- Consistent Hashing
- CAP Theorem
- Load Balancing
- Caching
- Data Partitioning
- Indexes
- Proxies
- Queues
- Replication
- SQL vs. NoSQL.
- Latency vs Throughput
- Trie algorithm
- Reverse index
- Frugal Streaming
- Geo-hashing
- Leaky bucket, Token bucket and its variation
- Bloom Filters
- Operational transformation
- Quadtree / Rtree
- Loose Counting
- XMPP / Web Sockets uses
- HTTP Long polling
- Consistent Hashing
Credit - Soumyajit Bhattacharyay Post
ACID Transaction, ACL, AES, Alerting, Apache Kafka, Asymmetric Encryption, Availability, Availability Zone, Blob Storage, Cache, Cache Eviction Policy, Cache Hit, Cache Miss, CAP Theorem, Certificate Authority, Client, Client-Server Model, Cloud Pub-Sub, Configuration, Consensus Algorithm, Consistent Hashing, Concurrency, Content Delivery network, Cypher, Database Index, Database Lock, Databases, DDoS Attack, Disk, Distributed File System, DNS, DOS Attack, Etcd, Eventual Consistency, File System, Forward Proxy, Google Cloud Storage, Gossip Protocol, Graph Database, Hadoop, Hashing Function, High Availability, Horizontal Scaling, Hot Spot, HTTP, HTTPS, Idempotent Operation, InfluxDB, IP, IP Address, IP Packet, JSON, Key-Value Store, Latency, Leader Election, Load Balancer, Logging, Man In The Middle Attack, Map Reduce, Memory, Microservice Architecture, MongoDB, Monitoring, Monolithic Architecture, MySQL, Neo4j, Nginx, Nines, Node/Instance/Host, Non-Relational Database, NoSQL Database, Pagination, Paxos & Raft, Zookeeper, YAML, Worker Pool Pattern, Virtual Machine, Vertical Scaling, TLS Handshake, TLS, Time Series Database, Throughput,TCP, Symmetric Encryption, Strong Consistency, Streaming, Stateless, Stateful, SSL Certificate, SQL Database, SQL, Spatial Database, Socket, SLO, SLA, Sharding, SHA, Server-Selection Strategy, Server, S3, Reverse Proxy, Replication, Rendezvous Hashing, Redundancy, Redis, Rate Limiting, Quadtree, Publish/Subscribe Pattern, Prometheus, Process, Postgres, Port, Polling, Persistent Storage, Percentiles, Peer-To-Peer Network
Scalability, Availability, Efficiency, Reliability, Serviceability, Manageability, Extensible, Client-Server, Protocol, Proxy, Gateway, DNS, Latency, Throughput, Read Heavy, Write Heavy,
- Clarifying Questions
- Functional Requirements
- Non Functional Requirements
- Capacity/Storage Estimation
- Drawing Constraints
- Design Database Schema
- Design APIs
- Basic Architecture And Data Flow
- Components or Functionality Implementation
- Trade offs And Corner Cases
| Component Or Platform | Unit Per Second | Unit Per Day | Highest At Single Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Server | 1000 Request | ||
| 3M Search Query | 5B | ||
| 10K+ Tweets | |||
| Internet Traffic | 0.11M GB | ||
| Youtube Upload |
See What's happening at every second in the world at these giant platforms
| Availability level | Downtime per year | Downtime per quarter | Downtime per month | Downtime per week | Downtime per day | Downtime per hour |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% ("one nine") | 36.5 days | 9 days | 3 days | 16.8 hours | 2.4 hours | 6 minutes |
| 95% | 18.25 days | 4.5 days | 1.5 days | 8.4 hours | 1.2 hours | 3 minutes |
| 99% ("two-nines") | 3.65 days | 21.6 hours | 7.2 hours | 1.68 hours | 14.4 minutes | 36 seconds |
| 99.50% | 1.83 days | 10.8 hours | 3.6 hours | 50.4 minutes | 7.20 minutes | 18 seconds |
| 99.9%("three nines") | 8.76 hours | 2.16 hours | 43.2 minutes | 10.1 minutes | 1.44 minutes | 3.6 seconds |
| 99.95% | 4.38 hours | 1.08 hours | 21.6 minutes | 5.04 minutes | 43.2 seconds | 1.8 seconds |
| 99.99%("four nines") | 52.6 minutes | 12.96 minutes | 4.32 minutes | 60.5 seconds | 8.64 seconds | 0.36 seconds |
| 99.999%("five nines") | 5.26 minutes | 1.30 minutes | 25.9 seconds | 6.05 seconds | 0.87 seconds | 0.04 seconds |
| System Design Concept | Technology Used To Implement | Others |
