- Updated to be compatible with Numpy 2.0 (thanks Ashley Anderson @aganders3)
- Removed leftover debugging
print()statement fromkl_boolean functions (thanks Bakhrom Oripov @bakhromtjk)
- Path.interpolate() now allows easy placement of objects alongside a path (e.g. for placing vias). See the tutorial for more information
- Allow
Device.get_ports()to be used with arrays - Allow setting
num_cpuin the newpg.kl_boolean(),pg.kl_offset,pg.kl_invert()functions. Global defaults for the number of CPU to be used can be set with e.g.phidl.config["NUM_CPU"] = 8 - Added
pg.flatten()convenience function. This is identical toDevice.flatten()but instead of modifying the geometry in-place, returns a flattened copy (thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt) - Fixed an issue from
gdspywhere property keys are incorrectly interpreted as signed integers when importing GDS files usingimport_gds()(thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt)
- Fixed rare problem with mew
pg.kl_invert()function whentile_sizewas too small
Major optimization update!
- New KLayout-based boolean/offset/outline functions! These are under the name
pg.kl_boolean(),pg.kl_offset, etc. They utilize the excellent KLayout tile processor, which allows breaking down & parallelizing these operations--in a nutshell, these operations should be much, much faster. - Added
D.simplify(), which allows you to significantly reduce memory usage of a geometry by discarding unnecessarily-precise points from all polygons within a Device. Uses the very robust Ramer–Douglas–Peucker algorithm for simplification. - Now
pg.gridsweep()allowsparam_xorparam_yto be integers, which creates copies of the same parameters in the x or y direction.
- 20x speedup to the internal operation
_merge_nearby_floating_points()which should significantly speed up large operations (thanks Alex Tait @atait) - New pre-commit using ruff (thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt)
- Grammar fix to documentation (thanks Ashish Panigrahi @paniash)
- Optimized/vectorized point rotation, speeding up the
rotate()operation by as much as 150x(!) (thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt) - Added proper
pg.fill_rectangle()examples and documentation
- Fixed
pg.grid()to allow for emptyshapeparameter (thanks Samuel Gyger @gyger) - Allow
pg.grid()spacing to be a single integer (thanks Samuel Gyger @gyger) - Fix to np.bool
- Fixed error in
pg.euler()andpp.smooth()for edge case of nearly-colinear points - Specify certain numpy arrays as
objectto avoid numpy deprecation (thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt and Samuel Gyger @gyger) - Corrected docstring for
pg.union()as it does not accept lists of Devices (improvement for future, thanks Samuel Gyger @gyger)
- Addition of
pg.snspd_candelabra()which creates an optimally-rounded SNSPD with low current crowding and arbtitrarily-high fill factor (thanks Dileep Reddy @dileepvr) - Lazy loading of
matplotlib, allowing loading the base phidl libraries much faster (thanks Joaquin Matres @joamatab)
- Modification to
pg.boolean()s othatOR/union will merge all shapes within one Device, even if the second Device isNone(thanks Stijn Balk @sbalk)
- Modifying the
parentof aDeviceReferencenow correctly updates the reference cell (thanks Joaquin Matres @joamatab) - Fix bug in
pg.outline()whendistance < 0(thanks @yoshi74ls181) - GDS path objects now copy over when using
pg.import_gds()(thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt) - Preserve Polygon.properties and DeviceReference.properties when saving and loading (thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt)
D.remove_layers()works also with GDS path objects (thanks Joaquin Matres @joamatab)
- Re-added
Device.get_info()that gathers the Device.info dictionaries from every sub-Device and returns them in a list. Useful for collecting information about every Device in a layout - Updated documentation
- Deprecated Python 2
- Removal of 1023-character limit for labels (will only show warning instead now)
- Deprecated
reflect()has been fully removed, usemirror()instead
- Much code sanitization under the hood (thanks Bas Nijholt @basnijholt)
Device.absorb()now preserves labels from the parent component (thanks Joaquin Matres @joamatab)- Fixed extrusion error of
pp.spiral()caused by overlapping points - Bugfix for
pg.optimal_step(), now works correctly whenstart_width == end_width - Fixed naming of some previously-unnamed geometries
- Future-proofing for upcoming Numpy changes
- Bugfix for
CrossSection.extrude()since cross_section parameter renamed towidth
- Huge new routing rewrite for
phidl.routing, including automatic manhattan routing with custom cross-sections! See the routing documentation for details. Big thanks to Jeffrey Holzgrafe @jolzgrafe for this contribution Paths can now be used to produce sharp angles, in addition to smooth bends. See the Path documentation
- The
Path()constructor no longer forces the path to start at (0,0)
- Interactive zoom for
quickplot()is now disabled by default in Jupyter-type notebooks to avoid strange scrolling behavior. This can be manually changed usingset_quickplot_options(interactive_zoom = True)
- Hotfix to guarantee Python 2 compatibility
- New
pg.gridsweep()function, allowing for easy creation of parameter sweeps on a grid. See the documentation for details.
