Welcome to the "Linked Lists" folder in this repository! This folder contains code examples, explanations, and resources related to linked lists data structures. Whether you're new to linked lists or looking for specific operations and implementations, you'll find useful information here.
- Introduction to Linked Lists
- Singly Linked Lists
- Doubly Linked Lists
- Circular Linked Lists
- Common Operations
- External Resources
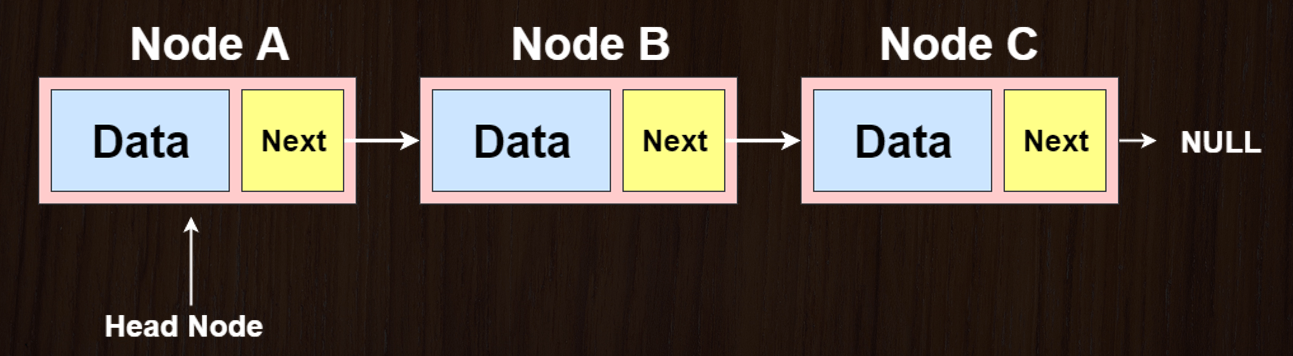
A linked list is a fundamental data structure consisting of nodes, each containing data and a reference to the next (and possibly previous) node. This folder provides an introduction to various types of linked lists and their usage.
Singly Linked Lists are a type of linked list where each node points to the next node in the sequence. They consist of nodes, where each node contains a data element and a reference (or pointer) to the next node in the sequence. The last node typically points to NULL to indicate the end of the list.
- Each node contains two components:
- Data: The value or payload stored in the node.
- Next: A reference (pointer) to the next node in the sequence.
- Insertion: Adding a new node to the list.
- Deletion: Removing a node from the list.
- Traversal: Iterating through the list to access or manipulate nodes.
class Node {
public $data;
public $next;
public function __construct($data) {
$this->data = $data;
$this->next = null;
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
public $head;
public function __construct() {
$this->head = null;
}
// Inserting a new node at the beginning of the list
public function insertAtBeginning($data) {
$newNode = new Node($data);
$newNode->next = $this->head;
$this->head = $newNode;
}
// Inserting a new node at the end of the list
public function insertAtEnd($data) {
$newNode = new Node($data);
if ($this->head === null) {
$this->head = $newNode;
return;
}
$current = $this->head;
while ($current->next !== null) {
$current = $current->next;
}
$current->next = $newNode;
}
// Traversing the list and printing its elements
public function display() {
$current = $this->head;
while ($current !== null) {
echo $current->data . " ";
$current = $current->next;
}
}
}
// Example usage:
$linkedList = new SinglyLinkedList();
$linkedList->insertAtBeginning(3);
$linkedList->insertAtBeginning(2);
$linkedList->insertAtBeginning(1);
$linkedList->insertAtEnd(4);
$linkedList->insertAtEnd(5);
$linkedList->display(); // Output: 1 2 3 4 5Doubly Linked Lists are a type of linked list where each node points to both the next and the previous nodes in the sequence. They consist of nodes, where each node contains a data element, a reference (or pointer) to the next node, and a reference (or pointer) to the previous node. This bidirectional linkage allows traversal in both forward and backward directions.
- Each node contains three components:
- Data: The value or payload stored in the node.
- Next: A reference (pointer) to the next node in the sequence.
- Previous: A reference (pointer) to the previous node in the sequence.