|---|---|---|
| Cache | Redis, Daynamo DB, Memecached | |
| Message Queue | RabbitMQ, Amazon SQS | |
| NoSQL DB | MongoDB | |
| SQL DB | MYSQL DB | |
| Proxy /Load Balancing | HAProxy, Nginx | |
| Cross Language Service Development | Thrift | |
| Centralized Service For Distributed Systems | Apache Zookeeper | |
| Distributed RESTful Search Engine | Elasticsearch | |
| Streaming | Kafka | |
| Distributed File System | Hadoop | |
| CDN(Content Delivery Network) | Openconnect(Used By Netflix), AWS, Clodflare, Google Cloud CDN | |
| Key, Value Store | Amazon Daynamo DB, Redis, Zookeeper | |
| Column Based DB's | Cassandra, HBase, Sylla | |
| Image/Video Storage, Large Datasets, Time Series Database | Amazon S3, GCP Bucket | |
| Distributed Consensus/ Leader Election | Zookeeper, Etcd | |
| Real Time Communication(Audio, Video) | WebRTC | |
| Kraken (Uber) | Peer To Peer Communication | Kraken, Uber Blog |
| Tool Name | Use Case | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Postman | API development lifecycle | Software |
| Dbeaver | SQL client for all types of relational DBs | Software |
| Snakeviz | viewer for Python profiling data | Web-Based package tool |
| OpenAPI | Standards to Define Restful web services | Standard Documentation |
| Swagger, MkDocs | Software Documentation, API Documentation | Tool |
| Coala | linting, Coding Standards, fixing code | pacakge |
| netcat | all ports listing | linux command |
| ps | list all running processes | linux command |
| Git | version control system | cli tool |
| Github, Gitlab, Bitbucket | Remote collaboration dev | web based tool |
| tracert | Server Router Hops Path Routing | linux command |
| Developer Tools Browser | API Analysis | browser built in tools |
| SSH | secure server protocol to communicate over unsecured server | cli tool |
| Vim Editor | developer CLI editor | cli tool |
| Pre-commit-hooks | linting, testing | git cli tool |
| Junit, pytest, jest | unit testing (java, python, javascript | packages |
| maven, gradle | project management tool | |
| logging | ||
| Port Forwarding | ngrok |
- Latency
- Throughput
- Availability
- Consistency
- Maintainability
- Reliability
- Bandwidth
- Layered Architecture
- Pipe and Filter
- Client Server
- Model View Controller
- Event Driven Architecture
- Microservices Architecture
- The complete guide to crack the System Design interview
- Scalable Web Architecture and Distributed Systems
- System Design Interview Questions – Concepts You Should Know
- 25 Software Design Interview Questions to Crack Any Programming and Technical Interviews
- Top 10 System Design Interview Questions and Answers
- Getting Started With System Design
- How To Crack System Design Round in Interviews
- Internet And Protocols IP TCP HTTP
- Introduction to architecting systems for scale
- Consistent Hashing
- Uber System Design
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-web-socket-and-how-it-is-different-from-the-http/
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/websockets/index.htm
- https://javascript.info/long-polling
- https://www.pubnub.com/blog/http-long-polling/
- https://hackernoon.com/understand-service-discovery-in-microservice-c323e78f47fd
- https://dzone.com/articles/service-discovery-in-a-microservices-architecture
- HighScalability
- The Architecture of Open Source Applications
- A Distributed Systems Reading List
- Interviewbit System Design
- Linkedin Engineering
- Hike Blogs
- Locate Cache in Your Browser
- System design primer in Github
- AWS Documentation
- System Design Cheatsheet
- System Design Prepration
- Grokking System Design Interview Github
- High Availability and Nines Chart
- AWS vs Azure vs GCP
- Basic Project Ideas For Distributed Systems
- Crio Byte System Design Repo
- System Design Cheat sheet
- Gaurav Sen
- Gaurav Sen System Design Playlist
- Tech Dummies
