Reactivity architecture allows the system to face an unpredictible load of data when the users, the data sources or even the resources of some parties inside the information system scale.
This is why all the core architecture heavily uses the reactive streams where each service acts as a consumer and/or as a producer, emphasing an event-driven model in all layers.
The event driven system is ready to route messages from source to sink in both live and batch contexts.
This need comes from the necessity to cover messaging based communication between the users and also asynchronous streams processing to prepare the data for some views.
Since everything is message, it’s mandatory to expect that a message is going to be consumed by different consumers for different purpose.
This case is typically well illustrating by RabbitMQ documentation when talking about direct exchange routing.
We can see that there is as many consumer with different purpose as many routing keys are declared. But it’s important to notice that two consumers for the same purpose can be registered, and only one of them will consume the message.
Reactivity architecture expects a various number of streams and transformations of those streams.
The transformation phase requires messages to be delivered in the same order they are publishing.
This means also that if a consumer fails to acknowledge a message consumption, it must be able to easily retry to process the same message before treating a new one.
Transformation can be also aggregations to satisfy some user views requirements. This means that a stream can be composed of different streams.
There is no reason to exclude some system interractions from the asynchronous messaging model. Even a click from a user can be considered as a stream source.
This consideration can be wrong in a few cases where technical constraints make more realistic a different technique.
Routing messages with guarantee of delivery, ordering preservation, acknowledgement mechanism and high performance must be addressed by a distributed streaming platform. That streaming platform will allow all producers and consumers to register themselves. This is that platform that will receive all messages from producers and push them to consumers.
The streaming platform will interact with producers and consumers in respect of microservice architecture definition. This mainly means that a consumer or a producer is considered as a component serving one purpose, exposing a clear API and easy to replace in the information system.
A microservice is autonomous as much as possible which is possible when control of data is decentralized. Consumers and producers can take advantage of this by embedding their own database, which can lead to a duplication of data. A consistency check mechanism should be considered to regularly make sure that a database is not incorrectly synchronized with others. In case of unexpected desynchronization (typically a state that is expected to be synchronized regarding the messages that are delivered and those who are not), a re-initialization of that data should be possible. Message streaming should be used as much as possible to replicate a data from scratch, including transformations process.
Reactivity has a core concept but producing and consuming data can take different forms.
This is why Reactivity must be extensible by providing a pluggable API allowing extensions to register to the system.
An extension can cover different capabilities.
An extension connects to a different source of data and import from it a set of data stored as a set of Artifacts.
The extension must be reactive to changes in that source and incrementally update Reactivity.
The extension can be notified by changes in Reactivity in order to leverage bi-directional synchronization.
An extension defines additional build-it functionalities allowing to manage more information and interractions inside an Artifact.
This means that the original data model inside an Artifact can be extended by each extension.
This also means that specific actions defined by the extensions can be trigerred when user interracts with that data.
Most of the time, an Artifact extension will embed data synchronization capabilities.
Technologies selected in respect of architecture principles must be open source.
Selection process must have a particular attention to the license to avoid patent or viral clause in the open source license.
Apache 2.0 and MIT licenses are the typical open source license recommended for the technologies used by Reactivity.
The latest version of Java is the version 8.
This version will be used in the core of Reactivity as it’s well maintained by Oracle, provides new features (especially around the Stream API) and is required by different technologies selected in the next section.
The goal of Reactivity is also to take advantage from the features introduced in next Java releases and be upgraded to Java 9 when available.
Progressive web apps are a set of technologies and concepts designed to give the best possible user experience, whatever the device. The main concepts will be implemented in Reactivity wep-application:
-
Offline loading: Thanks to Service Workers, which manage the absence of network; the user must always have something displayed on the screen
-
Loading performance: The app must load fast
-
Access on the homescreen: By defining a JSON-based manifest
-
Notifications: which allow to update the application for the user (even in the absence of a network, thanks to Service Worker)
-
Responsive design: So that the application is adapted to any device
-
Speed: 60 fps everywhere
-
Security: https everywhere
In order to leverage those concepts, Reactivity will use Polymer, in its 2.0 version (preview for the moment). Polymer is based on the web-components and provides some.
There are several advantages to relying on web components, and especially two that have a definite interest compared to Reactivity:
-
each component is insulated, and possibly developed in the desired technology
-
it is easy to contribute to the project thereafter, given that we provide a basis, it will be easy to iterate over
Moreover, as Reactivity must load fast, the code-splitting pattern, and the PRPL pattern are two solutions.
