Basic client only epub2 reader
Make sure to install git and npm before you start then:
- git clone https://github.com/atomicjolt/react_client_starter_app.git my_project_name
- Rename .env.example to .env. This file contains the port the server will use. The default 8080 should be fine, but you can also use a local domain or ngrok if you wish.
- npm install
- Start server with:
npm run hot
then visit http://localhost:8081?contentName=lesson1
Live version deployed to: http://www.epubmix.com.s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com/?contentName=lesson1
##### General
epubUrl - The url where the epub is served from. Ex. '?epubUrl=http://goodpubs/my-fav-pub'
locale - Sets the language for the epub reader controls. Ex. '?locale=en'
loggingApiUrl - Sets the api url for the analytics logging. Ex. '?loggingApiUrl=https://localhost:8888/api'
loggingApiPath - Sets the api path for the analytics logging. Ex. '?loggingApiPath=appdata'
React code can be found in client/js. We use Redux and the React-Router.
All html files live in client/html. The build process will properly process ejs in any html files as well as process markdown for files that end in .md. All front matter in .md files will be available to the ejs templates. See about.md for an example.
Any files added to the assets directory can be used by in code and assigned to a variable. This allows for referring to assets using dynamically generated strings. The assets will be built according to the rules specified in your webpack configuration. Typically, this means that in production the names will be changed to include a SHA.
First importing the assets:
import assets from '../libs/assets';
Then assign the assest to a variable:
const img = assets("./images/atomicjolt.jpg");
The value can then be used when rendering:
render(){ const img = assets("./images/atomicjolt.jpg"); return<div> <img src={img} /> </div>; }
Files added to the static directory will be copied directly into the build. These files will not be renamed.
Karma and Jasmine are used for testing. To run tests run:
npm run test
Inside the client directory run:
npm-check-updates
- Install the s3_website gem:
`gem install s3_website`
- Create s3_website.yml:
`s3_website cfg create`
- Setup and AWS user:
1. Login to your AWS console
2. Find Identity & Access Management (IAM)
3. Click 'Users'
4. Click 'Create New Users'
5. Save the user's credentials
6. Click on the user
7. Click the permissions tab.
8. Under 'Inline Policies' create a new custom policy and paste in the policy below. Be sure to change the domains:
For more details see the [s3_website gem instructions](https://github.com/laurilehmijoki/s3_website).
###IAM Policy:
```json
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::www.epubmix.com"
},
{
"Action": "s3:*",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::www.epubmix.com",
"arn:aws:s3:::www.epubmix.com/*"
]
}
]
}
```
- Configure bucket as website:
`s3_website cfg apply`
If you want to see what your application will look like in production run
npm run live
This will serve files from the build/prod directory.
Build a development release without deploying:
npm run build_dev
Build a release without deploying:
npm run build
Build a release and deploy:
npm run release
As noted above in the settings, there exist two logging related configuration settings: loggingApiUrl and loggingApiPath. These two settings let you send content player log events to an OSID-compliant logging endpoint, via a POST event. The player logs events like:
- Play / Pause / Stop / Seek on media objects
- Click on image zoom
- Click on
iframe,figure,a, andbuttonelements - Click on the left-hand navigation menu
- Click on the toggle-transcript element
Data is reported in the form of:
{
data: {
action: “<verb> <media type>”,
mediaTime: “00.00.10”, (depends on action)
mediaId: “<DOM ID, if available>”, (depends on action)
source: “<src>”,
elementText: “<textContent of DOM element>”, (depends on action),
unit: “<something like Class 9 -- EB>”,
subject: “<something like English -- Lesson 1>”,
activity: “<div with class c-book-item--selected>”,
sessionId: “<configurable ID, like external_id>”
}
}
Example data blobs:
{
data: {
action: “play video”,
mediaTime: “00.00.10”,
mediaId: “ee_u1l01a01v01”,
unit: “Class 9 -- EB”,
subject: “English -- Lesson 1”,
activity: “Introduction”,
sessionId: “f00123”
}
}
{
data: {
action: “click nav”,
unit: “Class 9 -- EB”,
subject: “English -- Lesson 1”,
activity: “Introduction”, (depending on the event timing, can this be the “previous” nav element?)
elementText: “StoryTime”,
sessionId: “foo123”
}
}
Specific actions that should trigger a logged event:
- User played an audio clip (include audio source)
- Audio clip ends (include audio source)
- User “seeked” an audio clip
- User paused an audio clip
- User played a video clip (include video Id or source)
- Video clip ends (include video Id or source)
- User “seeked” a video clip
- User paused a video clip
- User clicked on video caption button
- User clicked an image with a class of zoom-but-sm or zoom-but-md (include image source)
- User clicked left-hand nav
- User clicked a link to another tool / section (any link on the page, plus tags in tags)
To make sure that the correct language is applied to the content player UI and children assessment players, the ePub needs to be configured with the correct language setting. In the OEBPS/content.opf file, you need to set the dc:language value to the two-letter ISO code of the ePub. For example, Hindi would appear as:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<package version="3.0" unique-identifier="BookId" xmlns="http://www.idpf.org/2007/opf">
<metadata xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/">
<dc:language>hi</dc:language>
Supported language codes are en, hi, and te.
In order to get the ePub metadata to appear correctly in the sidebar:
You need to include two dc:title tas in the OEBPS/content.opf metadata section, like:
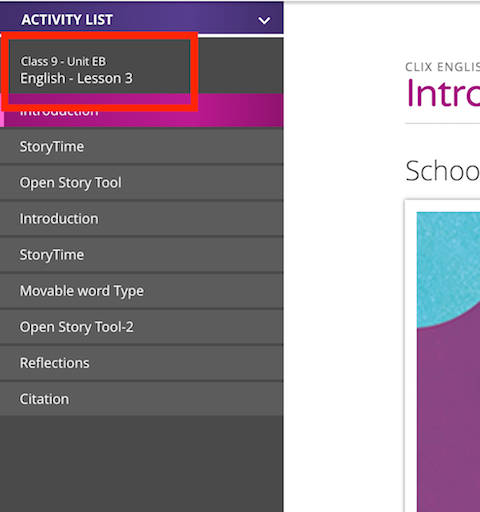
<dc:title id="subj-lesson">English - Lesson 3</dc:title>
<dc:title id="grd-unit">Class 9 - Unit EB</dc:title>
For any ePub with a "Citation" page (i.e. Text/Citation.html), you can optionally flag it as a bibliography, which means the content player will show that page in a separate drawer, and leave it out of the side-nav on the left. A new button will appear in the footer to show the drawer. See this wiki page for images and more details.
To flag it as a bibliography, there are two changes you need to make.
- In the
Citation.htmlpage, change theepub:typefromchaptertobibliography. So thesectiontag would look like:<section epub:type="bibliography">. - In
content.opf, in theguidesection, add an entry for thebibliography, so it looks like the following. Thehrefof thereferenceMUST match thesrcof thecontenttag, in thetoc.ncxfile'snavPointtag that corresponds to the citation page:
content.opf
<guide>
<reference type="toc" title="Table of Content" href="Text/nav.html"/>
<reference type="bibliography" title="Citations" href="Text/Citation.html"/>
</guide>
toc.ncx
<navPoint id="navPoint9">
<navLabel>
<text>Citation</text>
</navLabel>
<content src="Text/Citation.html"/>
</navPoint>
NOTE: you should leave the Citation.html page in the content.opf's spine section, so that other ePub readers still display the citations properly.
MIT