|
| 1 | +# Chat microservices |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +Example of 3 microservices and a database working in a Kubernetes cluster. |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +The objetive of this project is to show a real example of our library [PyMS](https://github.com/python-microservices/pyms), |
| 6 | + [the template](https://github.com/python-microservices/microservices-template) and |
| 7 | +the [scaffold](https://github.com/python-microservices/microservices-scaffold). |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +The tutorial of "how to create a cluster" is based of this [bitnami tutorial](https://docs.bitnami.com/kubernetes/get-started-kubernetes/) |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | +## Step 1: Configure The Platform |
| 13 | +The first step for working with Kubernetes clusters is to have Minikube installed if you have selected to work locally. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +Install Minikube in your local system, either by using a virtualization software such as VirtualBox or a local terminal. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +* Browse to the [Minikube latest releases page](https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases). |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +* Select the distribution you wish to download depending on your Operating System. |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | + NOTE: This tutorial assumes that you are using Mac OSX or Linux OS. The Minikube installer for Windows is under development. To get an experimental release of Minikube for Windows, check the Minikube releases page. |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +* Open a new console window on the local system or open your VirtualBox. |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +* To obtain the latest Minikube release, execute the following command depending on your OS. Remember to replace the X.Y.Z and OS_DISTRIBUTION placeholders with the latest version and software distribution of Minikube respectively. Check the Minikube latest releases page for more information on this. |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | + ```bash |
| 28 | + curl -Lo minikube https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/vX.Y.Z/minikube-OS_DISTRIBUTION-amd64 && chmod +x minikube && sudo mv minikube /usr/local/bin/ |
| 29 | + ``` |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +## Step 2: Create A Kubernetes Cluster |
| 32 | +By starting Minikube, a single-node cluster is created. Run the following command in your terminal to complete the creation of the cluster: |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +```bash |
| 35 | +minikube start |
| 36 | +``` |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +Set the environment of docker |
| 39 | +```bash |
| 40 | +eval $(minikube docker-env) |
| 41 | +``` |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +To run your commands against Kubernetes clusters, the kubectl CLI is needed. Check step 3 to complete the installation of kubectl. |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +## Step 3: Install The Kubectl Command-Line Tool |