- New tutorial on layers
- Can now define layer to be
Noneto prevent creation of polygons - Added
pg.litho_ruler()for creation of lithographic rulers/measurement
- pg.grid() bugfix:
shapenow in format (x,y), and array size correctly calculated when makingshapee.g. (4,-1)
- Better interactive windows for
quickplot()! Now you can use the mousewheel/trackpad scroll to zoom in and out, and right-click or left-click to zoom to a region. - Added
blockingoption forquickplot()(thanks @giumc)
- Quickplot options (such as displaying ports, subports, or aliases) are now set using
set_quickplot_options()
- Fix for Path function
smooth(), which broke when sequential waypoints were co-linear (thanks @giumc) - Fix for non-C-continguous arrays in
hash_geometry()(thanks Joaquin Matres @joamatab)
Bugfix release
- Allow labels imported through
import_gds()to be moved (thanks Joaquin Matres @joamatab) - Fix to Path.smooth() to prevent right-angle turns from accidentally having an additional +180 degrees applied to them (thanks Jeffrey Holzgrafe @jolzgrafe)
- Added
open_portsargument topg.outline, which allows you to cut holes in the outline at Port locations on a Device. See the outline reference here (thanks to Owen Medeiros @omedeiro)
- Easier-to-read quickstart tutorial
- Added
num_squarestoinfodictionary ofpg.optimal_step(thanks Ekkehart Schmidt)
- Fixed bug in
pp.smooth()that forced paths to start out traveling to the right (orientation = 0 degrees) (thanks to Sebastian Pauka @spauka)
Bugfix release
- Fix for Device xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax property assignment (e.g.
D.xmin = 30) causing incorrect movement of references and labels
- Added font support to
pg.text()- Now you can use built-in fonts or specify a .TTF/.OTF font, including full unicode support (thanks to Sebastian Pauka @spauka). See the geometry reference library here - Added new
smooth()function that allows you to construct a smooth path by defining waypoints. The corners are smoothed either with the circularpp.arc()function or the adiabatic straight-to-bendpp.euler()function. See the path/waveguide tutorial here
- Added
route_turn_manhattan()function for more flexible manhattan routing (thanks to @mr-roger-a)
- Fix to start/end angles for
pp.spiral() - Style consistency fix for
pp.arc()when angle negative
- Fix to casting issue when moving components with labels #78 (thanks to Joaquin Matres @joamatab)
Huge update with lots of quality-of-life improvements.
- New path / waveguide module featuring intuitive and fast path building, sub-millisecond polygon generation, and modular cross-sections (thanks to Alex Tait @atait, Dylan Oh @dmwo, Samuel Gyger @gyger, and Florian Vogelbacher).
