Name
双向均线回归交易策略Bidirectional-Moving-Average-Reversion-Trading-Strategy
Author
ChaoZhang
Strategy Description
双向均线回归交易策略(Bidirectional Moving Average Reversion Trading Strategy)是一个利用价格平均回归原理构建的量化交易策略。该策略通过设置多组移动均线来捕捉价格反转机会,在价格偏离均线一定幅度后进入场内,等待价格回归均线的时候平仓套利。
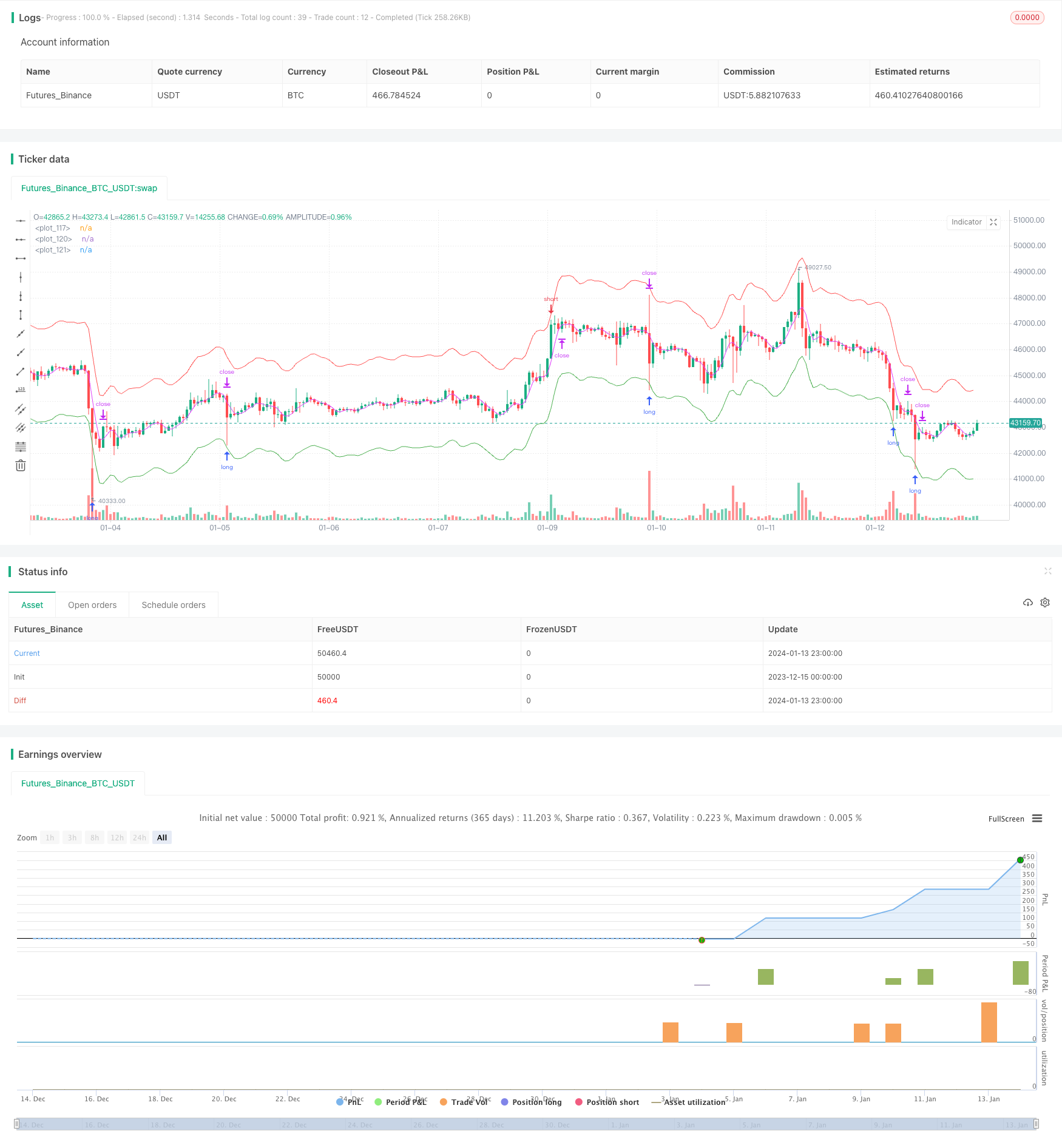
该策略主要基于价格平均回归理论。它认为,价格总是围绕着一个平均值波动,当价格严重偏离平均值时就更有可能回归均值。具体来说,该策略同时设置三组均线:开仓均线、平仓均线和限位均线。当价格触及开仓均线时,会打开对应的做多或做空仓位。当价格触及平仓均线时,会平掉之前的仓位。最后,如果价格继续运行没有回归,限位均线可以控制损失。
从代码逻辑上看,开仓均线分为做多线和做空线,分别由长线和短线组成。它们与价格之间的偏离程度决定了仓位大小。此外,平仓均线是单独的均线,用于决定平仓的时机。当价格运行到此均线时,仓位会被平掉。
双向均线回归策略的优势主要体现在:
- 捕捉价格反转,适合趋势盘整市
- 通过限位损失控制风险
- 可自定义参数组合,适应性强
- 容易理解,便于参数优化
该策略适用于低波动、价格波动范围较小的品种,特别是进入盘整阶段的品种。它能有效捕捉价格临时性反转的机会。同时,它的风险控制措施也较为完善,即使价格没有回归也能控制损失在一定范围内。
双向均线回归策略也存在一些风险:
- 追涨杀跌风险。当价格出现一波剧烈行情时,该策略有可能连续打开仓位最终爆仓。
- 价格震荡过大风险。如果价格震荡幅度过大,仓位有可能到达限位损失而被强制平仓。
- 参数优化风险。该策略的参数设置对于其盈利能力有重要影响,如果参数设置不当,会大幅降低获利概率。
针对上述风险,可以从以下几个方面进行优化:
- 加大开仓限制,避免过于频繁开仓
- 适当缩小仓位规模,防止爆仓风险
- 优化均线周期、平仓线参数等设置
该策略还具有很大的优化空间,主要可以从以下几个角度进行:
- 增加开仓条件逻辑,防止趋势行情下的追涨杀跌
- 添加降低仓位逻辑,防止价格大幅震荡带来的风险
- 尝试不同类型的均线指标,寻找更好参数组合
- 利用机器学习方法自动优化参数
- 增加自动止损策略,更好地控制风险
双向均线回归交易策略通过捕捉价格偏离移动均线后的回归机会进行盈利。它有效控制了风险,并且可通过参数优化获得更好收益。虽然该策略也存在一些风险,但可以通过完善开仓逻辑、降低仓位规模等方法加以控制。该策略简单易懂,值得量化交易者进一步研究与优化。
||
The Bidirectional Moving Average Reversion Trading Strategy is a quantitative trading strategy built on the theory of price mean reversion. This strategy captures price reversal opportunities by setting up multiple moving averages and entering the market when the price deviates significantly from the moving averages, and exiting when it reverts back.
The core idea of this strategy is price mean reversion, which suggests that prices tend to fluctuate around an average value, and have a higher chance of reverting back when they deviate too far from the average. Specifically, this strategy sets up three groups of moving averages: entry moving averages, exit moving averages, and stop-loss moving averages. It will open corresponding long or short positions when prices hit the entry moving averages; close positions when prices hit the exit moving averages; and control losses with stop-loss moving averages in case prices continue to trend without reverting back.
