Click link to get to the Zenodo website, where you will find the DOI for your version. This is the lastest DOI:
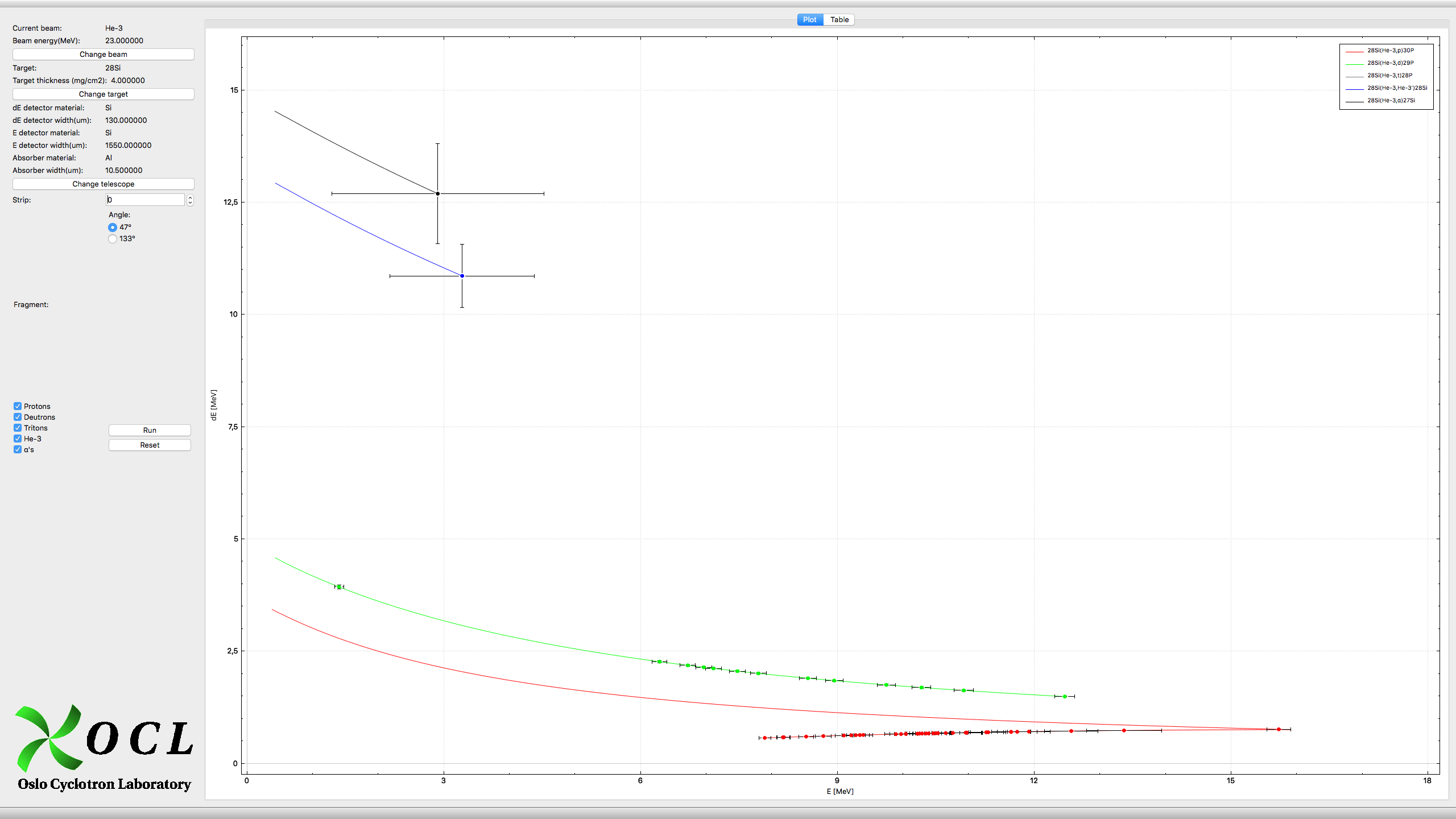
Application for simulating the kinematics in Oslo Cyclotron Laboratory. The application uses stopping powers from J.F. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, and U. Littmark, The Stopping and Range of Ions in Solids, Pergamon Press, New York (1985) for materials
The software is based on the Qt SDK. Currently it has only been built using Qt 5.5 on OS X, but might also work with other versions of Qt. It also requires an compiler supporting C++11. In order to build, run:
qmake Qkinz.pro
make
####OS X: The latest version for OS X can be downloaded here(compatible with OS X 10.9 and later).