- Now you can easily
Groupobjects for easier manipulation. See the Group tutorial here - Significantly extended documentation, including new tutorials, geometry library description with images, and API / function reference. See https://phidl.readthedocs.io/
- Docstrings added for all functions
- Addition of
pg.grid()a grid-placement function for creating 2D arrays of devices (thanks to Samuel Gyger @gyger)
filenameargument inwrite_gds()can now acceptpathlibor file buffer (thanks to Samuel Gyger @gyger)
- int-casting fix in
routing(thanks to Samuel Gyger @gyger) - Fix for
pg.optimal_step()ifstart_width==end_widthandsymmetric==True(thanks to Ekkehart Schmidt) - Fix capitalization errors of color names in
Layer(thanks to Jeff Shainline) - Fix to
@endpoints.setter
- Now introducing the automatic
pg.packer()geometry-packing tool: - New documentation for
pg.packer(),align(), anddistribute(). See Geometry + function documentation
- Configurable toplevel
cellnameargument inwrite_gds() - Change to the arguments available in
distribute(). See the Geometry + function documentation - Rename
reflect()tomirror(). Note thatreflect()will continue to work until May 2021 so as not to break any existing code
- Int-casting compatibility fix with latest numpy (thanks @gyger)
- Bugfix to
pg.basic_die()for non-square die (thanks @jonnyfountain) - Fixed harmless but annoying warning if PyQt was not installed
- Small under-the-hood optimizations
- Fixed extremely rare bug with
write_gds()which could potentially cause cell name collisions pg.boolean()no longer errors when passed empty geometries
- Maintenance update to work with
gdspy1.5
- References, arrays and polygons can all be assigned to a Device using
D['myname'] =
- Default precision changed to
1e-4on boolean functions (for 1 unit = 1 micron, this corresponds to 0.1 nanometer precision) - Added
join,miterandmax_pointsarguments topg.offsetto match the arguments with gdspy - The
Device.label()function is going to be move toDevice.add_label()- both will still work for now, but when usinglabel()a warning will pop up suggesting you switch toadd_label()since it will be removed in future versions.
- Maintenance update to work with
gdspy1.5 (specificallypg.import_gds()fixes) - Allow DeviceReferences to be used with
pg.port_to_geometry()(thanks Alex Tait @atait )
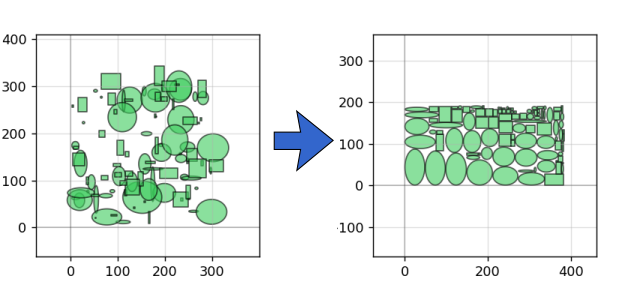
- Major optimization of
pg.boolean(),pg.offset(),pg.outline(), andpg.invert(): Thenum_divisionsargument can now be used to divide up the geometry into multiple rectangular regions and process each region sequentially (which is much, much more computationally efficient). If you have a large geometry that takes a long time to process, try usingnum_divisions = [10,10]to optimize the operation -- you may see speed improvements well over 100x for very large geometries (>1 million points). - New geometry documentation with quick picture references and code examples! See Geometry + function documentation
- Big update to
quickplot(), should be faster now and not have issues with overlapping polygons generating whitespace. - Can now use
port.center, which is identical toport.midpoint
- Allow labels to be correctly moved/rotated
- Fix fontsize and figure initialization of
quickplot() - Bugfix for 'd' shape in
pg.flagpole()
- New online notebook to try out PHIDL! Try now in an interactive online notebook: Link
- Added full CellArray support, use the
D.add_array()function (see the tutorial for more details) - Allow plotting of
DeviceReferences directly inquickplot
- Added
connector_symmetricargument topg.snspd_expanded()
- Bounding box cache speed improvement
- Maintenance release to work with
gdspy 1.4 - Removal of
scipyfrom strict installation requirements
- Minor fix to
distribute()
- Added tutorial section for phidl.geometry library lithographic shapes (resolution tests, calipers, stars, etc)
- Added
symmetricargument to pg.optimal_step() - Experimental port phidl.geometry function
pg.ports_to_geometry()andpg.geometry_to_ports()which converts Ports in a Device into polygon-geometry (and vice-versa) so they can be saved into the GDS file (in the style of SiEPIC). (contribution thanks to Alex Tait @atait) - Added support for
magnificationandrotationofLabels (contribution thanks to Alex Tait @atait)
- Precision for boolean functions set to 1e-6 by default now
positionargument removed from pg.text()
- Fixed rare but persistent bug affecting boolean operations (e.g.
pg.offset(),pg.outline(),pg.boolean(),pg.union()) on polygons with sub-precision floating point errors. Will no longer cause jagged edges when two points are misaligned by very small amounts (e.g. when points that should be equal differ by 1e-27 due to floating point imprecision) - Fix for
pg.import_gds()so that items can be moved/rotated correctly after importing - Fix for
remove_layers()correctly preserves references now (contribution thanks to Alex Tait @atait) - Suppressed unecessary warnings
D.remove()can now remove Ports as well as references/polygons
- Can't have a major release without at least one bug! Fixed errors introduced by optimized-rotation algorithm.