| 47 | +In order to start working on a Kubernetes cluster, it is necessary to install the Kubernetes command line (kubectl). Follow these steps to install the kubectl CLI: |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +* Execute the following commands to install the kubectl CLI. OS_DISTRIBUTION is a placeholder for the binary distribution of kubectl, remember to replace it with the corresponding distribution for your Operating System (OS). |
| 50 | + |
| 51 | + ```bash |
| 52 | + curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/OS_DISTRIBUTION/amd64/kubectl |
| 53 | + chmod +x ./kubectl |
| 54 | + sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl |
| 55 | + ``` |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | + TIP: Once the kubectl CLI is installed, you can obtain information about the current version with the kubectl version command. |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | + NOTE: You can also install kubectl by using the sudo apt-get install kubectl command. |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +* Check that kubectl is correctly installed and configured by running the kubectl cluster-info command: |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | + ```bash |
| 64 | + kubectl cluster-info |
| 65 | + ``` |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | + NOTE: The kubectl cluster-info command shows the IP addresses of the Kubernetes node master and its services. |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +  |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +* You can also verify the cluster by checking the nodes. Use the following command to list the connected nodes: |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | + ```bash |
| 74 | + kubectl get nodes |
| 75 | + ``` |
| 76 | +  |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | +* To get complete information on each node, run the following: |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | + ```bash |
| 82 | + kubectl describe node |
| 83 | + ``` |
| 84 | + 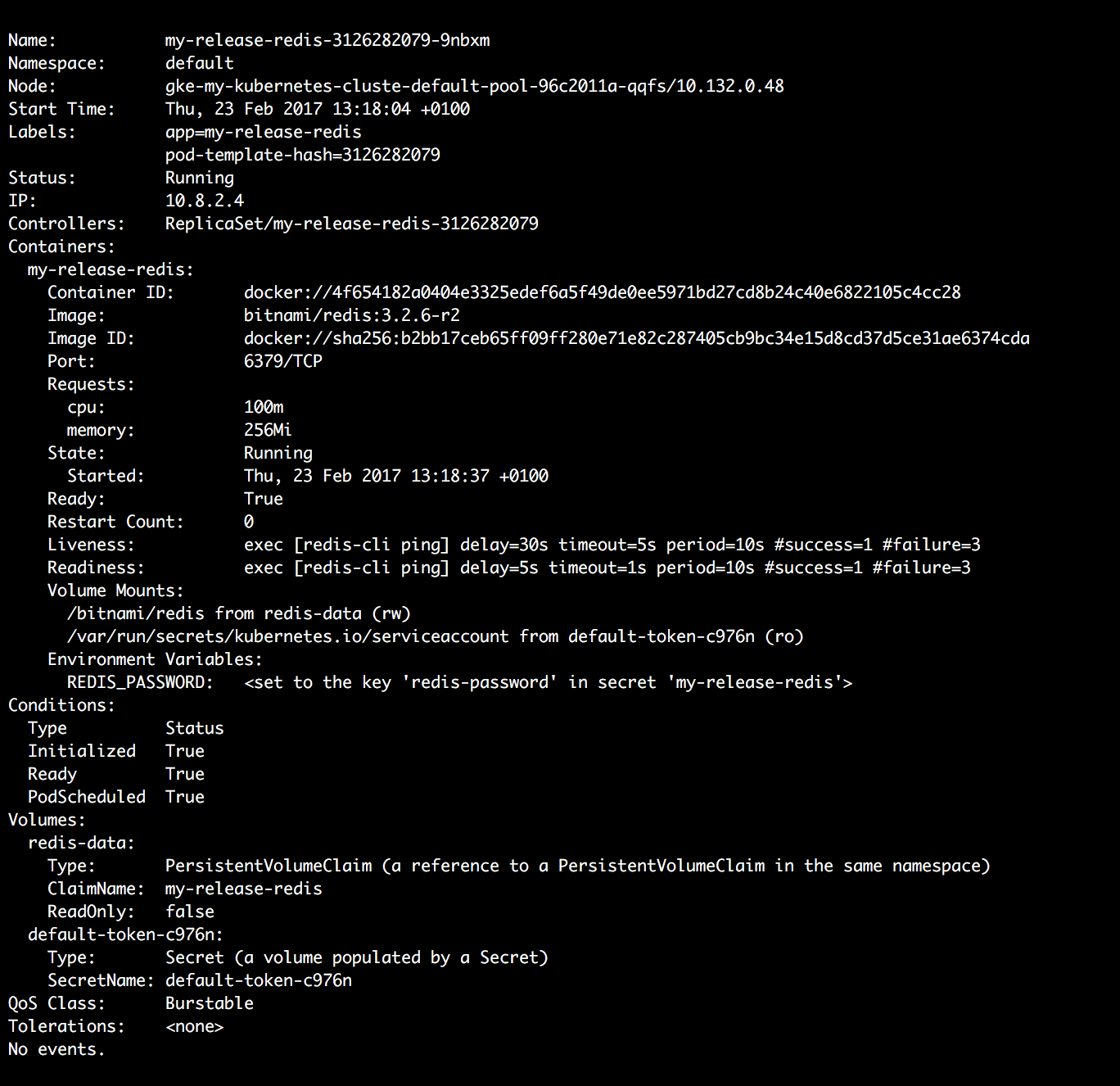 |
| 85 | + |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | +[Learn more about the kubectl CLI](https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/kubectl-overview/). |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +## Step 4: Install And Configure Helm And Tiller |
| 90 | +The easiest way to run and manage applications in a Kubernetes cluster is using Helm. Helm allows you to perform key operations for managing applications such as install, upgrade or delete. Helm is composed of two parts: Helm (the client) and Tiller (the server). Follow the steps below to complete both Helm and Tiller installation and create the necessary Kubernetes objects to make Helm work with Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | +* To install Helm, run the following commands: |
| 93 | + |
| 94 | + ```bash |
| 95 | + curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/helm/master/scripts/get > get_helm.sh |
| 96 | + chmod 700 get_helm.sh |
| 97 | + ./get_helm.sh |
| 98 | + ``` |
| 99 | + |
| 100 | + TIP: If you are using OS X you can install it with the brew install command: brew install kubernetes-helm. |
| 101 | + |
