This module contains the time series model support extension with GluonTS.
Right now, the package provides the BaseTimeSeriesTranslator and transform package that allows
you to do inference from your pre-trained time series model.
Now it contains:
- Translator for preprocess and postprocess data, and also includes the corresponding data transform modules.
- Components for building and training new probabilistic prediction models.
- Time series data loading and processing.
- A M5-forecast dataset.
- Two pre-trained model.
- A pre-built trainable model (DeepAR).
An abstract class representing the forecast result.
It contains the distribution of the results, the start date of the forecast, the frequency of the time series, etc. User can get all these information by simply invoking the corresponding attribute.
SampleForecastextends theForecastthat contain all the sample paths in the form ofNDArray. User can query the prediction results by accessing the data in the samples.
The data entry for managing timing data in preprocessing as an input to the transform method.
It contains a key-value pair list mapping from the time series name field to NDArray.
- FieldName -- The name field for time series data including START, TARGET, and so on.
This module contains all the methods for generating time features from the predicted frequency.
- Lag -- Generates a list of lags that are appropriate for the frequency.
- TimeFeature -- Generates a list of time features that are appropriate for the frequency.
In general, it gets the TimeSeriesData and transform it to another TimeSeriesData that can
possibly contain more fields. It can be done by defining a set of of "actions" to the raw dataset
in training or just invoking at translator in inference.
This action usually create some additional features or transform an existing feature.
- Convert -- Convert the array shape to the preprocessing.
- VstackFeatures.java -- vstack the inputs name field of the
TimeSeriesData. We make it implement - the
TimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature.
- Feature -- Add time features to the preprocessing.
- AddAgeFeature -- Creates the
FEAT_DYNAMIC_AGEname field in theTimeSeriesData. Adds a feature that its value is small for distant past timestamps and it monotonically increases the more we approach the current timestamp. We make it implement theTimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature. - AddObservedValueIndicator -- Creates the
OBSERVED_VALUESname field in theTimeSeriesData. Adds a feature that equals to 1 if the value is observed and 0 if the value is missing. We make it implement theTimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature. - AddTimeFeature -- Creates the
FEAT_TIMEname field in theTimeSeriesData. Adds a feature that its value is based on the different prediction frequencies. We make it implement theTimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature.
- Field -- Process key-value data entry to the preprocessing. It usually add or remove the
feature in the
TimeSeriesData. - RemoveFields -- Remove the input name field. We make it implement the
TimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature. - SelectField -- Only keep input name fields. We make it implement the
TimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature. - SetField -- Set the input name field with
NDArray. We make it implement theTimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature.
- Split -- Split time series data for training and inferring to the preprocessing.
- InstanceSplit -- Split time series data with the slice from
Samplerfor training and inferring to the preprocessing. We make it implement theTimeSeriesTransforminterface for training feature.
Sample index for splitting based on training or inferring.
PredictionSampler extends InstanceSampler for the prediction including test and valid.
It would return the end of the time series bound as the dividing line between the future and past.
Existing time series model translators and corresponding factories. Now we have developed
DeepARTranslator and TransformerTranslator for users.
The following pseudocode demonstrates how to create a DeepARTranslator with arguments.
Map<String, Object> arguments = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
arguments.put("prediction_length", 28);
arguments.put("use_feat_dynamic_real", false);
DeepARTranslator.Builder builder = DeepARTranslator.builder(arguments);
DeepARTranslator translator = builder.build();If you want to customize your own time series model translator, you can easily use the transform package for your data preprocess.
See examples for more details.