- 1.0 release! The core functionality of phidl has been stable for over 18 months, and all major planned features have been implemented. Time to reflect that in the version number!
- Significant upgrades to
quickplot2: now shows coordinates, a help message box (press ?), and a scale notation (along with several under-the-hood optimizations) - Added
D.hash_geometry()-- use to generate a SHA1-based hash of the polygons in a Device - Added
phidl.utilities.load_lyp(), which loads a KLayout layer properties (.lyp) file and converts it into a LayerSet (contribution thanks to Alex Tait @atait)
- Optimized rotation so 90-degree rotations (contribution thanks to Alex Tait @atait)
- Function documentation for geometry module (contribution thanks to Jimmy Gammell @jgammell and Dylan Oh @dmwo)
pytestimplementation for internal consistency checking
- Added
pg.union()- a handy convenience function to join (union) polygons together, either by-layer or all together (see tutorial for full details) - Added
phidl.utilities.write_svg()- allows you to write your geometry directly to SVG for the sake of publishing figures easily (see tutorial for full details) - Added pg.xor_diff(A,B) - Produces an XOR operation between Devices A and B, which can by used to compare differences between A and B (see tutorial for full details)
- Allow usage of a Python
set(e.g. {3,5,6}) as an input to thelayerargument of add_polygon (and thus all geometry-creation functions in phidl.geometry) to create the polygons on multiple layers. (see tutorial for full details)
- None
- Minor upkeep bugfixes
- The addition of the argument
max_cellname_lengthadded toD.write_gds(). It is28by default, to guarantee maximum compatibility with GDS specifications (32 is generally the lower limit, andwrite_gds()applies a # afterwards to prevent duplicate cellnames). - New documentation backend (contribution thanks to Alex Tait @atait)
- Added
D.remap_layers()which allows you to to move all polygons contained on a layer within your Device to another layer. See tutorial for details - Added
D.remove_layers()which lets you remove all polygon geometry (optionally including labels) from a Device on the specified layers. See tutorial for details
- Further fixes to
D.write_gds()for rare edge cases
- You can now add any shape to multiple layers at once by passing a whole
LayerSetto thelayerargument. See tutorial for details - Update to
D.write_gds()which guarantees cell names within a Device will never overlap. If you want to disable this feature for more control over cell names, change theauto_renameargument toFalse(D.write('myfile.gds', auto_rename = False))
- Modifications made to work with gdspy>=1.3.1
- Minor bugfixes to
pg.litho_calipers()andpg.litho_star()
D.absorb(my_reference)can be used to easily absorb references into a Device; polygons will be extracted from the reference, added to the Device, and then the reference will be removed. See the tutorial for more details- Added lithographic-resolution test structures including stars (
pg.litho_star()), calipers (pg.litho_calipers()), and variable-size negative-tone and positive-tone steps (pg.litho_steps()) (Contribution from Dylan Oh @dmwo).
- Made
write_gds()autofix names to guarantee no duplicates cell names ever appear
- The gdspy bounding box caching has been reallowed
- Single-layer flatten fix for
D.flatten() quickplotandquickplot2now fail gracefully if the user does not have matlplotlib or Qt respectively.