- Tech Dummies's System Design Playlist
- sudoCODE
- sudoCODE System Design's Basics Playlist
- System Design Interview
- Think Software
- Think Software's System Design Playlist
- Amazon Web Services
- Tech Takshila
- codeKarle
- Success in Tech
- Basics Of System Design Playlist
- The Stupid CS Guy
- Tushar Roy's System Design Playlist
- Tech Primers
- Distributed Systems Course
- Udit Agarwal
Note Content is under continuous development phase. it contains some terminologies and concepts which really helps when you are thinking about systems.
- Long Polling
- Websockets
- Service Discovery
- Heartbeats
- SQL vs NoSQL
Web app developers can implement a technique called HTTP long polling, where the client polls the server requesting new information. The server holds the request open until new data is available. Once available, the server responds and sends the new information. When the client receives the new information, it immediately sends another request, and the operation is repeated. This effectively emulates a server push feature.
 The flow:
The flow:
- A request is sent to the server.
- The server doesn’t close the connection until it has a message to send.
- When a message appears – the server responds to the request with it.
- The browser makes a new request immediately.
Web sockets are defined as a two-way communication between the servers and the clients, which mean both the parties, communicate and exchange data at the same time. This protocol defines a full duplex communication from the ground up. Web sockets take a step forward in bringing desktop rich functionalities to the web browsers. It represents an evolution, which was awaited for a long time in client/server web technology.
- Real-time web application
- Gaming application
- Chat application
A gateway is a piece of networking hardware used in telecommunications for telecommunications networks that allows data to flow from one discrete network to another. Gateways are distinct from routers or switches in that they communicate using more than one protocol to connect a bunch of networks and can operate at any of the seven layers of the open systems interconnection model (OSI).
A gateway is a network node that connects two networks using different protocols together. While a bridge is used to join two similar types of networks, a gateway is used to join two dissimilar networks.
Gateways can take several forms and perform a variety of tasks:
- Web application firewall - filters traffic to and from a web server and look at application-layer data
- Cloud gateway - provides basic protocol translation and simple connectivity to allow the incompatible technologies to communicate transparently
- API, SOA or XML gateway - manages traffic flowing into and out of a service, microservices-oriented architecture or an XML-based web service
- IoT gateway - aggregates sensor data, translates between sensor protocols, processes sensor data before sending it onward and more
- Cloud storage gateway - translates storage requests with various cloud storage service API calls
- Media gateway - converts data from the format required for one type of network to the format required for another
- Amazon API Gateway - allows a developer to connect non-AWS applications to AWS back-end resources
- VoIP trunk gateway - facilitates the use of plain old telephone service (POTS) equipment, such as landline phones and fax machines, with a voice over IP (VoIP) network
- Email security gateway - prevents the transmission of emails that break company policy or will transfer information with malicious intent
Service discovery is the automatic detection of devices and services offered by these devices on a computer network. A service discovery protocol (SDP) is a network protocol that helps accomplish service discovery. Service discovery aims to reduce the configuration efforts from users.
