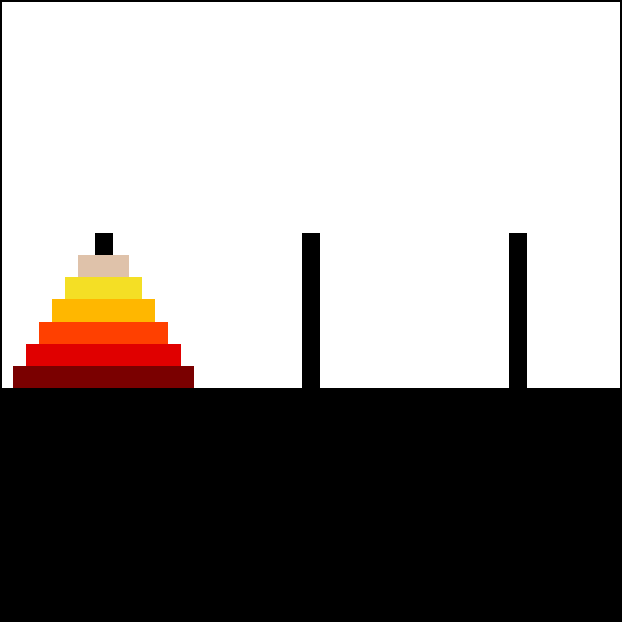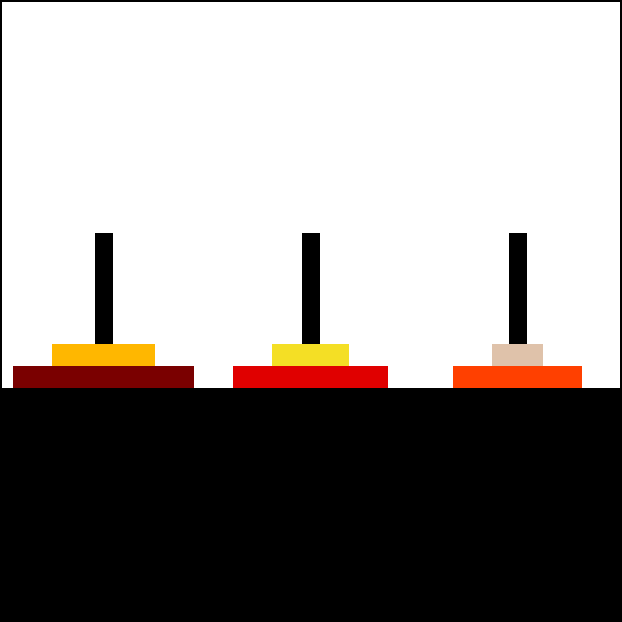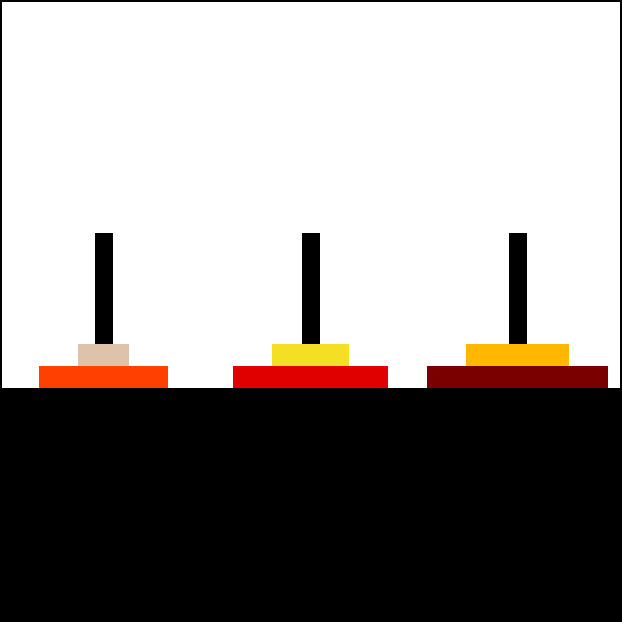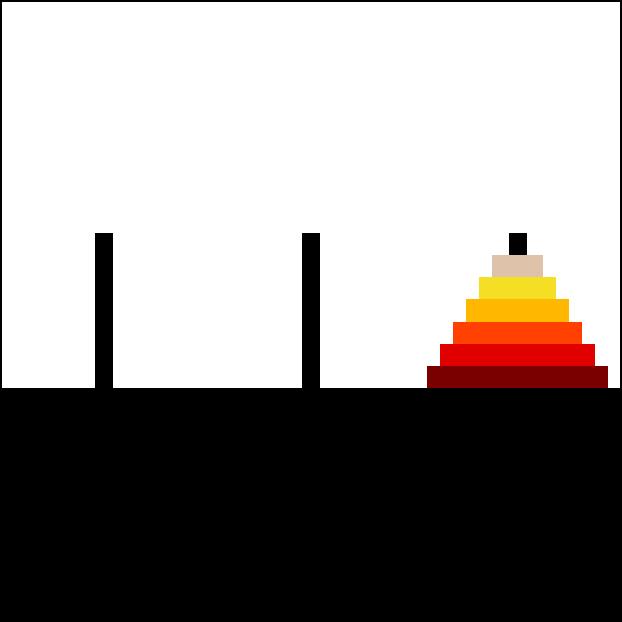The Tower of Hanoi (also called the Tower of Brahma or Lucas' Tower) is a mathematical game or puzzle. It consists of three rods and a number of disks of different diameters, which can slide onto any rod. The puzzle starts with the disks stacked on one rod in order of decreasing size, the smallest at the top, thus approximating a conical shape.
The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to the last rod, obeying the following simple rules:
- Only one disk may be moved at a time.
- Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack or an empty rod.
- No disk may be placed on top of a disk that is smaller than it.
Let's take number of disks as 3 i.e, n = 3. There are 3 rods A, B, C.
Initially all the disks are stacked in a order in rod A. With the help of rod B we will stack the disks to rod C in the same order they were in rod A.
So we have to perform TowerOfHanoi(3,'A','C','B') task.
if (n(3) === 1) --> False
TowerOfHanoi(n(3)-1 = 2, 'A','B','C') <----------
|. 4. "Move Disk 3 from A to C" |
| ---- TowerOfHanoi(n(3)-1 = 2, 'B', 'C', 'A')<-|--------------------
| | | |