From the code logic perspective, there are two entry moving averages - long and short - consisting of fast and slow moving averages respectively. The deviation between them and the price determines the position size. In addition, the exit moving average is a separate moving average that signals when to close the positions. When prices hit this line, existing positions will be flattened.
The main advantages of the bidirectional moving average reversion strategy include:
- Capturing price reversals, suitable for range-bound markets
- Controlling risks through stop losses
- Highly customizable parameters for adaptability
- Easy to understand, convenient for parameter optimization
This strategy works well with low volatility instruments that have relatively small price swings, especially when entering range-bound cycles. It can effectively capture opportunities from temporary price reversals. Meanwhile, the risk control measures are quite comprehensive, capping losses within reasonable ranges even if prices do not revert back.
There are also some risks associated with this strategy:
- Chasing trends risk. Consecutive new positions may lead to liquidation during strong trending moves.
- Excessive price swings risk. Stop losses could be hit by increased volatility.
- Parameter optimization risk. Inappropriate parameter settings may lead to significant underperformance.
Some ways to mitigate the above risks include:
- Limiting new entries to avoid overtrading
- Reducing position sizes to limit liquidation risks
- Optimizing parameters like moving average periods and exit line multipliers
There is also ample room to further optimize this strategy:
- Add additional entry logic to prevent trend chasing
- Incorporate adaptive position sizing against volatility
- Experiment with different types of moving averages
- Machine learning for automated parameter optimization
- Incorporate trailing stops for more dynamic risk management
The bidirectional moving average reversion trading strategy aims to profit from price reversals after significant deviations from its moving average levels. With proper risk control measures, it can achieve consistent profits through parameter tuning. While risks like chasing trends and excessive volatility still exist, they can be addressed through improving entry logic, reducing position sizes and more. This easy-to-understand strategy deserves further research and optimization from quantitative traders.