Service discovery requires a common language to allow software agents to make use of one another's services without the need for continuous user intervention.
Service discovery involves 3 parties: service provider, service consumer and service registry.
- service provider registers itself with service registry when it enters and deregister itself when it leaves the system.
- service consumer gets the location of a provider from registry, and then talks to the provider.
- service registry maintains the latest location of providers.
complexities to handle:
- The service may not deregister itself when it’s gone. Then the registry provides an invalid address to the consumer. To tackle this problem, service provider needs to send its heartbeat periodically (every 5 second maybe). If the provider hasn’t send any heartbeat for sometime, the registry will assume the death of provider, and deregister it.
- Querying registry before calling provider every time? It’s place too much load on registry and impose unnecessary performance impact. It’s better to keep a copy in consumer itself.
- If kept in consumer, how to notify consumer about the changes in provider? There are 2 ways to do it. 1) consumer use polling to get latest version. Since the locations usually don’t change so frequently, this still works. The drawback is the possible downtime between polling. 2) pubsub pattern. It provides more immediate update of locations, but it will hold up additional thread of consumer.
- Sending back all data of a provider may not be necessary. We can keep a global versioning of providers and consumer only needs to update its local copy when version got incremented.
- Single point of failure. If the service registry (e.g. the redis instance we are using here) is down, all consumer and provider will be affected. To alleviate this, we can use a distributed database as service registry, such as
zookeeper/etcd/consul.
When to pick a SQL database?
If you are writing a stock trading, banking, or a Finance-based app or you need to store a lot of relationships, for instance, when writing a social networking app like Facebook, then you should pick a relational database. SQL queries data in disk that's why SQL is more favourable then other DBs. Here’s why:
-
Transactions & Data Consistency
If you are writing software that has anything to do with money or numbers, that makes transactions, ACID, data consistency super important to you. Relational DBs shine when it comes to transactions & data consistency. They comply with the ACID rule, have been around for ages & are battle-tested.
-
Storing Relationships
If your data has a lot of relationships like which friends of yours live in a particular city? Which of your friend already ate at the restaurant you plan to visit today? etc. There is nothing better than a relational database for storing this kind of data.
Relational databases are built to store relationships. They have been tried & tested & are used by big guns in the industry like Facebook as the main user-facing database.
Popular relational databases:
- MySQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- PostgreSQL
- MariaDB
When to pick a NoSQL database
Here are a few reasons why you want to pick a NoSQL database:
-
Handling A Large Number Of Read Write Operations
Look towards NoSQL databases when you need to scale fast. For example, when there are a large number of read-write operations on your website and when dealing with a large amount of data, NoSQL databases fit best in these scenarios. Since they have the ability to add nodes on the fly, they can handle more concurrent traffic and large amounts of data with minimal latency.
-
Running data analytics
NoSQL databases also fit best for data analytics use cases, where we have to deal with an influx of massive amounts of data.