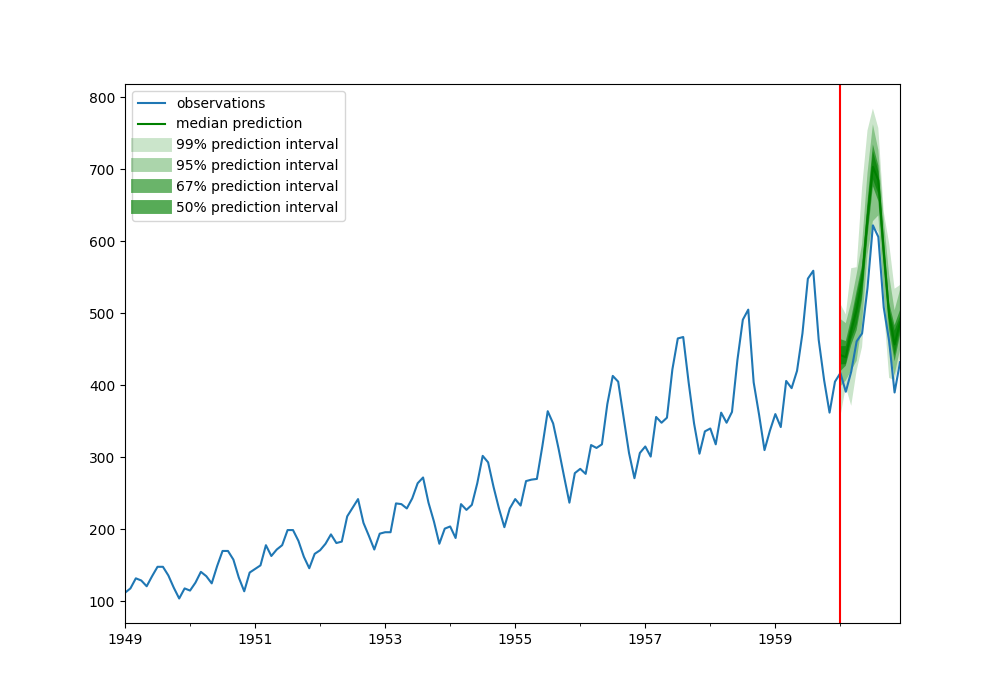
To demonstrate how to use the timeseries package, we trained a DeepAR model on a simple dataset and used it for prediction. This dataset contains monthly air passenger numbers from 1949 to 1960. We will train on the first 9 years of data and predict the last 36 months of data.
In order to realize the preprocessing of time series data, we define the TimeSeriesData as the
input of the Translator, which is used to store the feature fields and perform corresponding
transformations.
Here we define how to get TimeSeriesData from the dataset.
public static class AirPassengers {
private Path path;
private AirPassengerData data;
public AirPassengers(Path path) {
this.path = path;
prepare();
}
public TimeSeriesData get(NDManager manager) {
LocalDateTime start =
data.start.toInstant().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toLocalDateTime();
NDArray target = manager.create(data.target);
TimeSeriesData ret = new TimeSeriesData(10);
// A TimeSeriesData must contain start time and target value.
ret.setStartTime(start);
ret.setField(FieldName.TARGET, target);
return ret;
}
/** prepare the file data */
private void prepare() {
Path filePath = path.resolve("test").resolve("data.json.gz");
try {
URL url = filePath.toUri().toURL();
try (GZIPInputStream is = new GZIPInputStream(url.openStream())) {
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(is);
data =
new GsonBuilder()
.setDateFormat("yyyy-MM")
.create()
.fromJson(reader, AirPassengerData.class);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid url: " + filePath, e);
}
}
private static class AirPassengerData {
Date start;
float[] target;
}
}In djl we need to define Translator to help us with data pre- and post-processing.
public static float[] predict() throws IOException, TranslateException, ModelException {
Map<String, Object> arguments = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// set parameter
arguments.put("prediction_length", 12);
arguments.put("freq", "M");
arguments.put("use_" + FieldName.FEAT_DYNAMIC_REAL.name().toLowerCase(), false);
arguments.put("use_" + FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_CAT.name().toLowerCase(), false);
arguments.put("use_" + FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_REAL.name().toLowerCase(), false);
// build translator
DeepARTranslator translator = DeepARTranslator.builder(arguments).build();
// create criteria
Criteria<TimeSeriesData, Forecast> criteria =
Criteria.builder()
.setTypes(TimeSeriesData.class, Forecast.class)
.optModelPath(Paths.get(modelUrl))
.optTranslator(translator)
.optProgress(new ProgressBar())
.build();
// load model
try (ZooModel<TimeSeriesData, Forecast> model = criteria.loadModel();
Predictor<TimeSeriesData, Forecast> predictor = model.newPredictor()) {
NDManager manager = model.getNDManager();
AirPassengers ap = new AirPassengers(Paths.get("Not implemented"));
TimeSeriesData data = ap.get(manager);
// prediction
Forecast forecast = predictor.predict(data);
return forecast.mean().toFloatArray();
}
}Note that the prediction results are displayed in the form of probability distributions, and the shaded areas represent different prediction intervals.
Since djl doesn't support drawing yet, you can find our script for visualization here.
The full source code for this example is available here
The latest javadocs can be found on here.
You can also build the latest javadocs locally using the following command:
./gradlew javadocThe javadocs output is built in the build/doc/javadoc folder.
You can pull the module from the central Maven repository by including the following dependency in your pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.djl.timeseries</groupId>
<artifactId>timeseries</artifactId>
<version>0.19.0</version>
</dependency>