This project aims to generate a title from the given abstract for academic articles. The project uses four different models fine-tuned with PEFT techniques using the ArXiv dataset:
- BART with LoRA
- T5 with LoRA
- LLaMA with QLoRA and Instruction Tuning
- Mistral with QLoRA and Instruction Tuning
Only articles in the computer science category were selected from the ArXiv dataset. The base models are available via HuggingFace spaces:
The project implements back translation using MarianMT models to create augmented training data. The process involves:
- Translating English abstracts to French using Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-fr
- Translating back to English using Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-fr-en This creates paraphrased versions of the original abstracts while maintaining their meaning.
Using TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat model, the project generates synthetic abstract-title pairs to augment the training data. The model is prompted to create academic-style abstracts and corresponding titles, increasing the diversity of the training dataset.
LLaMA and Mistral models are fine-tuned using QLoRA (Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation) with instruction-based training. This approach helps the models better understand the specific task of title generation through explicit instructions.
The training process implements curriculum learning, where models are trained progressively from simpler to more complex examples. This approach helps improve model performance and generalization capability.
The project includes:
- Low Rank Adaptation Method (LoRA)
- Parameter Efficient Fine Tuning (PEFT)
- HuggingFace model trainings (T5-base, BART-base)
- Evaluation metric of
Rouge Score - One-shot, zero-shot evaluation and addition of instruction prompt
- Model merging and uploading to HuggingFace
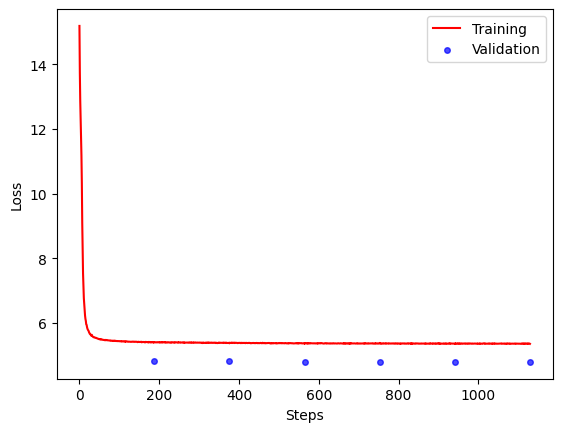
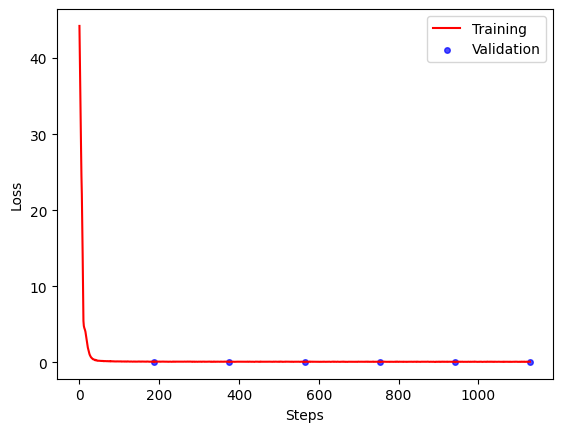
- Tracking logs, memory usage, elapsed time for preprocessing, training, evaluation processes, visualization of training/testing loss
- EDA and script for filtering the ArXiv dataset with only Computer Science (CS) articles.
- Filtering and converting .json dataset to .csv format
External libraries and packages:
- Torch
- HuggingFace
- Transformers
- BitsAndBytes
- PEFT
- Accelerate
- Evaluate (Rouge score)
- LoraLib
- Trl
- Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, tqdm, time
Training Parameters and Limitations
- 6000 training samples, 1000 validation samples, 250 test samples are filtered from the dataset.
- (Number of CS related papers is 299131. However, one of the aims of this project is check the efficiency of small LLMs with PEFT/LORA. Therefore, the less training data samples and less training epochs are considered.)
- Models are trained for 6 epochs.
- Lora attention
R=8,alpha=64,dropout=0.01,learning rate=2e-4,paged_adamW_32bit optimizer
- Memory Cached: 11.2 GB
- Training time: 11423.89 s
- Memory Cached: 13.7 GB
- Training time: 9793.74 s
The models are evaluated using multiple metrics to ensure comprehensive performance assessment:
-
BLEU Score:
- BLEU-1 and BLEU-2 scores to measure word overlap
- Uses smoothing function for better handling of zero-match cases
-
ROUGE Score:
- Measures overlap between generated and reference titles
- Includes ROUGE-1, ROUGE-2, and ROUGE-L variants
-
METEOR Score:
- Evaluates semantic similarity between generated and reference titles
- Takes into account synonyms and paraphrases
| Original Title | Generated Title | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Quantum circuits for strongly correlated quantum systems | Quantum Simulation of strongly correlated Many-Body Hamiltonians |
| 2 | TeKo: Text-Rich Graph Neural Networks with External Knowledge | Text-rich Graph Neural Networks with External Knowledge |
| 3 | CARGO: Effective format-free compressed storage of genomic information | CARGO: Compressed ARchiving for GenOmics |
| 4 | Energy-Efficient Power Control of Train-ground mmWave Communication for | Energy Efficiency of train-ground mmWave communication for high speed trains |
| 5 | A survey on bias in machine learning research | Understanding the sources and consequences of bias in machine learning |
| 6 | SA-UNet: Spatial Attention U-Net for Retinal Vessel Segmentation | Spatial Attention U-Net: Spatial Attention for Eye-related Diseases |
| 7 | A new heuristic algorithm for fast k-segmentation | A novel heuristic algorithm for k-segmentation |
| 8 | Progression and Challenges of IoT in Healthcare: A Short Review | Smart Healthcare and Healthcare: A Comparative Analysis of Smart Healthcare and Security |
| 9 | FVC: A New Framework towards Deep Video Compression in Feature Space | Feature-space Video Compression for Learning Based Video Coding |