Types Of NoSQL DBs:
- Key-Value Store (Cache Implementation, Hashmap Architecture)
- Document Based DBs (Schema Undefined, R/W Heavy)
- Column Based DBs (Events Store, Read Heavy)
- Search Based DBs (Image/Video Store, Time Series Database)
Popular NoSQL databases:
- MongoDB
- Redis
- Cassandra
- HBASE
Data Travelling speed from one place to another Place
| Data Size | Medium | Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| 1 MB | Memory | 250 µs |
| 1MB | SSD | 1000 µs |
| 1MB | 1GBps Network | 10000 µs |
| 1MB | HDD | 20000 µs |
| packet | Country To Country | 150000 µs |
Latency Comparison Numbers (~2012)
----------------------------------
L1 cache reference ......................... 0.5 ns
Branch mispredict ............................ 5 ns
L2 cache reference ........................... 7 ns
Mutex lock/unlock ........................... 25 ns
Main memory reference ...................... 100 ns
Compress 1K bytes with Zippy ............. 3,000 ns = 3 µs
Send 2K bytes over 1 Gbps network ....... 20,000 ns = 20 µs
SSD random read ........................ 150,000 ns = 150 µs
Read 1 MB sequentially from memory ..... 250,000 ns = 250 µs
Round trip within same datacenter ...... 500,000 ns = 0.5 ms
Read 1 MB sequentially from SSD* ..... 1,000,000 ns = 1 ms
Disk seek ........................... 10,000,000 ns = 10 ms
Read 1 MB sequentially from disk .... 20,000,000 ns = 20 ms
Send packet CA->Netherlands->CA .... 150,000,000 ns = 150 ms
Notes
-----
1 ns = 10^-9 seconds
1 us = 10^-6 seconds = 1,000 ns
1 ms = 10^-3 seconds = 1,000 us = 1,000,000 ns
Credit
------
By Jeff Dean: http://research.google.com/people/jeff/
Originally by Peter Norvig: http://norvig.com/21-days.html#answers
Contributions
-------------
'Humanized' comparison: https://gist.github.com/hellerbarde/2843375
Visual comparison chart: http://i.imgur.com/k0t1e.png
Performance of System Component In Given amount of time Example:
- Number of API calls served per unit Time
Must Read for Latency vs Throughput vs Bandwidth
- Throughput of system depends on Bandwidth
- Throughput of system depends on Latency
Throughput ∝ Bandwidth Throughput ∝ Latency
Cache is used to access data at the earliest convenience to reduce network calls and recomputation.
- Reducing Repetitive Network Calls
- Avoiding Recomputation
in progress Load Balancing With Practical Implementation
in progress Consistent Hashing
in progress Must Read
in progress
Applications
- Avoid One Hit Wonders
- Check Username Available or Not
- Weak password detection.
- Internet Cache Protocol.
- Safe browsing in Google Chrome.
- Wallet synchronization in Bitcoin.
- Hash based IP Traceback.
- Cyber security like virus scanning.
Types Of Sharding
- Vertical Sharding : Separating large dbs in columns into multiple smaller subset dbs known as shards.
- Horizontal Sharding: Separating large dbs in with same schema but unique rows into multiple smaller dbs known as shards.
Horizontal sharding is effective when queries tend to return a subset of rows that are often grouped together. For example, queries that filter data based on short date ranges are ideal for horizontal sharding since the date range will necessarily limit querying to only a subset of the servers.
