 GPIB / HPIB protocol.
License: gplv2+
Annotation classes:
- items: Items
- gpib: DAT/CMD
- eoi: EOI
Annotation rows:
- bytes (Bytes): items
- gpib (DAT/CMD): gpib
- eoi (EOI): eoi
Required channels:
- d0 (D0): Data I/O bit 1, ch 0
- d1 (D1): Data I/O bit 2, ch 1
- d2 (D2): Data I/O bit 3, ch 2
- d3 (D3): Data I/O bit 4, ch 3
- d4 (D4): Data I/O bit 5, ch 4
- d5 (D5): Data I/O bit 6, ch 5
- d6 (D6): Data I/O bit 7, ch 6
- d7 (D7): Data I/O bit 8, ch 7
- eoi (EOI8): End or identify, ch 8
- dav (DAV9): Data valid (clock), ch 9
- nrfd (NRFD10): Not ready for data, ch 10
- ndac (NDAC11): Not data accepted, ch 11
- ifc (IFC12): Interface clear, ch 12
- srq (SRQ13): Service request, ch 13
- atn (ATN14): Attention, ch 14
- ren (REN15): Remote enable, ch 15
Optional channels:
None.
Options:
- sample_total: Total number of samples (default 0)
- state: state analysis ('False', 'True', default 'False')
Documentation:
This protocol decoder can decode the GPIB (IEEE-488) protocol.
If the clock channel DAV is set, GPIB decoding is shown.
If the total sample number is given, the last byte is shown.
If option "state" is set "True", a GPIB "State Analysis" is printed
in the terminal.
Below is a decoder sample print of the before mentioned ID poll. It is made with the command:
$ pulseview -i hp1631ID.sr
The first picture shows in detail the GPIB handshake.

The second picture shows in detail the last 4 bytes, notice the EOI signal at the last data byte.

The third picture shows the whole GPIB session: command ID, answer HP1631D.

The GPIB rows contain the following data:
-
gpib:Bytes: the data bytes in hexadecimal format
-
gpib:DAT/CMD: either data bytes in ASCII format, or decoded commands
-
gpib:EOI: will show EOI if this signal accompanies the last data byte
When you collect a data stream with sigrok (command line), or pulseview (sigrok with GUI), you have the possibility to save the data to a session file with the extension xxx.sr. In order to test decoder software, you can replay the collected data with the command line option -i file-name.
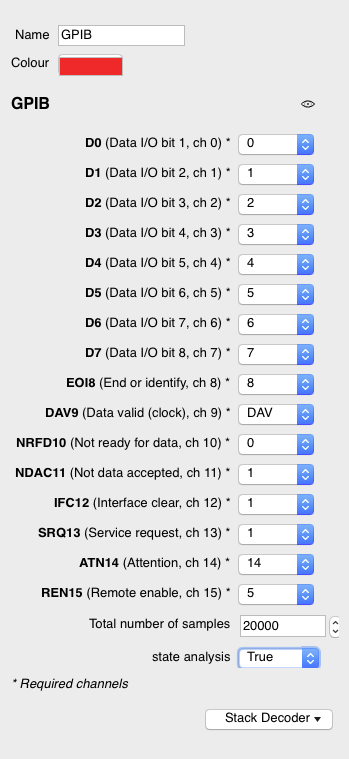
On the right you see a picture of the gpib decoder attributes, seen when you click on the flag gpib on the left in the picture above.
The following is important:
-
total number of samples: must be set, in order to decode the last byte.
-
channel ATN: must be set to pin 14
-
channel CLK: must be set to pin DAV
The total number of bytes 20000 was from the capture session:
- 20 k samples at 500 KHz sample rate = 40 ms
A short explanation for the GPIB command decoding, when line ATN was active:
-
L4 = set device with GPIB address 4 to Listener
-
T4 = set device with GPIB address 4 to Talker
-
UNL = UNLISTEN
-
UNT = UNTALK
-
LF = LineFeed (end of line)
-
EOI = End Or Identify
If you set in attributes window the state analysis flag to True, you will get in the terminal the following print, like a State Analysis:
GPIB State Analysis
0; 3F; 63; UNL ;
9; 5F; 95; UNT ;
18; 24; 36; L4 ;
25; 49; 73; I ;
4031; 44; 68; D ;
5843; 0A; 10; LF ; EOI
5852; 3F; 63; UNL ;
5860; 5F; 95; UNT ;
5869; 44; 68; T4 ;
14830; 48; 72; H ;
15417; 50; 80; P ;
15536; 31; 49; 1 ;
15656; 36; 54; 6 ;
15775; 33; 51; 3 ;
15895; 31; 49; 1 ;
16106; 44; 68; D ; EOI
16123; 3F; 63; UNL ;
16130; 5F; 95; UNT ;
The data colums are:
- sample number, in our case * 2µs = [µs], total session length = 40,000 µs
- data byte in hexadecimal
- data byte in decimal
- ASCII or gpib decoding
- EOI flag
The logic of the GPIB session is:
- Controller set the GPIB to UNLISTEN and UNTALK (neutral state)
- Controller set Device with GPIB address number 4 to LISTEN
- Controller send command 'ID LF+EOI' to Device with GPIB address number 4 (request Idendity string)
- Controller set the GPIB to UNLISTEN and UNTALK (neutral state)
- Controller set Device with GPIB address number 4 to TALK
- Device with GPIB address number 4 send the ID string 'HP1631D+EOI' to Controller
- Controller set the GPIB to UNLISTEN and UNTALK (neutral state)