| 102 | +* Create a ClusterRole configuration file with the content below. In this example, it is named clusterrole.yaml. |
| 103 | + |
| 104 | + ```yaml |
| 105 | + apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 |
| 106 | + kind: ClusterRole |
| 107 | + metadata: |
| 108 | + annotations: |
| 109 | + rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true" |
| 110 | + labels: |
| 111 | + kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults |
| 112 | + name: cluster-admin |
| 113 | + rules: |
| 114 | + - apiGroups: |
| 115 | + - '*' |
| 116 | + resources: |
| 117 | + - '*' |
| 118 | + verbs: |
| 119 | + - '*' |
| 120 | + - nonResourceURLs: |
| 121 | + - '*' |
| 122 | + verbs: |
| 123 | + - '*' |
| 124 | + ``` |
| 125 | +
|
| 126 | +* To create the ClusterRole, run this command: |
| 127 | +
|
| 128 | + ```bash |
| 129 | + kubectl create -f clusterrole.yaml |
| 130 | + ``` |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | +* To create a ServiceAccount and associate it with the ClusterRole, use a ClusterRoleBinding, as below: |
| 133 | + |
| 134 | + ```bash |
| 135 | + kubectl create serviceaccount -n kube-system tiller |
| 136 | + kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller |
| 137 | + ``` |
| 138 | + |
| 139 | +* Initialize Helm as shown below: |
| 140 | + |
| 141 | + ```bash |
| 142 | + helm init --service-account tiller |
| 143 | + ``` |
| 144 | + If you have previously initialized Helm, execute the following command to upgrade it: |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | + ```bash |
| 147 | + helm init --upgrade --service-account tiller |
| 148 | + ``` |
| 149 | +* Check if Tiller is correctly installed by checking the output of kubectl get pods as shown below: |
| 150 | + |
| 151 | + ```bash |
| 152 | + kubectl --namespace kube-system get pods | grep tiller |
| 153 | + tiller-deploy-2885612843-xrj5m 1/1 Running 0 4d |
| 154 | + ``` |
| 155 | + |
| 156 | +Once you have installed Helm, a set of useful commands to perform common actions is shown below: |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | +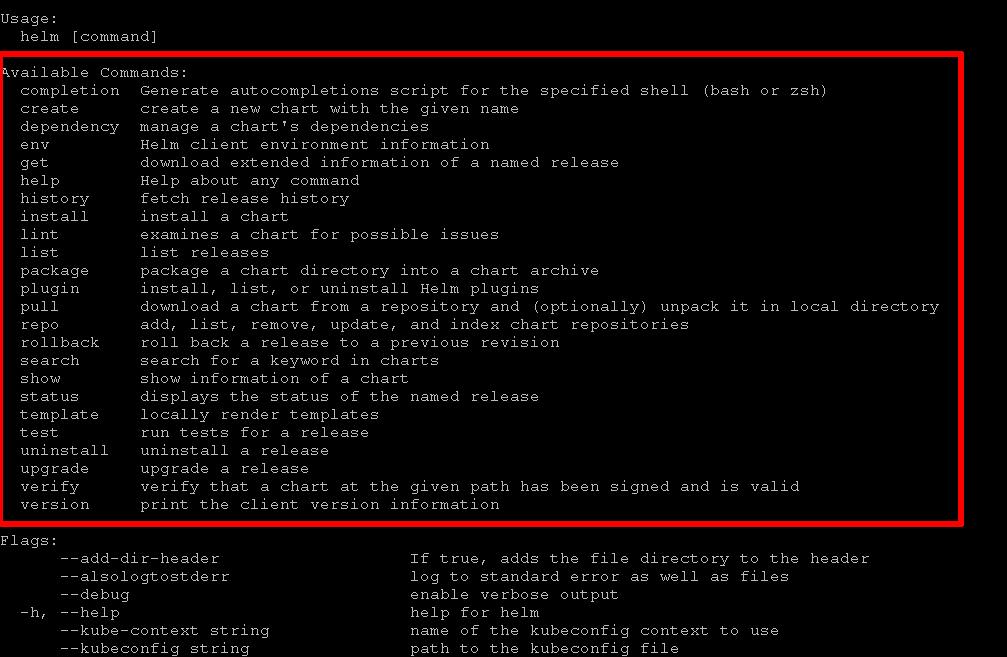 |
| 159 | + |
| 160 | +## Step 5 |
| 161 | + |
| 162 | +Create the docker images: |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | + ```bash |
| 165 | + docker build -t chat_db:v1 -f chat_db/Dockerfile chat_db/ |
| 166 | + docker build -t chat_svc:v1 -f chat_svc/Dockerfile chat_svc/ |
| 167 | + docker build -t chat_front:v1 -f chat_front/Dockerfile chat_front/ |
| 168 | + |
| 169 | + ``` |
| 170 | + |
| 171 | +Check your helm charts: |
| 172 | + |
| 173 | + ```bash |
| 174 | + helm install --dry-run --debug ./chat_db/chat_db/ |
| 175 | + helm install --dry-run --debug ./chat_svc/chat_svc/ |
| 176 | + helm install --dry-run --debug ./chat_front/chat_front/ |
| 177 | + ``` |
| 178 | + |
| 179 | +Install helm charts: |
| 180 | + |
| 181 | + ```bash |
| 182 | + helm install --name chat-db ./chat_db/chat_db/ |
| 183 | + helm install --name chat-svc ./chat_svc/chat_svc/ |
| 184 | + helm install --name chat-front ./chat_front/chat_front/ |
| 185 | + ``` |
| 186 | + |
| 187 | +# Step 6 |
| 188 | + |
| 189 | +Open http://127.0.0.1.nip.io/ and see the magic! ;) |
0 commit comments