Vertical sharding is effective when queries tend to return only a subset of columns of the data. For example, if some queries request only names, and others request only addresses, then the names and addresses can be sharded onto separate servers.
Very Good Read On Sharding Strategies
| Sharding Startergy | Database | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consistent Hash Sharding | DaynamoDB Cassandra | Ideal For Scalabale Workloads, Adding Removing Nodes Easy | Performing Range Queries Are inefficient |
| Simple Hashing Modulo based Sharding (Algorithmic Sharding | Memecahced, Redis | No Need Of DB Load Balancer | Inefficient For Adding Removing Shard Nodes |
| Range Based Sharding | Google Spanner, HBase | Efficient For Range Queries | Database Warming, Hotspots |
in progress Must Read
in progress
in progress
Important Terms
- PAXOS
- RAFT
- Zookeeper
- Etcd
- 2PC
- 3PC
- MVCC (Multi Version Concurrency Control)
Advantages
- Communication
- Abstraction
- Platform Agnostic
Examples
- Private APIs
- Public APIs
- Web APIs
- SDK/Library APIs
Standards
- RPC
- SOAP
- REST
Some API Strategies For Different Purpose
- API Security (OAuth2)
- Rate Limiting
- Throttling
- Session Login
REST stands for Representational State Transfer it is a lifecycle or pattern on which client and server both agrees to exchange data between them
Rest Guidelines
- Client-Server Architecture
- Cacheable
- Layered
- Stateless
- Uniform Interface
- Code on Demand
Format
protocol/domain_name/resource_path
most used protocol: HTTP, HTTPS
Types Of HTTP Method
- GET
- POST
- DELETE
- PUT/update
Example Of Path Parameter and Query parameter
Path Parameter https://domain.io/resource/path/:ID_or_KEY
Query Parameter https://domain.io/resource/path/?range_or_condition_isEqual_to
HTTP Status Codes
| Status Code Format | Summary |
|---|---|
| 2XX | Request Response Successful |
| 4XX | Request Failed Because Of Client Mistake |
| 5XX | Request Failed Because Of Server Mistake |
| 3XX | Redirection Of Resource |
| 1XX | Informational |
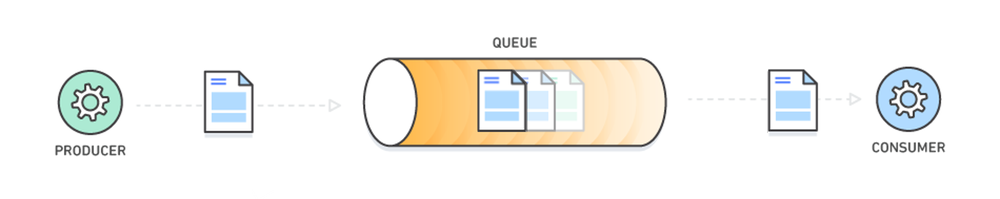
A message broker service which provides asynchronous communication between producer and consumer services.
Example:
- Dominos Pizza Serivce Queue
- Ticket Window Queues
Note Suggestions are Welcome
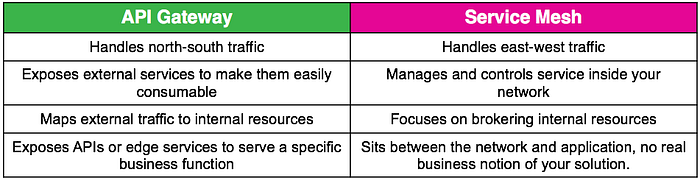
A service mesh’s primary purpose is to manage internal service-to-service communication, while an API Gateway is primarily meant for external client-to-service communication.
Popular apps: Zuul, Amazon API Gateway.
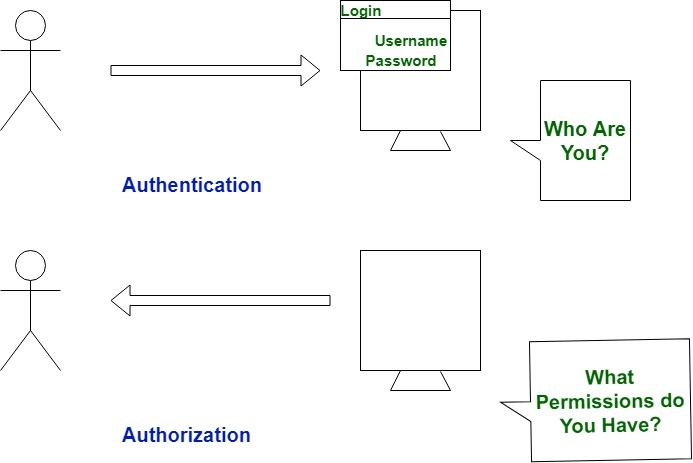
| S. No. | Authentication | Authorization |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | In authentication process, the identity of users are checked for providing the access to the system. | While in authorization process, person’s or user’s authorities are checked for accessing the resources. |
| 2 | In authentication process, users or persons are verified. | While in this process, users or persons are validated. |
| 3 | It is done before the authorization process. | While this process is done after the authentication process. |
| 4 | It needs usually user’s login details. | While it needs user’s privilege or security levels. |
| 5 | Authentication determines whether the person is user or not. | While it determines What permission do user have? |
Credit - GFG Post