-----> if (n(2) === 1) --> False | |
| | |
| TowerOfHanoi(n(2)-1 = 1, 'A', 'C', 'B') <----------- |
| | 2. "Move Disk 2 from rod A to B". | | |
| - | --- TowerOfHanoi(n(2)-1 = 1, 'C','B','A') <-- | ---- |
| | | | | |
| | ----> if (n(1) === 1) --> True | | |
| | 1. "Move Disk 1 from rod A to rod C" | | |
| | return *----------------------------- | |
| | | |
| ---------------> if(n(1) === 1) --> True | |
| 3. "Move Disk 1 from rod C to B". | |
| return *---------------------------------- |
| |
----------------------> if(n(2) === 1) --> False |
|
TowerOfHanoi(n(2)-1 = 1, 'B', 'A', 'C') <---
| 6. "Move Disk 2 from rod B to rod C" | |
--- | -- TowerOfHanoi(n(2)-1 = 1, 'A','C','B')<|--------
| | | |
| ---> if (n(1) === 1) --> True | |
| 5. "Move Disk 1 from B to A" | |
| return *-------------------------- |
| |
| |
-------------> if (n(1) === 1) --> True |
7. "Move Disk 1 from rod A to rod C |
return *------------------------------
With 3 disks, the puzzle can be solved in 7 moves. The minimal number of moves required to solve a Tower of Hanoi puzzle is 2^n − 1, where n is the number of disks.
The below animation is an iterative algorithm solving 6-disk problem
To know more about the origin of Tower of Hanoi please do visit Tower-Of-Hanoi-Wiki