- Insertion: Adding a new node to the list.
- Deletion: Removing a node from the list.
- Traversal: Iterating through the list to access or manipulate nodes.
class Node {
public $data;
public $next;
public $prev;
public function __construct($data) {
$this->data = $data;
$this->next = null;
$this->prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
public $head;
public $tail;
public function __construct() {
$this->head = null;
$this->tail = null;
}
// Inserting a new node at the beginning of the list
public function insertAtBeginning($data) {
$newNode = new Node($data);
if ($this->head === null) {
$this->head = $newNode;
$this->tail = $newNode;
} else {
$newNode->next = $this->head;
$this->head->prev = $newNode;
$this->head = $newNode;
}
}
// Inserting a new node at the end of the list
public function insertAtEnd($data) {
$newNode = new Node($data);
if ($this->tail === null) {
$this->head = $newNode;
$this->tail = $newNode;
} else {
$newNode->prev = $this->tail;
$this->tail->next = $newNode;
$this->tail = $newNode;
}
}
// Traversing the list forward and printing its elements
public function displayForward() {
$current = $this->head;
while ($current !== null) {
echo $current->data . " ";
$current = $current->next;
}
}
// Traversing the list backward and printing its elements
public function displayBackward() {
$current = $this->tail;
while ($current !== null) {
echo $current->data . " ";
$current = $current->prev;
}
}
}
// Example usage:
$doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList();
$doublyLinkedList->insertAtBeginning(3);
$doublyLinkedList->insertAtBeginning(2);
$doublyLinkedList->insertAtBeginning(1);
$doublyLinkedList->insertAtEnd(4);
$doublyLinkedList->insertAtEnd(5);
echo "Forward traversal: ";
$doublyLinkedList->displayForward(); // Output: 1 2 3 4 5
echo "\n";
echo "Backward traversal: ";
$doublyLinkedList->displayBackward(); // Output: 5 4 3 2 1Circular Linked Lists are a type of linked list where each node points to the next node in the sequence, and the last node points back to the first node, creating a circular structure. They consist of nodes, where each node contains a data element and a reference (or pointer) to the next node in the sequence.
- Each node contains two components:
- Data: The value or payload stored in the node.
- Next: A reference (pointer) to the next node in the sequence.
- Insertion: Adding a new node to the list.
- Deletion: Removing a node from the list.
- Traversal: Iterating through the list to access or manipulate nodes.
class Node {
public $data;
public $next;
public function __construct($data) {
$this->data = $data;
$this->next = null;
}
}
class CircularLinkedList {
public $head;
public function __construct() {
$this->head = null;
}
// Inserting a new node at the end of the list
public function insert($data) {
$newNode = new Node($data);
if ($this->head === null) {
$this->head = $newNode;
$newNode->next = $newNode; // Point to itself for circularity
} else {
$current = $this->head;
while ($current->next !== $this->head) {
$current = $current->next;
}
$current->next = $newNode;
$newNode->next = $this->head; // Point back to the head for circularity
}
}
// Traversing the circular list and printing its elements
public function display() {
if ($this->head === null) {
return;
}
$current = $this->head;
do {
echo $current->data . " ";
$current = $current->next;
} while ($current !== $this->head);
}
}
// Example usage:
$circularLinkedList = new CircularLinkedList();
$circularLinkedList->insert(1);
$circularLinkedList->insert(2);
$circularLinkedList->insert(3);
$circularLinkedList->display(); // Output: 1 2 3-
Description: Inserting a new node into the linked list at a specified position or at the beginning/end of the list.
-
Approaches:
- Insertion at the Beginning: Adding a new node at the beginning of the linked list.
// Insertion at the beginning of the linked list public function insertAtBeginning($data) { $newNode = new Node($data); $newNode->next = $this->head; $this->head = $newNode; }
- Insertion at the End: Adding a new node at the end of the linked list.
// Insertion at the end of the linked list public function insertAtEnd($data) { $newNode = new Node($data); if ($this->head === null) { $this->head = $newNode; return; } $current = $this->head; while ($current->next !== null) { $current = $current->next; } $current->next = $newNode; }