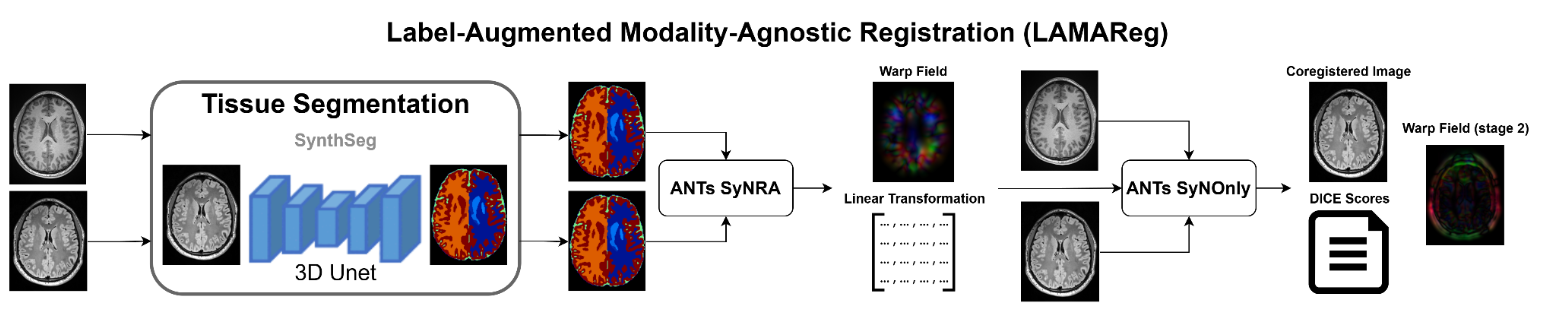
We introduced a novel approach for more accurate registration between modalities. This python based workflow combines deep learning-based segmentation and numerical solutions (ANTs) to generate precise warpfields, even for modalities with low signal-to-noise ratio, signal dropout and strong geometric distortions, such as diffusion MRI and fMRI acquisitions.
LAMAReg provides contrast-agnostic registration between different MRI modalities by using SynthSeg's brain parcellation to enable robust alignment between images with different contrasts (e.g., T1w to T2w, FLAIR to T1w, DWI to T1w).
This Python-based workflow combines deep learning-based segmentation (SynthSeg) and numerical optimization (ANTs) to generate precise warpfields, even for modalities with low signal-to-noise ratio, signal dropout, and strong geometric distortions, such as diffusion MRI and fMRI acquisitions.
!lamar_workflow
pip install -e .LAMAReg offers three main workflows and direct access to individual tools:
Parcellate both input images, register them, and apply the transformation:
lamar register [options]Create warpfields without applying them to the input image:
lamar generate-warpfield [options]Apply previously created warpfields to an input image:
lamar apply-warpfield [options]Run individual components directly:
lamar synthseg [options] # Run SynthSeg brain parcellation
lamar coregister [options] # Run ANTs coregistration
lamar apply-warp [options] # Apply transformations
lamar dice-compare [options] # Calculate Dice similarity coefficient--moving PATH: Input image to be registered--fixed PATH: Reference image (target space)--output PATH: Output registered image--moving-parc PATH: Path for moving image parcellation--fixed-parc PATH: Path for fixed image parcellation--registered-parc PATH: Path for registered parcellation--affine PATH: Path for affine transformation--warpfield PATH: Path for warp field--inverse-warpfield PATH: Path for inverse warp field--inverse-affine PATH: Path for inverse affine transformation
--registration-method STR: Registration method (default: SyNRA)--synthseg-threads N: SynthSeg threads (default: 1)--ants-threads N: ANTs threads (default: 1)--qc-csv PATH: Path for QC Dice score CSV file
Same arguments as full registration, but without --output
--moving PATH: Input image to transform--fixed PATH: Reference space image--output PATH: Output registered image--warpfield PATH: Path to warp field--affine PATH: Path to affine transformation
--ants-threads N: ANTs threads (default: 1)
--i PATH: Input image--o PATH: Output segmentation
--parc: Output parcellation--cpu: Use CPU--threads N: Number of threads
--ref PATH: Path to reference parcellation image--reg PATH: Path to registered parcellation image--out PATH: Output CSV file path
LAMAReg uses a subcommand-based CLI structure using the Python argparse library. Here's how it works:
- Main Parser: Defines the global command structure with subparsers for each workflow.