[/trans]
Strategy Arguments
| Argument | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| v_input_2 | true | long1on |
| v_input_float_1 | 0.96 | Long |
| v_input_int_4 | 10 | Lot 1 |
| v_input_3 | true | short1on |
| v_input_float_2 | 1.04 | short |
| v_input_int_6 | 10 | Lot 1 |
| v_input_4 | timestamp(01 Jan 2010 00:00 +0000) | Start date |
| v_input_5 | timestamp(31 Dec 2030 23:59 +0000) | Final date |
| v_input_1 | false | (?Options)Entry on close |
| v_input_int_1 | false | |
| v_input_int_2 | false | Trade |
| v_input_bool_1 | false | Use Kalman filter |
| v_input_string_1 | 0 | (?MA Opening Long)maopeningtyp_l: SMA |
| v_input_source_1_ohlc4 | 0 | maopeningsrc_l: ohlc4 |
| v_input_int_3 | 3 | maopeninglen_l |
| v_input_string_2 | 0 | (?MA Opening Short)maopeningtyp_s: SMA |
| v_input_source_2_ohlc4 | 0 | maopeningsrc_s: ohlc4 |
| v_input_int_5 | 3 | maopeninglen_s |
| v_input_string_3 | 0 | (?MA Closing)maclosingtyp: SMA |
| v_input_source_3_ohlc4 | 0 | maclosingsrc: ohlc4 |
| v_input_int_7 | 3 | maclosinglen |
| v_input_float_3 | true | mul |
Source (PineScript)
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-15 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-14 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy(title = "hamster-bot MRS 2", overlay = true, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, initial_capital = 100, default_qty_value = 30, pyramiding = 1, commission_value = 0.1, backtest_fill_limits_assumption = 1)
info_options = "Options"
on_close = input(false, title = "Entry on close", inline=info_options, group=info_options)
OFFS = input.int(0, minval = 0, maxval = 1, title = "| Offset View", inline=info_options, group=info_options)
trade_offset = input.int(0, minval = 0, maxval = 1, title = "Trade", inline=info_options, group=info_options)
use_kalman_filter = input.bool(false, title="Use Kalman filter", group=info_options)
//MA Opening
info_opening = "MA Opening Long"
maopeningtyp_l = input.string("SMA", title="Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "TEMA", "DEMA", "ZLEMA", "WMA", "Hma", "Thma", "Ehma", "H", "L", "DMA"], title = "", inline=info_opening, group=info_opening)
maopeningsrc_l = input.source(ohlc4, title = "", inline=info_opening, group=info_opening)
maopeninglen_l = input.int(3, minval = 1, title = "", inline=info_opening, group=info_opening)
long1on = input(true, title = "", inline = "long1")
long1shift = input.float(0.96, step = 0.005, title = "Long", inline = "long1")
long1lot = input.int(10, minval = 0, maxval = 10000, step = 10, title = "Lot 1", inline = "long1")
info_opening_s = "MA Opening Short"
maopeningtyp_s = input.string("SMA", title="Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "TEMA", "DEMA", "ZLEMA", "WMA", "Hma", "Thma", "Ehma", "H", "L", "DMA"], title = "", inline=info_opening_s, group=info_opening_s)
maopeningsrc_s = input.source(ohlc4, title = "", inline=info_opening_s, group=info_opening_s)
maopeninglen_s = input.int(3, minval = 1, title = "", inline=info_opening_s, group=info_opening_s)
short1on = input(true, title = "", inline = "short1")
short1shift = input.float(1.04, step = 0.005, title = "short", inline = "short1")
short1lot = input.int(10, minval = 0, maxval = 10000, step = 10, title = "Lot 1", inline = "short1")
//MA Closing
info_closing = "MA Closing"
maclosingtyp = input.string("SMA", title="Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "TEMA", "DEMA", "ZLEMA", "WMA", "Hma", "Thma", "Ehma", "H", "L", "DMA"], title = "", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
maclosingsrc = input.source(ohlc4, title = "", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
maclosinglen = input.int(3, minval = 1, maxval = 200, title = "", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
maclosingmul = input.float(1, step = 0.005, title = "mul", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
startTime = input(timestamp("01 Jan 2010 00:00 +0000"), "Start date", inline = "period")
finalTime = input(timestamp("31 Dec 2030 23:59 +0000"), "Final date", inline = "period")
HMA(_src, _length) => ta.wma(2 * ta.wma(_src, _length / 2) - ta.wma(_src, _length), math.round(math.sqrt(_length)))
EHMA(_src, _length) => ta.ema(2 * ta.ema(_src, _length / 2) - ta.ema(_src, _length), math.round(math.sqrt(_length)))
THMA(_src, _length) => ta.wma(ta.wma(_src,_length / 3) * 3 - ta.wma(_src, _length / 2) - ta.wma(_src, _length), _length)
tema(sec, length)=>
tema1= ta.ema(sec, length)
tema2= ta.ema(tema1, length)