####Ubuntu: The easiest way to install for ubuntu is to run the following lines in the command-line:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:v-w-ingeberg/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install qkinz
Binaries can also be downloaded from here.
####Windows: Currently, no binaries are provided but can be build from source.
Qkinz now supports input files that specifies the calculations wanted, making the process of running for all angles much less time consuming. Such a file might be (see comments for explanations):
# This is a comment, lines starting with '#'!
# Where to dump the output of the program. The user have to provide the full path to the output file.
# Example:
output /Path/To/Output/File.txt
# Specify the telescope.
# telescope X Z W u
# Where X spesifies the component of the telescope, Z the element number of the component,
# W is the width and u is the width unit.
# X can be:
# dE is for the front detector.
# E is the back detector.
# A is the absorber.
# u can be gcm2, mgcm2 or um.
# Example:
telescope dE 14 284 um
telescope E 14 982 um
telescope A 73 54 mgcm2
# Beam used. Specified by:
# projectile A Z E
# where A is the mass number, Z the proton number and E the beam energy in [MeV]
# Example:
projectile 86 36 299.51
# Fragment is the particle measured in the particle telescope. It is specified by:
# fragment A Z
# where A is the mass number and Z is the proton number.
# Example:
fragment 1 1
# The target is specified by:
# target A Z W U
# where A is the mass number, Z is the proton number, W is the width of the target
# and U is the width unit.
# U can be gcm2, mgcm2 or um.
# Example:
target 2 1 191.0 mgcm2
# It is also possible to provide tabulated stopping powers for the projectile and
# fragment in the target. This is useful if the target is a compound. If custom
# stopping power is given, then it has to be given for both the projectile and the fragment.
# The tabulated stopping powers will be used if specified. The file still have to specify the
# target with the target nucleus and the correct width. It is extremly important that the number
# for the width provided in the "target" command is in the same units as the tabulated stopping
# powers. If the tabulated stopping powers are in MeV/(g/cm^2) units then the number for the
# width 'W' in the target command has to be in g/cm^2. The value of 'U' in the target command
# is not important and can be any of the allowed values, but will not affect the calculations.
# The command for tabulated stopping powers for the target is:
custom projectile /Path/To/Tabulated/Stopping/Powers/Of/The/Projectile/In/The/Target.txt
custom fragment /Path/To/Tabulated/Stopping/Powers/Of/The/Fragment/In/The/Target.txt
# The format of the tabulated values have to be:
# <Kinetic energy of the particle> <Stopping power in [MeV/(cm or g/cm^2 or ug/cm^2, etc.)]>
# Eg.:
# "1.0 3.2
# 2.0 4.5"
# The angles that are being calculated is specified as:
# "angle siri f" for all forward SiRi angles.
# "angle siri b" for all backward SiRi angles.
# "angle custom x /Path/To/File/With/Angles.txt" is a file with the wanted angles
# that should be calculated.
# Each line in the file should be on the format:
# "<angle>", "<i> <angle i>" or "<i> <j> <angle i,j>"
# where x is either 0, 1, or 2, respectively.
# The value for "<angle>" should be in radians.
# The full path should be provided for the custom angles file.
# Example:
angle custom 2 /Path/To/Angles.txt
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/