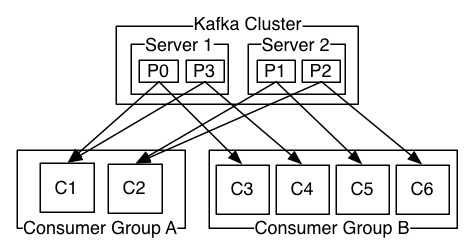
Apache Kafka is the central platform of Reactivity that takes messages sent by producers and delivers them to consumers.
Kafka provides the key following benefits that make it a perfect solution for Reactivity requirements:
-
Scalability:
Kafkais distributed, which make that solution highly scalable. It uses ZooKeeper as service discovery system to keep the nodes in touch, which ease operations. -
Ordering:
Kafkastores the messages in a partition that is ordered, giving the guarantee that messages have been consumed in the order they are emitted. This aspect is a key requirements forReactivityas described in the architecture principles. -
Acknowledgment: Thanks to the offset commit technique,
Kafkaprovides a very simple acknowledgement capability that consumers can use to guarantee that messages will be consumed inReactvitysystem. -
Consumer group:
Kafkaallows consumers to be grouped with a simple label attached to them. This allows a message to be consumed for different purpose and to let the consumers scale without the risk to perform an action twice because of consumption duplication.
Spring version 5 comes with a Spring Web Reactive support which allows to exchange data in respect of reactive streams.
The core API implementation for reactive streams with Spring is Reactor.
Web Reactive support relies on servers without the requiring Servlet API, which means that Netty can be used as well as Tomcat.
The more focused, low-level approach of Netty fits nicely the scope of the consumer and the producer in Reactivity, which makes it a preferable solution.
On top of that, consumers and producers will be able to use the REST support in Spring WEB to easily collaborate with the other components of the system.
This communication interface can complement with additional Spring components described in the next sections.
In addition to the WEB module, Spring Data also uses Reactor to provide a complete asynchronous streaming pipeline from the database to the HTTP response.
The project offers a good level of abstraction with the different database providers and remains a strong partner in development using Spring when interractions with database are required.
Obviously, data need to be stored and read in Reactivity.
Spring Data will be key for this kind of manipulations.
Spring Cloud Stream is a project that helps interacting with message driven middleware.
It provides a dedicated support for Kafka with an unified API that brings some abstractions in provider interractions.
This project will help consumers and producers to connect with Kafka in order to receive and emit messages.
Spring Cloud brings a lot of key components to address deployment issues for a application supposed to be scalable and highly available:
-
Service discovery of consumers and producers in the system to automatically scale
-
Circuit breaker in consumers and producers in the system to be more fault-tolerant
-
Property management to coordinate all consumers and producers configuration
-
Client load balancing to easily control the trafic between components without the need to install a load balancer everywhere
Spring REST Docs provides a very handy way to document and test the APIs in a single activity.
It extends the integration testing API of Spring to build AsciiDoc files regarding the assertions performed on the services that are test.
This projects answer the need to documentation in an easy maintainance way.
Spring Security project provides a very large of techniques that allows to secure Reactivity.
This framework will be leverage on the consumers and producers that need to deal with user authentication and authorizations.
Hazelcast allows Spring Security manage a distributed session across several JVM, allowing to scale the micro services without any issue at authentication level.
Hazelcast also has the advantage of being a lighweight solution directly embedded in the Spring Boot application and does not require to be launched as an additional standalone component.
Spring Boot allows to quickly build a standalone component, easy to package in a uber JAR that make it easy to deploy and run. This completely emphasizes the Microservice architecture style and will be a key framework to support consumers and producers development.
Almost all the Spring projects has support in Spring Boot that ease their integration with a conventions over configuration approach.
It also brings the key capabilities covering various issues of Reactivity:
-
Monitoring of the different consumers and producers in the system with the
Actuatormodule -
Integration testing of the services provided by the consumers and the producers
-
Development tool with per environment configuration and hot reload support
WEB technologies such as Javascript describe object structures in JSON format.
This format is also used in document oriented databases.
Each artefact can be represented in a single document that will be loaded by the database when requested by the user in a particular view.
Some transformation results can be also represented in a document, which makes document database adapted for Reactivity requirements.