- Added
pg.optimal_90deg(), the optimal 90-degree turn for superconducting nanowires from Clem & Berggren
quickplot2visual improvement: Ports now show up on top of subportsquickplot2visual improvement: Port colors now colorblind-friendly- Fixed very rare
make_device()error
- Added
<<operator to add references.r = D.add_ref(Rect)can now be (optionally) written asr = D << Rect. - Added
D.get_ports()which allows you to gather the locations and information about all ports in Device. - A
LayerSetcan now be previewed. Running the geometry functionpg.preview_layerset()will generate aDevicewhich shows all of the layers, useful for previewing color schemes. quickplot()now shows zero-width ports (e.g. a "pin") as a + sign.quickplot()now defaults to redrawing within a single window, rather than creating a new window for every call- Added a
.infodictionary toPort, useful for recording information about a port (e.g.myport.info['wavelength'] = 1550) - Updated tutorial
pg.optimal_hairpin(),pg.snspd(), andpg.snspd_expanded()now have the argumentturn_ratiowhich defines how wide the turn is w.r.t. the argumentwire_width- The
layerargument inD.add_polygon()can now accept lists ofLayers. Use this if you want to a single polygon shape to multiple layers. - Rearranged an argument location: The
nameargument for theLayer()class is now the third argument to allow the ability to makeLayers like Layer(1,0) - Removed some deprecated old geometry
- Minor bugfix to guarantee quickplot() shows up from the Python/IPython console.
- Minor bugfix in tutorial example file
- Added the LayerSet class. See the tutorial, but essentially this class makes a convenient container to stores layers
- Added
phidl.utilities.write_lyp()(Contribution from Dylan Oh @dmwo). Using a LayerSet, you can now create KLayout-compatible .lyp files. This allows you to get the same coloring in the KLayout viewer as you have specified in PHIDL. - Several new electrical test structures (Contribution from Jacob Melonis @melonisj) Specifically: via chain tests (
pg.test_via()), inter- and intra-layer comb insulation tests (pg.test_comb()), and critical current test structures (pg.test_ic). add_ref()can now take a list of input Devices and will return a list of the generated references, e.g.ref_a,ref_b,ref_c = D.add_ref([A,B,C])
- Fixed issue with pg.import_gds() when
layers(remapping argument) was None. - Bugfix in pg.copy() which produced incorrectly-copied ports
- New function
pg.extract()which extracts all the polygons from a set of specified layers from a Device, and creates a new Device with those polygons in them. See tutorial for details - New Device-copying functions
pg.copy()andpg.deepcopy()which allows you to copy a Device wholesale (very useful if you want to flatten() a Device but not destroy the original).pg.copymaintains the underlying connections & references to other Devices, whilepg.deepcopycreates completely new copies of every underlying polygon and reference. See tutorial for details - Introduced an LRU cache for computationally-intensive Device-making functions. By using the
@device_lru_cachedecorator, any function which returns a Device can be memoized. See tutorial for more details
- Since the
extract()process creates new geometry,D.extract()has been removed in favor of placing it in the geometry librarypg.extract() pg.import_gdsdefault argument is nowflatten = False- Updated tutorial text
- Fixed port deepcopy bug, should result in large performance enhancement for Devices with lots of sub-references and ports
- Fixed some rare errors with D.flatten()
- Some internal changes to make working with Device.uid easier
pg.import_gds()can now import without flattening all the polygons to a single layer- Added
Device.flatten()function to flatten references into raw polygons. See tutorial for details - Added
Device.remove()function to remove geometry. See tutorial for details - Added more informative error messages
__repr__and__str__implemented for Device & DeviceReference: You can now quickly get useful information about a Device by just typing the variable into the console. For instance enteringDorprint(D)into the Python console will printDevice (name "Myshape003191", ports ['R_center', 'bottom', 'input'], aliases ['hello'], 13 elements, 13 references)
- Using a config dictionary as a specification is no longer done with
Device(device_function, config = myconfig). Now it is done with an explicit function,make_device(device_function, config = myconfig)(importable asimport phidl.make_device). See the tutorial for more info Device.metais now being replaced withDevice.infofor clarity of nomenclature.Device.metawill still work but will issue a warning.Device.annotate()is now being replaced withDevice.label()to be more consistent with GDS naming conventions.Device.annotate()will still work but will issue a warning.
- Made compatible with gdspy >= 1.2
- Specified names for phidl.geometry objects
- Updated tutorial text
- Large changes to pg.import_gds(). If your GDS file only has one toplevel cell, you do not need to specify a cellname, pg.import_gds() will automatically grab that cell. Also, it imports all layers by default now, although you can still choose which layers and even create a layer mapping based on whether you pass the
layersargument a list or dict. See tutorial for more information.