- Subparsers: Each workflow (
register,generate-warpfield, etc.) has its own subparser with specific arguments. - Command Routing: The
main()function routes commands to the appropriate functions in the lamar module. - Default Help: If no command is provided, the comprehensive help message is shown.
- Unknown Arguments: For commands like
synthseg, additional arguments are parsed fromunknown_argsto handle SynthSeg-specific options. - Direct Tool Access: Commands like
coregisterandapply-warpforward arguments to their respective modules.
All output files require explicit paths to ensure deterministic behavior and prevent accidental file overwrites.
lamar register --moving example_data/sub-HC001_ses-02_space-dwi_desc-b0.nii.gz --fixed example_data/sub-HC001_ses-01_T1w.nii.gz \
--output output/sub-001_dwi_in_T1w.nii.gz --moving-parc output/sub-001_dwi_parc.nii.gz \
--fixed-parc output/sub-001_T1w_parc.nii.gz --registered-parc output/sub-001_dwi_reg_parc.nii.gz \
--affine output/dwi_to_T1w_affine.mat --warpfield output/dwi_to_T1w_warp.nii.gz \
--inverse-warpfield output/T1w_to_dwi_warp.nii.gz --inverse-affine output/T1w_to_dwi_affine.mat \
--synthseg-threads 4 --ants-threads 8lamar synthseg --i subject_t1w.nii.gz --o t1w_parcellation.nii.gz --parc
lamar synthseg --i subject_flair.nii.gz --o flair_parcellation.nii.gz --parclamar register --moving subject_flair.nii.gz --fixed subject_t1w.nii.gz \
--output registered_flair.nii.gz --moving-parc flair_parcellation.nii.gz \
--fixed-parc t1w_parcellation.nii.gz --registered-parc registered_parcellation.nii.gz \
--affine flair_to_t1w_affine.mat --warpfield flair_to_t1w_warp.nii.gz \
--inverse-warpfield t1w_to_flair_warp.nii.gz --inverse-affine t1w_to_flair_affine.matlamar apply-warpfield --moving subject_flair.nii.gz --fixed subject_t1w.nii.gz \
--output registered_flair.nii.gz --warpfield flair_to_t1w_warp.nii.gz \
--affine flair_to_t1w_affine.matlamar dice-compare --ref reference_parcellation.nii.gz \
--reg registered_parcellation.nii.gz --out dice_scores.csvLAMAReg is designed to work with both new and existing parcellations:
-
Generate New Parcellations: If you provide paths to non-existing parcellation files, LAMAReg will generate them using SynthSeg.
-
Use Existing Parcellations: If the parcellation files already exist, LAMAReg will use them directly without regenerating them.
This flexibility allows you to:
- Process data end-to-end in a single command
- Pre-compute parcellations for reuse across multiple registrations
- Mix existing and new parcellations in your workflow
LAMAReg's registration approach consists of three main steps:
- Brain Parcellation: SynthSeg generates contrast-agnostic parcellations of both the moving and fixed images.
- Registration: ANTs registers the parcellations using the SyNRA method (rigid + affine + SyN).
- Transformation Application: The resulting transformation is applied to the original moving image.
This approach enables accurate registration between images with different contrast properties where direct intensity-based registration might fail.
LAMAR/
├── setup.py
├── requirements.txt
├── README.md
├── lamar/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── cli.py
│ ├── scripts/
│ │ ├── lamar.py
│ │ ├── apply_warp.py
│ │ ├── coregister.py
│ │ ├── synthseg.py
│ │ └── dice_compare.py
│ ├── SynthSeg/
│ │ └── ... (SynthSeg code files)
│ └── ext/
│ ├── lab2im/
│ └── neuron/
- LAMAReg works with any MRI modality combination
- If parcellation files already exist, they will be used directly
- All output files need explicit paths to ensure deterministic behavior
- The transforms can be reused with the apply-warpfield command
- Use dice-compare to evaluate registration quality
- Billot, Benjamin, et al. "Robust machine learning segmentation for large-scale analysis of heterogeneous clinical brain MRI datasets." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 120.9 (2023): e2216399120.
- Avants, Brian B., Nick Tustison, and Gang Song. "Advanced normalization tools (ANTS)." Insight j 2.365 (2009): 1-35.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
- Ian Goodall-Halliwell
- Paul Bautin
- Nya Yazdi
- Kevin Du
- Raul R. Cruces