Couchbase is document oriented database and distributed by design that meets the scalability requirements of Reactivity.
This database also provides additional interesting products like embedded database for mobile that can be leveraged to cover new features.
This is why our primary choice goes for Couchbase server to store the data of Reactivity.
Since a JSON document data model can be easily extended by addibg more properties to it, Couchbase also offers the opportunity to dynamically add extensions to Reactivity.
Front-end architecture will balance the requests coming from the web clients to different instances.
This will be achieved by Traefik, a moden reverse proxy dealing with microservices architecture.
A ZooKeeper support is provided out of the box, allowing to detect all available back-ends and remove them in case of failure.
Different components will interract with different roles:
-
Service discovery
-
Producers and consumers
-
Web application
-
Database
-
Streaming platform
-
Extensions
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ + + REST + Service discovery + + +-------------->+-------------------------------+ REST + + + ZooKeeper +<-----+--------+------+ + Streaming Platform + +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ | | | + + | | | + + KAFKA CLIENT ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ | | | + +<------------>+ Broadcaster +------+ | | + + +--------------------------------+ | | +----------------------------+ + Spring Boot + | | + KAFKA + ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ | | ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ REST ^ + STATICS + | | | ^ + API +<-------+ | +++++++++++ | | | | +++++++ | SSE | ^ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | ++++++++++++++++ HTTP | | DB DRIVER | | | + WebApp +----------+ +--------------+ | | | +--------------+ | | | | + JAVASCRIPT + | | | | ++++++++++++++++ v | | | +++++++++++++ | | DB DRIVER + Database + | | +----------->+-----------+ | | | + Couchbase + | | +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ +++++++++++++ | | KAFKA CLIENT + Extensions -> Validation API -> Persistance Component + | +------------->+ ------------------------------------------------------+ | + Spring Boot +------------------+ +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
ZooKeeper is used as a centralized system to resolve all microservices.
It’s deployed in a highly available cluster where nodes replicate their configuration to each others.
Microservices register themselves to ZooKeeper and retrieve dependencies through it.
The streaming platform implemented with Kafka offers a REST API that can be consumed to produce new artifacts.
When a new event is received by Kafka, it keeps it until it has been delivered and acknowledge by a consumer.
Kafka is deployed as a cluster of multiple distributed nodes.
All nodes register to ZooKeeper.
Couchbase is the document oriented database that stores data of Reactivity.
This distributed system is deployed as a cluster where nodes register to ZooKeeper.
Asynchronous driver is available to read and write documents to the database.
A Spring Boot application which represents a microservice that suspends SSE connections to stream data from Couchbase.
It also receives new message notifications from Kafka that are broadcasted to all suspended SSE connections.
The broadcaster can be deployed as a set of instances where SSE connections are balanced.
This means that each instance must be in a different consumer group to be notified by Kafka when a notification is sent.
In fact, a notification must be sent to all suspended connections.
Therefore, each instance of the broadcaster must receive the events from Kafka.
A Spring Boot application which receives from Kafka new data to be serialized through Couchbase and aknowledges their consumption.
Before a message is persisted, a validation API must be invoked to make sure no data consistency rule is violated.
If the message is not valid, it’s discarded.
If the message is valid, it’s persisted and sent to the broadcaster through a Kafka topic.
The validation API has a pluggable architecture where extensions can be registered to customize the validation logic for the built-in topics but also additional topics.
Additional statics (JS, CSS, HTML) can be also served to the web application in order to extend the user experience of Reactivity.
The microservice can be deployed as a set of instances where messages sent by Kafka will be balanced.
This means that all instances must be part of the same consumer group to make sure only one of them will be notified.
In fact, we don’t want to persist the same event and send the same notification twice.
In this architecture, Traefik is in charge of balancing requests coming from web application to:
-
Kafkacluster where nodes expose a REST API to send message -
Spring Bootapplications that serve statics (JS,CSS,HTML) including extensions and alsoSSEconnections
Traefik will use ZooKeeper to retrieve the correct backends instances.
Other components will retrieve their dependent services also via ZooKeeper but a client load balancing approach will be used:
-
Spring Bootapplications will balance requests toCouchbasethanks to it’s client driver -
Spring Bootapplications will naturally balance messages toKafkasince the cluster has a different leader for each partition -
Kafkawill balance messages toSpring Bootconsumers according to server list retrieved fromZooKeeper