- Many small ones under the hood
- Updated tutorial text significantly
- Added import_gds() function! You can now import existing GDS files and use them in your geometry. Try adding premade organization logos and hand-drawn test structures without having to code them from scratch. See tutorial for full explanation.
- Added
overlapkeyword argument to the connect() function. Now when connecting two ports together, you can force them to overlap. See tutorial for full explanation. - Added point_path() function to phidl.routing. It takes a width value and list of points and and will create path of constant width which follows the list of points.
- Text scaling has been changed to be more sensible; now pg.text('abc', size = 100) will produce letters 100 units tall (previously would produce text 125 units tall).
- Many small ones under the hood
- Added pg.boolean() to perform AND/NOT/OR/XOR operations on shapes
- Added pg.outline() to create outlines of shapes, useful for positive-tone resist processes
- Switched development to Python 3. Python 2 will still be supported going forward however
- The function to expand/contract polygons pg.inset() has been deprecated in favor of the more aptly-named pg.offset(). pg.offset(D, distance = -1) will contract the shapes in D, pg.offset(D, distance = 1) will expand them.
- Fixes necessary to make compatible with Python 3
- Fixed pg.connector() midpoint argument
- Compatibility fixes to make compatible with gdspy>=1.1.2
- Added "quickplot2", a more robust/easier to use viewer which instead of being based on matplotlib is based Qt.
- Zoom/scroll uses same buttons as KLayout
- Toggle labels for ports/aliases with F1, F2, F3
- Reset view with Escape key
- Under the hood
- Added label_aliases=False default option to quickplot. Do quickplot(D, label_aliases = True) to draw text with aliases on it
- Added Device.extract(). See the tutorial for details
- Device.add_polygon() can now receive lists of polygons, and will return lists in kind
- pg.snspd() and pg.snspd_expanded() can now be defined using any 2 constrains of: xsize, ysize, or num_squares.
- Nomenclature change on pg.fill_rectangle(), from exclude_layers to avoid_layers
- Changed pg.ytron_round() variable names, fixed layer error on cross
- Fixed SNSPD squares calculation and added num_squares constraints
- Added ability to make "alias" for DeviceReference. See the tutorial
- Can now use Port.x and Port.y instead of calling Port.midpoint[0] and Port.midpoint[1]
- Added Device.size property. Returns the equivalent of [Device.xsize, Device.ysize]
- Added include_layers to pg.fill_rectangle, allowing you to override exclude_layers
- Added pg.circle(), pg.cross(), and pg.ellipse()
- None
- Fixed route_manhattan, had issue with using Device.add() instead of Device.add_ref()
- Fixed pg.snspd layer = 0 by default
- Fixed Port.endpoints
- phidl.geometry.route() works still but is being deprecated, will now be in phid.routing.route_basic(). pg.route() will be deleted in the near future
- Several new photonic geometries by Sonia Buckley
- Advanced Manhattan routing written by Jeff Chiles
- Very likely we added more bugs than we fixed in this version!
- Fixes to phidl.geometry.hecken_taper()
- pg.taper() now has a default argument of width2=None
- Fill tool (phidl.geometry.fill_rectangle) now allows you to invert the fill
- New function pg.invert() which will perform a boolean inversion on elements
- Problem with route() and inset() caused by implementation of Layer(). You can now pass route() and inset() a Layer and it will parse it correctly
- A few under-the-hood optimizations
- Fixed error with quickplot where the last edge of a polygon was not rendered
- Problem with route() and inset() caused by implementation of Layer(). You can now pass route() and inset() a Layer and it will parse it correctly
- Layers() are now implemented. See tutorial_example.py "Using Layers" section for a demonstration
- You can now construct a Device using a set of parameters. See "Constructing a Device from set of parameters" in tutorial_example.py
- Usage of the annotate() function has been added to tutorial_example.py
- quickplot rendering speed has been sped up by a factor of 10x
- pg.rectangle() now takes "size" as a parameter rather than "point1" and "point2"
- Large number of upgrades
- Initial release!