tema3= ta.ema(tema2, length)
tema_r = 3*tema1-3*tema2+tema3
donchian(len) => math.avg(ta.lowest(len), ta.highest(len))
ATR_func(_src, _len)=>
atrLow = low - ta.atr(_len)
trailAtrLow = atrLow
trailAtrLow := na(trailAtrLow[1]) ? trailAtrLow : atrLow >= trailAtrLow[1] ? atrLow : trailAtrLow[1]
supportHit = _src <= trailAtrLow
trailAtrLow := supportHit ? atrLow : trailAtrLow
trailAtrLow
f_dema(src, len)=>
EMA1 = ta.ema(src, len)
EMA2 = ta.ema(EMA1, len)
DEMA = (2*EMA1)-EMA2
f_zlema(src, period) =>
lag = math.round((period - 1) / 2)
ema_data = src + (src - src[lag])
zl= ta.ema(ema_data, period)
f_kalman_filter(src) =>
float value1= na
float value2 = na
value1 := 0.2 * (src - src[1]) + 0.8 * nz(value1[1])
value2 := 0.1 * (ta.tr) + 0.8 * nz(value2[1])
lambda = math.abs(value1 / value2)
alpha = (-math.pow(lambda, 2) + math.sqrt(math.pow(lambda, 4) + 16 * math.pow(lambda, 2)))/8
value3 = float(na)
value3 := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(value3[1])
//SWITCH
ma_func(modeSwitch, src, len, use_k_f=true) =>
modeSwitch == "SMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.sma(src, len)) : ta.sma(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "RMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.rma(src, len)) : ta.rma(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "EMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.ema(src, len)) : ta.ema(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "TEMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(tema(src, len)) : tema(src, len):
modeSwitch == "DEMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(f_dema(src, len)) : f_dema(src, len):
modeSwitch == "ZLEMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(f_zlema(src, len)) : f_zlema(src, len):
modeSwitch == "WMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.wma(src, len)) : ta.wma(src, len):
modeSwitch == "VWMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.vwma(src, len)) : ta.vwma(src, len):
modeSwitch == "Hma" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(HMA(src, len)) : HMA(src, len):
modeSwitch == "Ehma" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(EHMA(src, len)) : EHMA(src, len):
modeSwitch == "Thma" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(THMA(src, len/2)) : THMA(src, len/2):
modeSwitch == "ATR" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ATR_func(src, len)): ATR_func(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "L" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.lowest(len)): ta.lowest(len) :
modeSwitch == "H" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.highest(len)): ta.highest(len) :
modeSwitch == "DMA" ? donchian(len) : na
//Var
sum = 0.0
maopening_l = 0.0
maopening_s = 0.0
maclosing = 0.0
pos = strategy.position_size
p = 0.0
p := pos == 0 ? (strategy.equity / 100) / close : p[1]
truetime = true
loss = 0.0
maxloss = 0.0
equity = 0.0
//MA Opening
maopening_l := ma_func(maopeningtyp_l, maopeningsrc_l, maopeninglen_l)
maopening_s := ma_func(maopeningtyp_s, maopeningsrc_s, maopeninglen_s)
//MA Closing
maclosing := ma_func(maclosingtyp, maclosingsrc, maclosinglen) * maclosingmul
long1 = long1on == false ? 0 : long1shift == 0 ? 0 : long1lot == 0 ? 0 : maopening_l == 0 ? 0 : maopening_l * long1shift
short1 = short1on == false ? 0 : short1shift == 0 ? 0 : short1lot == 0 ? 0 : maopening_s == 0 ? 0 : maopening_s * short1shift
//Colors
long1col = long1 == 0 ? na : color.green
short1col = short1 == 0 ? na : color.red
//Lines
// plot(maopening_l, offset = OFFS, color = color.new(color.green, 50))
// plot(maopening_s, offset = OFFS, color = color.new(color.red, 50))
plot(maclosing, offset = OFFS, color = color.fuchsia)
long1line = long1 == 0 ? close : long1
short1line = short1 == 0 ? close : short1
plot(long1line, offset = OFFS, color = long1col)
plot(short1line, offset = OFFS, color = short1col)
//Lots
lotlong1 = p * long1lot
lotshort1 = p * short1lot
//Entry
if truetime
//Long
sum := 0
strategy.entry("L", strategy.long, lotlong1, limit = on_close ? na : long1, when = long1 > 0 and pos <= sum and (on_close ? close <= long1[trade_offset] : true))
sum := lotlong1
//Short
sum := 0
pos := -1 * pos
strategy.entry("S", strategy.short, lotshort1, limit = on_close ? na : short1, when = short1 > 0 and pos <= sum and (on_close ? close >= short1[trade_offset] : true))
sum := lotshort1
strategy.exit("Exit", na, limit = maclosing)
if time > finalTime
strategy.close_all()
Detail
https://www.fmz.com/strategy/438778
Last Modified
2024-01-15 12:15:14